(Press-News.org) Older adults who keep a clean and orderly home--because of the exercise it takes to get the job done--tend to feel emotionally and physically better after tackling house chores, according to new findings by a Case Western Reserve University school of nursing researcher.
"House cleaning kept them up and moving," said Kathy D. Wright, PhD, RN, CNS, a postdoctoral KL2 Scholar at the university's Frances Payne Bolton School of Nursing. "A clean environment is therapeutic."
Wright and a research team set out to test a theory called House's Conceptual Framework for Understanding Social Inequalities in Health and Aging. It's considered a blueprint for understanding how factors such as income, education, environment and health behaviors, like smoking and exercise, influence an older person's health.
The study's 337 participants, from 65 to 94 years old, had to have at least one chronic illness, be enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid, have physical restrictions that prevented them from doing at least one basic daily task, such as bathing and dressing, and be unable to manage such responsibilities as taking medicines, handling finances or accessing transportation. All lived in Ohio's Summit and Portage counties.
They discussed their backgrounds and physical and emotional well-being in interviews. The researchers then used the University of Utah's Digit Lab, where Wright earned her doctorate degree while working for the Summa Health System, to link geographic and socioeconomic information on the neighborhoods with health data.
Wright said she was surprised to learn that housework and maintaining their property affected the participants' physical and mental well-being more than such factors as neighborhood or income.
"What I found was that neighborhood poverty did not directly affect mental or physical health," she said.
The study provided evidence that Wright had observed in her visits: people living in a chaotic environment seemed less satisfied than those in a place that was neat and tidy.
Wright hopes the study shows how important it is for sedentary older adults with disabilities and chronic illnesses to continue physical activities, such as doing reaching exercises while sitting, arm curls and standing up and sitting down in a chair.
Wright and her team's findings were reported in the recent Geriatric Nursing article, "Factors that Influence physical function and emotional well-being among Medicare-Medicaid enrollees."
INFORMATION:
Ginette A. Pepper, PhD, RN, FAAN; Michael Caserta, PhD; Bob Wong, PhD; and Cherie P. Brunker, MD, CMD, FACP (the University of Utah); Diana L. Morris, PhD, RN, FAAN, and Christopher J. Burant, PhD, MACTM (Case Western Reserve); Susan Hazelett, MS, RN, (Summa Health System); Denise Kropp, BS, CCRP (Northeast Ohio Medical University); and Kyle R. Allen, DO, AGSF (Riverside Health System Lifelong Health and Aging Related Services Administration), contributed to the study.
Data was used as a secondary analysis of findings from a previous study: After Discharge Care Management of Low-Income Frail Elderly, (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality grant #1 R01 HS014539-01A1 R01 HS014539-01A1).
CHICAGO (April 16, 2015): People with limited education and low income have higher odds of death within 30 days after undergoing an operation for lung cancer than those who are more educated and financially better off, according to new research published as an article in press on the website of the Journal of the American College of Surgeons in advance of print publication later this year.
"In order to get uniform superior outcomes for our patients, we need to identify the patients who are at risk for worse outcomes," said study co-author Felix G. Fernandez, MD, FACS, ...
A concentrated extract of maple syrup makes disease-causing bacteria more susceptible to antibiotics, according to laboratory experiments by researchers at McGill University.
The findings, which will be published in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology, suggest that combining maple syrup extract with common antibiotics could increase the microbes' susceptibility, leading to lower antibiotic usage. Overuse of antibiotics fuels the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria, which has become a major public-health concern worldwide.
Prof. Nathalie Tufenkji's research ...
Neutrinos are a type of particle that pass through just about everything in their path from even the most distant regions of the universe. The Earth is constantly bombarded by billions of neutrinos, which zip right through the entire globe, houses, animals, people - everything. Only very rarely do they react with matter, but the giant IceCube experiment at the South Pole can detect when there is a collision between neutrinos and atoms in the ice using a network of detectors. New research results from the Niels Bohr Institute among others have measured the neutrinos at the ...
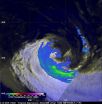
The GPM satellite showed the effects of wind shear and waning rainfall rates in Extra-tropical Cyclone Joalane as it was moving in a southeasterly direction through the Southern Indian Ocean.
The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) core observatory satellite had a last look at the remnants of Tropical Cyclone Joalane on April 14, 2015 at 1135 UTC (4:35 p.m. local time/7:35 a.m. EDT/U.S.).
GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) instrument found very little rainfall around Joalane's center and light to moderate rainfall in bands on the outer edges of the rapidly weakening tropical ...
Eating healthy is sometimes a challenge on its own, so technology should ease that burden - not increase it - according to new research from the Georgia Institute of Technology and University of Washington. Researchers studied how mobile-based food journals integrate into everyday life and specific challenges when using food journaling technology. Their research suggests how future designs might make it easier and more effective.
The research study uncovered three problem areas: barriers to reliable food entry, negative nudges in current food journal apps and challenges ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Pre-eclampsia is a disease that affects 5 to 8 percent of pregnancies in America. Complications from this disease can lead to emergency cesarean sections early in pregnancies to save the lives of the infants and mothers. Scientists believe pre-eclampsia is caused by a number of factors, including shallow placentas that are insufficiently associated with maternal blood vessels. Now, researchers from the University of Missouri, in an effort to grow placenta cells to better study the causes of pre-eclampsia, serendipitously discovered a previously unknown form ...
New research might bring a frown to even the most heavily botoxed faces, with scientists finding how some of the potent toxin used for cosmetic surgery escapes into the central nervous system.
Researchers at The University of Queensland have shown how Botox - also known as Botulinum neurotoxin serotype A - is transported via our nerves back to the central nervous system.
Botox - best known for its ability to smooth wrinkles - has been extremely useful for the treatment of over-active muscles and spasticity as it promotes local and long-term paralysis.
UQ Queensland ...
WASHINGTON - Faced with requests to meet with potential doctoral students of easily identifiable gender, race or ethnicity, faculty in almost every academic discipline are significantly more responsive to white males than to women and minorities, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
And faculty in higher-paid disciplines, such as business, engineering/computer science and the life sciences, and those at private universities, show more of this bias than their counterparts in lower-paying disciplines and public universities, the study ...
Alexandria, VA--The massive 2011 Las Conchas Fire near Los Alamos, N.M., defied conventional fire science wisdom by racing downhill instead of uphill, and increasing intensity overnight. Now, EARTH Magazine brings you recent scientific analysis of the fire from a research team at Los Alamos National Lab.
A team led by atmospheric scientist Young-Joon Kim determined that two unique atmospheric effects -- mountain waves and pyro-cumulus clouds -- interacted in an explosive way to fan the flames over New Mexico. Read more about the new research and how it compares to traditional ...
A breakthrough study performed in an international collaboration led by Professor Tosso Leeb from the University of Bern and Professor Hannes Lohi from the University of Helsinki together with the veterinary neurologists and neuropathologists at the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine in the University of Helsinki has identified a gene mutation that causes a novel type of neurodegenerative disease in dogs. The results of the study shed light into the function of neurons, provide a new gene for human neurodegenration, and may aid in developing better treatments for neurodegenerative ...