Researchers increase energy density of lithium storage materials
Optimized storage principle and new material increase lithium storage density in batteries
2015-03-16
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
The lithium ion battery currently is the most widespread battery technology. It is indispensable for devices, such as laptops, mobile phones or cameras. Current research activities are aimed at reaching higher lithium storage densities in order to increase the amount of energy stored in a battery. Moreover, lithium storage should be quick for energy supply of devices with high power requirements. This requires the detailed understanding of the electrochemical processes and new development of battery components.
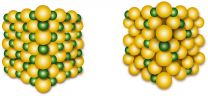
The materials used so far are based on intercalation storage of lithium in small cavities (so-called interstitials), in a host structure that usually consists of metal oxides. This method works well, but the storage densities reached are limited, as lithium cannot be packed very densely in the structure. In addition, intercalation storage of more than one lithium ion per formula unit is generally not possible, as the structure then is no longer stable and collapses. It would therefore be desirable to increase the packing density of lithium in the stable structure and to exceed the upper limits reached so far.
A team around Professor Maximilian Fichtner and Dr. Ruiyong Chen of KIT has now presented a new storage principle and a material on this basis, which allows for the reversible storage of 1.8 Li per formula unit. With a material of the composition Li2VO2F, storage capacities of up to 420 mAh/g were measured at a mean voltage of 2.5 V. As a result of the comparably high density of the material, a storage capacity of up to 4600 Wh/L relative to the active material is obtained.
Contrary to the materials used so far, the new system no longer stores lithium at the interstitials, but directly at the lattice sites of a cubic close packed structure. As a result, packing densities are increased significantly.
Surprisingly, the lithium ions are highly mobile in this structure and can be incorporated into the lattice and removed again easily. Vanadium takes up two charges or releases them again, while the lattice as a whole remains stable - a novelty in such storage materials. The structure has a high defect mobility, such that the lattice can stabilize itself.
"The high stability of the structure at a high defect mobility, associated with a very small volume change of 3 % only - this is what makes the new system unusual. The storage principle appears to be transferable to other compositions. Using other compounds of similar structure, we presently measure even higher energy densities than for the vanadium-based system," the head of the research team, Maximilian Fichtner, reports.
INFORMATION:
R. Chen, S. Ren, M. Knapp, D. Wang, R. Witter, M. Fichtner, and H. Hahn: Disordered Lithium-Rich Oxyfluoride as a Stable Host for Enhanced Li+ Intercalation Storage. Advanced Energy Materials. Article first published online: 3 FEB 2015. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201401814
About the Helmholtz Institute Ulm (HIU)
The HIU was established in January 2011 by KIT, member of the Helmholtz Association, in cooperation with Ulm University. With the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and the Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research Baden-Württemberg (ZSW), two other renowned institutions are involved in the HIU as associated partners. The international team of about 110 scientists at HIU works on the further development of the fundamentals of viable energy storage systems for stationary and mobile use.
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is a public corporation pursuing the tasks of a state university of Baden-Wuerttemberg and of a national research center of the Helmholtz Association. The KIT mission combines the three strategic lines of activity of research, higher education, and innovation. With about 9,400 employees and 24,500 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
For further information, please contact: Daniel Messling, HIU Public-Relations, Phone: +49 731 50 34013, E-Mail: daniel.messling@kit.edu
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-16
SAN DIEGO (March 16, 2015) -- Despite the advent of a new generation of stents, patients with multiple narrowed arteries in the heart who received coronary artery bypass grafting fared better than those whose arteries were opened with balloon angioplasty and stents in a study presented at the American College of Cardiology's 64th Annual Scientific Session.
The findings echo past studies, which have shown patients with multiple narrowed arteries have better outcomes with coronary artery bypass grafting, also known as CABG or heart bypass surgery, than with angioplasty, ...
2015-03-16
SAN DIEGO (March 16, 2015) -- Obese patients with atrial fibrillation who lost at least 10 percent of their body weight were six times more likely to achieve long-term freedom from this common heart rhythm disorder compared to those who did not lose weight, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology's 64th Annual Scientific Session.
The study is the first to track the long-term effects of weight loss and the degree of weight fluctuation on atrial fibrillation burden. Patients who lost more weight and maintained a more stable weight over four ...
2015-03-16
DURHAM, N.C. -- When March Madness kicks off this week, you might expect the bleachers to be filled with alumni and students from the competing colleges. In fact, only about a third of die-hard college sports fans are alumni of their teams' universities, and another third never attended college at all, according to a new Duke University study.
The new research by Charles Clotfelter, a professor of public policy, economics and law at Duke's Sanford School of Public Policy, draws upon an unusual source for its conclusions: obituaries.
Clotfelter's article, "Die-Hard ...
2015-03-16
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Subsistence farmers in Africa, the Americas and the Caribbean are learning how to construct raised planting beds and install drip irrigation systems to boost their agricultural productivity, conserve water and perhaps even halt the rapid advance of desertification in some drought-prone regions.
This educational effort, led in large part by nonprofit groups and private donors, is getting a boost from Scientific Animations Without Borders, an initiative that produces animated educational videos that can be played and shared on cellphones and other digital ...
2015-03-16
Commitment to well being of others difficult to sustain over long run
Personal redemption narrative sustains motivation to engage in prosocial behavior
African-Americans more likely to be motivated by stories of personal redemption
Redemptive stories sustain hope that sacrifices today may produce future dividends
EVANSTON, Ill. --- Middle-aged Americans who show high levels of societal involvement and positive mental health are especially likely to construe their lives as stories of personal redemption, according to new Northwestern University research.
Previous ...
2015-03-16
A review of clinical trial data suggests vitamin D supplementation was ineffective at lowering blood pressure (BP) and should not be used as an antihypertensive, according to an article published online by JAMA Internal Medicine.
Intervention studies have produced conflicting evidence on the BP-lowering effect of vitamin D. An increasing number of clinical trials of have studied vitamin D and cardiovascular health, according to the study background.
Miles D. Witham, B.M., B.Ch., Ph.D., of the University of Dundee, Scotland, and coauthors analyzed clinical trial data ...
2015-03-16
An analysis of publicly available outbreak data suggests that substandard vaccination compliance is likely to blame for the recent measles outbreak linked to Disneyland in California, according to an article published online by JAMA Pediatrics.
Without vaccination, measles is highly contagious. The recent outbreak started in December 2014, although the index case has not yet been identified. The rapid growth of cases indicates that a substantial percentage of the exposed population may be susceptible to measles infection due to lack of, or incomplete, vaccination, according ...
2015-03-16
A study of brain aging finds that being male was associated with worse memory and lower hippocampal volume in individuals who were cognitively normal at baseline, while the gene APOE ?4, a risk factor for Alzheimer disease, was not, according to an article published online by JAMA Neurology.
Typical cognitive aging may be defined as age-associated changes in cognitive performance in individuals free of dementia. To assess brain imaging findings associated with typical aging, the full adult age spectrum should be included, according to the study background.
Clifford ...
2015-03-16
Inadequate vaccine coverage is likely a driving force behind the ongoing Disneyland measles outbreak, according to calculations by a research team at Boston Children's Hospital. Their report, based on epidemiological data and published online by JAMA Pediatrics, indicates that vaccine coverage among the exposed populations is far below that necessary to keep the virus in check, and is the first to positively link measles vaccination rates and the ongoing outbreak.
By examining case numbers reported by the California Department of Public Health and current and historical ...
2015-03-16
There are only five bodies in our solar system that are known to bear rings. The most obvious is the planet Saturn; to a lesser extent, rings of gas and dust also encircle Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune. The fifth member of this haloed group is Chariklo, one of a class of minor planets called centaurs: small, rocky bodies that possess qualities of both asteroids and comets.
Scientists only recently detected Chariklo's ring system -- a surprising finding, as it had been thought that centaurs are relatively dormant. Now scientists at MIT and elsewhere have detected a possible ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers increase energy density of lithium storage materials
Optimized storage principle and new material increase lithium storage density in batteries

