(Press-News.org) Male offspring appear to benefit more than females from the positive effects of exercise during pregnancy, an animal study by UNSW medical researchers has found.
The study in rats also found mothers who exercised moderately while pregnant reduced their offspring's body weight, insulin and blood glucose levels, potentially lessening their risk of developing metabolic disorders such type-2 diabetes later in life.
The findings were published today in the journal PLOS ONE.
The UNSW team led by Professor Margaret Morris, Head of Pharmacology from the School of Medical Sciences, examined whether the detrimental effects of maternal obesity on offspring could be reduced by the mother's voluntary exercise, prior to and during pregnancy.
"We hypothesised that voluntary exercise during pregnancy would have beneficial effects on glucose levels and metabolism," Professor Morris said.
Female rats were fed a high fat diet, including pies, cakes, dim sims and biscuits, for six weeks before mating and throughout gestation and lactation. Half underwent voluntary exercise introduced 10 days prior to mating and available until their offspring were delivered, while others remained sedentary.
Gene expression relating to glucose, metabolism and inflammation in fat and muscle tissue were then measured 19 days after birth.
"Maternal exercise appeared to decrease the metabolic risk induced by maternal obesity, limiting fat deposits around the abdomen in the offspring and improving their insulin and glucose metabolism during the lactation window," Professor Morris said.
The effects were sex specific, with males appearing to benefit more from maternal exercise than females, the study showed.
"Maternal exercise significantly improved male offspring's insulin and glucose metabolism whereas female offspring showed only modest improvements," Professor Morris said.
"As to why male offspring seem to benefit more than females from the positive effects of exercise during pregnancy, that's a mystery that we hope to solve with further research."
"While this study was conducted in rats, the findings are a useful addition to the existing body of evidence that points to the importance of both diet and exercise for pregnant women to ensure the future health of their baby."
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council and UNSW's Australian Centre for Perinatal Science.
Given the alarming rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and the long lead-in time for developing novel drugs, the discovery of new ways to use the antibiotics already available and approved for use in humans is paramount. It is generally believed that to eliminate a bacterial infection before the onset of drug resistance one must treat with large doses of antibiotics, but recent research has indicated that this type of treatment might actually be driving the emergence of drug-resistant pathogens.
New research publishing April 8th in the Open Access journal PLOS Biology ...
Pioneering new research has unlocked a new technique to help combat the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, that cause debilitating and often life-threatening human illness.
Researchers from the University of Exeter has shown that the use of 'sequential treatments' - using alternating doses of antibiotics - might offer effective treatment against bacterial infection.
Crucially, the research also demonstrates this technique for administering treatment also reduces the risk of the bacteria becoming resistant to antibiotics, and so maintaining the long-term effectiveness ...
EVANSTON, Ill. --- A new approach to analyzing baseball-pitching biomechanics may one day give players more personalized feedback and help prevent elbow injuries.
In a computer simulation study of baseball pitching, Northwestern University biomedical engineers found that the strength of the elbow muscles of a baseball pitcher likely play a bigger role in injury risk and prevention than previously thought.
The motion analysis approach currently used in the baseball industry to provide athletes with injury-risk feedback is not sophisticated enough to estimate what an ...
WELLESLEY, Mass. - A new study by Heather Mattila, a leading honey bee ecologist and Assistant Professor of Biological Sciences at Wellesley College, published on April 8 in PLOS ONE, reveals that inadequate access to pollen during larval development has lifelong consequences for honey bees, leading not only to smaller workers and shorter lifespans, but also to impaired performance and productivity later in life. For the first time, this study demonstrates a crucial link between poor nutrition at a young age, and foraging and waggle dancing, the two most important activities ...
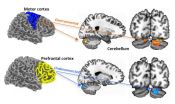
In early childhood, the neurons inside children's developing brains form connections between various regions of brain "real estate." As described in a paper published last week in the journal Biological Psychiatry, cognitive neuroscientists at San Diego State University found that in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder, the connections between the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum appear to be overdeveloped in sensorimotor regions of the brain. This overdevelopment appears to muscle in on brain "real estate" that in typically developing children is more ...
A single infusion of an experimental anti-HIV antibody called 3BNC117 resulted in significantly decreased HIV levels that persisted for as long as 28 days in HIV-infected individuals, according to Phase 1 clinical trial findings published online today in Nature. Major funding for the research was provided by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, The Rockefeller University, and supported in part by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), a component of the NIH. The research was led by long-time NIAID grantee Michel C. Nussenzweig, M.D., Ph.D., ...
The four collaborating organizations are the American College of Nurse-Midwives; the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; the Association of Women's Health, Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses; and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Additionally, these organizations partnered with VitalSmarts, a research and training organization.
The report, "Transforming Communication and Safety Culture in Intrapartum Care: A Multi-organization Blueprint," follows previous research on safety concerns during childbirth and communication among labor and delivery teams. ...
Washington, DC--Pesticide exposure, not obesity alone, can contribute to increased cardiovascular disease risk and inflammation in premenopausal women, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
The study looked at the effects of exposure to polychlorinated pesticides such as DDT. Although DDT was banned in many countries in the 1970s, it remains widespread in the environment and food supply.
DDT was one of the first recognized endocrine-disrupting chemicals, according to the introductory guide to endocrine-disrupting ...
A collaboration led by Shigeyuki Yokoyama of RIKEN and Takashi Kadowaki and Toshimasa Yamauchi of the University of Tokyo has used the SPring-8 synchrotron facility in Harima, Japan to elucidate the structure of two receptors of adiponectin, a protein that is associated with obesity and diabetes. The researchers hope that in the future this work, which was published in Nature today, will pave the way toward designing drugs that target these two receptors, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2, to reduce the early mortality associated with diabetes.
Adiponectin, a hormone secreted by fat ...
In the first results to emerge from HIV patient trials of a new generation of so-called broadly neutralizing antibodies, Rockefeller University researchers have found the experimental therapy can dramatically reduce the amount of virus present in a patient's blood. The work, reported this week in Nature, brings fresh optimism to the field of HIV immunotherapy and suggests new strategies for fighting or even preventing HIV infection.
In a person infected with HIV, there is an ongoing arms race between the virus and the body's immune system. Even as the body produces new ...