Stress granules ease the way for cancer metastasis
2015-03-23
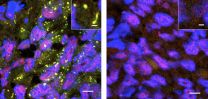
(Press-News.org) Tumors that produce more stress granules are more likely to metastasize, according to a study published in The Journal of Cell Biology. The results suggest that drugs to inhibit the formation of these structures might rein in cancer metastasis.
When cells are under duress, they curtail almost all protein synthesis and stash their mRNAs in stress granules. These structures help healthy cells, but they also allow tumor cells to survive harsh conditions. A protein named YB-1, which is overexpressed in many types of tumors, accumulates in stress granules, but researchers don't know how YB-1 affects these particles.
University of British Columbia scientist Poul Sorensen and his colleagues found that stressed-out cancer cells need YB-1 to assemble stress granules. Removing YB-1 decreased levels of one stress granule protein, G3BP1. The team discovered that YB-1 attaches to the mRNA encoding G3BP1 and stimulates the protein's production.
To determine the effects of YB-1 in animals, the researchers implanted mice with cancer cells that either made or lacked the protein. A month later, cells in the control tumors carried more stress granules than did the tumor cells missing YB-1. Sorensen and colleagues then implanted mice with tumors that either produced or lacked G3BP1. The control tumors harbored more stress granules than did the G3BP1-deficient tumors, and only the control tumors metastasized.
Further research is needed to find out how the reduction in stress granules curbs metastatic spread, but the results suggest that inhibiting their formation might be a way to curb cancer metastasis.
INFORMATION:
Somasekharan, S.P., et al. 2015. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201411047
About The Journal of Cell Biology
The Journal of Cell Biology (JCB) is published by The Rockefeller University Press. All editorial decisions on manuscripts submitted are made by active scientists in conjunction with our in-house scientific editors. JCB content is posted to PubMed Central, where it is available to the public for free six months after publication. Authors retain copyright of their published works, and third parties may reuse the content for non-commercial purposes under a creative commons license. For more information, please visit http://www.jcb.org.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-23
WASHINGTON - When it comes to adolescents with math and science homework, more isn't necessarily better -- an hour a day is optimal -- but doing it alone and regularly produces the biggest knowledge gain, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
Researchers from the University of Oviedo in Spain looked at the performance of 7,725 public, state-subsidized and private school students in the principality of Asturias in northern Spain. The students had a mean age of 13.78. Girls made up 47.2 percent of the sample. The article was published ...
2015-03-23
Research by biologists at the University of York has identified new mechanisms potentially driving progression of an aggressive form of dementia.
The research, which was funded by Alzheimer's Society and the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), is published today in The Journal of Cell Biology.
Working with scientists at the University of Massachusetts Medical School and University of Puerto Rico, the researchers studied how synapses - the connections between neurons - are affected by changes in the protein CHMP2B that are linked to Frontotemporal ...
2015-03-23
LOS ANGELES (March 23, 2015) - Men who exercise more have better erectile and sexual function, regardless of race, according to a recent study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine.
While past studies have highlighted the relationship between better erectile function and exercise, African-American men have been underrepresented in this literature.
"This study is the first to link the benefits of exercise in relation to improved erectile and sexual function in a racially diverse group of patients," said Adriana Vidal, PhD, senior author of the study and investigator ...
2015-03-23
DENVER, March 23, 2015 -- Saccharin, the artificial sweetener that is the main ingredient in Sweet 'N Low®, Sweet Twin® and Necta®, could do far more than just keep our waistlines trim. According to new research, this popular sugar substitute could potentially lead to the development of drugs capable of combating aggressive, difficult-to-treat cancers with fewer side effects.
The finding will be presented today at the 249th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society. The meeting features nearly ...
2015-03-23
DENVER, March 23, 2015 -- Squid are the ultimate camouflage artists, blending almost flawlessly with their backgrounds so that unsuspecting prey can't detect them. Using a protein that's key to this process, scientists have designed "invisibility stickers" that could one day help soldiers disguise themselves, even when sought by enemies with tough-to-fool infrared cameras.
The researchers will present their work today at the 249th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS, the world's largest scientific society, is holding the meeting ...
2015-03-23
DENVER, March 23, 2015 -- More than a year into Colorado's experiment legalizing marijuana, labs testing the plants are able for the first time to take stock of the drug's potency and contaminants -- and openly paint a picture of what's in today's weed. At the 249th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), one such lab will present trends -- and some surprises -- that its preliminary testing has revealed about the marijuana now on the market.
ACS, the world's largest scientific society, is holding the meeting here through Thursday. It features ...
2015-03-23
Researchers from the University of Copenhagen are the first in the world to develop a secure way of measuring the important protein apo-M. This could prove relevant for research into diseases such as diabetes, arteriosclerosis and sclerosis.
For the first time, researchers from the University of Copenhagen have managed to develop a secure way of measuring the protein apo-M in our blood. The protein is interesting because it may prove important to research into diseases such as multiple sclerosis, arteriosclerosis and diabetes.
'We know that apo-M is of importance to ...
2015-03-23
States that have expanded their Medicaid programs under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) are capturing an increased number of people with previously undiagnosed diabetes, allowing them to begin treatment earlier, potentially reducing complications and other negative outcomes, according to a study being published online today and in the May issue of Diabetes Care.
The release of the study coincides with the 5th anniversary of the ACA, which expanded Medicaid eligibility to reach nearly all non-elderly adults with incomes at or below 138 percent of the federal poverty level ...
2015-03-23
Coral Gables, Fla. (March 23, 2015) - A new study shows that providing women with skills to manage stress early in their breast cancer treatment can improve their mood and quality of life many years later. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the findings suggest that women given the opportunity to learn stress management techniques during treatment may benefit well into survivorship.
At the turn of the century, 240 women with a recent breast cancer diagnosis participated in a randomized trial that tested the effects ...
2015-03-23
Scientists have found that genetic changes in bowel tumours are linked to the way the body's immune system responds to the cancer, according to research published today (Monday) in the journal Oncoimmunology*.
For the first time, Cancer Research UK researchers at the University of Birmingham have found that certain genetic flaws in bowel cancer are more likely to trigger an immune response at the site of tumours, meaning that treatments to boost this immune response further could potentially be helpful for these patients.
Finding out what's happening in a cancer patient's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Stress granules ease the way for cancer metastasis



