Document analysis shows influence of sugar industry on 1971 US National Caries Program
2015-03-10
(Press-News.org) The sugar industry used several tactics to influence the setting of research priorities for the 1971 US National Caries Program (NCP), according to a study published by Cristin Kearns, Stanton Glantz and Laura Schmidt from the University of California San Francisco, US, in this week's PLOS Medicine.
The researchers analyzed an archive of 319 internal sugar industry documents from 1959 to 1971 (the "Roger Adams papers") and US National Institute of Dental Research (NIDR) documents to explore how the sugar industry sought to influence the setting of research priorities for the NCP. Their analysis indicates that, as early as 1950, sugar industry trade organizations had accepted that sugar damaged teeth and recognized that the dental community favored restricting sugar intake as a key way to control caries. The sugar industry therefore adopted a strategy to deflect attention towards public health interventions that would reduce the harms of sugar consumption. This included funding research on enzymes that break up dental plaque and looking into a vaccine against tooth decay, and cultivating relationships with the NIDR leadership. Notably, 78% of a report submitted to the NIDR by the sugar industry was directly incorporated into the NIDR's first request for research proposals for the NCP. Research that could have been harmful to sugar industry interests (specifically, research into methods to measure the propensity of specific foods to cause caries) was omitted from the research priorities identified at the launch of the NCP.
These findings, although limited by the researchers' reliance on a single source of industry documents and by the inability to interview key actors in the launch of the NCP, reveal an alignment of research agendas between the NIDR and the sugar industry in the early 1970s.
The authors say: "Actions taken by the sugar industry to impact the NIDR's NCP research priorities, which echo those of the tobacco industry, should be a warning to the public health community."
INFORMATION:
Research Article
Funding: This work was supported by the UCSF Philip R. Lee Institute for Health Policy Studies, a donation by the Hellmann Family Fund to the UCSF Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education, the UCSF School of Dentistry Department of Orofacial Sciences and Global Oral Health Program, National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research grant DE-007306 and National Cancer Institute Grant CA-087472. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Citation: Kearns CE, Glantz SA, Schmidt LA (2015) Sugar Industry Influence on the Scientific Agenda of the National Institute of Dental Research's 1971 National Caries Program: A Historical Analysis of Internal Documents. PLoS Med 12(3): e1001798. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001798
Author Affiliations:
University of California San Francisco, UNITED STATES
IN YOUR COVERAGE PLEASE USE THIS URL TO PROVIDE ACCESS TO THE FREELY AVAILABLE PAPER:
http://www.plosmedicine.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pmed.1001798
Contact:
Kristen Bole
Assistant News Director
University of California San Francisco University Relations
UNITED STATES
+1 415 476-2743
kristen.bole@ucsf.edu
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-10
A newly discovered cache of industry documents reveals that the sugar industry worked closely with the National Institutes of Health in the 1960s and '70s to develop a federal research program focused on approaches other than sugar reduction to prevent tooth decay in American children.
An analysis of those papers by researchers at UC San Francisco appears March 10, 2015 in the open-source scientific journal, PLOS Medicine.
The archive of 319 industry documents, which were uncovered in a public collection at the University of Illinois, revealed that a sugar industry ...
2015-03-10
A new technique for creating artificial DNA that is faster, more accurate and more flexible than existing methods has been developed by scientists at Imperial College London.
The new system - called BASIC - is a major advance for the field of synthetic biology, which designs and builds organisms able to make useful products such as medicines, energy, food, materials and chemicals.
To engineer new organisms, scientists build artificial genes from individual molecules and then put these together to create larger genetic constructs which, when inserted into a cell, will ...
2015-03-10
Most military battlefield casualties die before reaching a surgical hospital. Of those soldiers who might potentially survive, most die from uncontrolled bleeding.
In some cases, there's not much medics can do -- a tourniquet won't stop bleeding from a chest wound, and clotting treatments that require refrigerated or frozen blood products aren't always available in the field.
That's why University of Washington researchers have developed a new injectable polymer that strengthens blood clots, called PolySTAT. Administered in a simple shot, the polymer finds any unseen ...
2015-03-10
How much does health care really cost?
UCLA researchers have for the first time described cost across an entire care process for a common condition called benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) using time-driven activity-based costing. They found a 400 percent discrepancy between the least and most expensive ways to treat the condition.
The finding takes on even further importance as there isn't any proven difference in outcomes between the lower and higher cost treatments, said study first author Dr. Alan Kaplan, a resident physician in the UCLA Department of Urology.
"The ...
2015-03-10
Researchers at the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science and the Université Pierre et Marie Curie in Paris have identified a method for manufacturing longer-lasting and stronger forms of glass. The research could lead to more durable display screens, fiber optic cables, windows and other materials, including cement.
Glasses are liquids that are cooled in the manufacturing process to reach a stable "frozen liquid" state. However, as glass ages and is exposed to temperature variations, it continues to flow or "relax," causing it to change shape.
This ...
2015-03-10
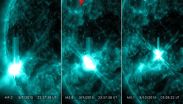
The sun emitted two mid-level solar flares on March 9, 2015: The first peaked at 7:54 pm EDT and the second at 11:24 pm EDT. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured images of the flares, which were classified as an M5.8-class and an M5.1-class, respectively.
These were the second and third flares from the same active region -- numbered Active Region 12297 -- after it rotated over the left side of the sun on March 7.
INFORMATION:
...
2015-03-10
An in-car alarm that sounds when sensors on the vehicle detect an imminent crash could cut crash rates from 1 in 5 to 1 in 10 for drivers over the of 60 suffering tiredness on long journeys, according to a study published in the International Journal of Human Factors and Ergonomics.
Psychologist Carryl Baldwin of George Mason University in Fairfax, Virginia, USA, and colleagues there and at the Sentara Norfolk General Sleep Center, emphasize how fatigue poses a persistent threat to transportation safety. Alarms that sound when a vehicle senses an imminent collision or ...
2015-03-10
NASA's Terra satellite provided an outside look at Tropical Cyclone Pam while the RapidScat instrument that flies aboard the International Space Station provided an inside look at the surface winds generated by the storm. The GPM core satellite provided another inside look at Pam and provided data on where the heavy rainfall was occurring within the storm.
On March 9 and 10, Tropical Cyclone Pam strengthened to hurricane-force as it neared Vanuatu in the Southern Pacific Ocean.
On March 10 (11 p.m. local time), the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) ...
2015-03-10
In an analysis of about 2,600 hospitalizations for severe sepsis, readmissions within 90 days were common, and approximately 40 percent occurred for diagnoses that could potentially be prevented or treated early to avoid hospitalization, according to a study in the March 10 issue of JAMA.
Patients are frequently rehospitalized within 90 days after having severe sepsis. Little is known, however, about the reasons for readmission and whether they can be reduced. Hallie C. Prescott, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues examined the most ...
2015-03-10
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes among 25,000 patients with familial hypercholesterolemia (a genetic disorder characterized by high low-density lipoprotein [LDL] cholesterol levels) was significantly lower than among unaffected relatives, with the prevalence varying by the type of gene mutation, according to a study in the March 10 issue of JAMA.
Statins have been associated with increased risk for diabetes, but the cause for this is not clear. One theory is that statins increase expression of LDL receptors and increase cholesterol uptake into cells including the pancreas, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Document analysis shows influence of sugar industry on 1971 US National Caries Program