Pruning of blood vessels: Cells can fuse with themselves
2015-04-20
(Press-News.org) Cells of the vascular system of vertebrates can fuse with themselves. This process, which occurs when a blood vessel is no longer necessary and pruned, has now been described on the cellular level by Prof. Markus Affolter from the Biozentrum of the University of Basel. The findings of this study have been published in the journal PLOS Biology.
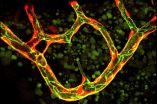
The vascular system is the supply network of the human organism and delivers oxygen and nutrients to the last corners of the body. So far, research on the vascular system has focused primarily on the formation of such vascular networks. Markus Affolter's research group at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel has now investigated the blood vessel pruning in the zebrafish and discovered that the cells have the ability to self-fuse at the membrane margins. Previously, it was unknown that blood vessel cells of vertebrates have this property.
Self-fusion observed in vertebrates for the first time
The formation of blood vessels follows a complicated architectural plan. "At a first glance, the plan for vascular regression seems to be the same but it must differ at the molecular level", explains Markus Affolter. During vascular regression, most of the cells consecutively migrate and incorporate into the neighboring functional vessels. The last single cell that remains in the pruning vessel reaches around the lumen and the membrane margins of this cell undergo fusion thus closing the vessel and assuring its tightness. This process, named cell self-fusion, ensures a controlled closure of a regressive blood vessel thus preventing blood leakage. For the first time this self-fusion of cells has been observed in vertebrates, the group humans also belong to. "Such cell behavior was so far only known in simpler organisms such as nematodes", explains Markus Affolter.
Greater plasticity through self-fusion
During the development of the vascular network, blood vessels are constantly formed but many of them are only required temporarily. Just like a disused arm of a highly branched river, the flow of fresh blood through these vessels is interrupted and the organism begins to prune this side arm. In this way the vascular system regulates itself, optimizing its blood circulation by pruning and recycling the unnecessary vessels with reduced blood flow and blood pressure. "This newly uncovered process is important for the understanding of blood vessel formation and regression on the cellular level, as this can also explain the extraordinary plasticity and changeability of the vascular system", says Anna Lenard, the first author of this publication. These investigations were performed on the zebrafish, as in this almost transparent fish the development of blood vessels can be observed in the living animal using modern microscopy techniques.
Relevance of self-fusion for cancer?
"How the cell recognizes its own membrane margins and how fusion with neighboring blood vessel cells is prevented, is not yet known", says Markus Affolter. Since a long time it has been postulated that each individual cell of an organism has its own code. "The regression process could partly confirm this theory", thinks Markus Affolter. Together with his team, he would like to investigate the self-fusion process more closely. As tumors require a well developed vascular system for their growth, a better understanding of the formation and regression of this network could open possibilities for the manipulation of such a system.
INFORMATION:
Original article:
Anna Lenard, Stephan Daetwyler, Charles Betz, Elin Ellertsdottir, Heinz-Georg Belting, Jan Huisken, Markus Affolter:
Endothelial Cell Self-fusion during Vascular Pruning.
PLOS Biology published online 17 April 2015 | DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002126
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-20
The horticulturist who came up with the concept of 'evolution by natural selection' 27 years before Charles Darwin did should be more widely acknowledged for his contribution, states a new paper by a King's College London geneticist.
The paper, published in the Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, argues that Patrick Matthew deserves to be considered alongside Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace as one of the three originators of the idea of large-scale evolution by natural selection.
Furthermore, Matthew's version of evolution by natural section captures ...
2015-04-20
Human emotion can be transferred by technology that stimulates different parts of the hand without making physical contact with your body, a University of Sussex-led study has shown.
Sussex scientist Dr Marianna Obrist, Lecturer at the Department of Informatics, has pinpointed how next-generation technologies can stimulate different areas of the hand to convey feelings of, for example, happiness, sadness, excitement or fear.
For example, short, sharp bursts of air to the area around the thumb, index finger and middle part of the palm generate excitement, whereas sad ...
2015-04-20
Philadelphia, PA, April 20, 2015 - The search for genes that contribute to the risk for autism has made tremendous strides over the past 3 years. As this field has advanced, investigators have wondered whether the diversity of clinical features across patients with autism reflects heterogeneous sources of genetic risk.
If so, it was reasoned, then selecting a group of patients with very similar clinical features might result in a "purer", i.e., more genetically homogenous, group of patients, making it easier to find autism-related genes.
Results from a new study published ...
2015-04-20
Research has shown that, for a number of reasons, lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender people are significantly more likely than heterosexuals to avoid or delay medical care.
For instance, LGBT individuals who are between the ages of 18 and 44 and single are less likely than heterosexuals to have the money or insurance for care, and even partnered gays and lesbians are twice as likely to be uninsured. The fear of stigma and homophobia can also keep LGBT people from seeking care. And many are afraid to disclose their sexual or gender identity to their physicians, which ...
2015-04-20
PHILADELPHIA - A protein produced by nerve cells appears to be elevated in the blood of those with an aggressive form of neuroblastoma. The finding, presented today at the American Association for Cancer Research 2015 Annual Meeting in Philadelphia, could potentially lead to a prognostic test for the disease or be used to monitor its progress.
Neuroblastoma is a pediatric cancer with varying types, ranging from spontaneously regressing to untreatable fatal tumors. Consequently, treatment strategies vary significantly between patients, encompassing different approaches ...
2015-04-20
A decrease in the amount of time spent eating and an increase in overnight fasting reduces glucose levels and may reduce the risk of breast cancer among women, report University of California, San Diego School of Medicine researchers in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
The findings were presented at the American Association of Cancer Research's annual meeting in Philadelphia.
"Increasing the duration of overnight fasting could be a novel strategy to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer," said Catherine Marinac, UC San Diego doctoral candidate ...
2015-04-20
Early data in a preliminary human study show that an experimental immune system drug is generally safe and well tolerated in women with metastatic, triple-negative breast cancer, a persistently difficult form of the disease to treat.
Results of the early-phase clinical trial of the therapy, called MPDL3280A, which aims to restore the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells, are expected to be presented at the American Association for Cancer Research's 2015 Annual Meeting in Philadelphia from April 18-22. Triple-negative breast cancer cells lack expression ...
2015-04-20
TORONTO, April 20, 2015--Although ultrasound remains the primary imaging modality used in prenatal imaging, fetal MRI is playing an increasing role in further evaluation of fetuses suspected of congenital anomalies. As 3-T MRI scanners become more common due to their improved image signal-to-noise ratio and anatomical detail, the benefits of 3-T MRI must be weighed against potential risks to the fetus that may result from the higher field strength.
"MRI is playing an increasingly important role in the assessment of complex prenatal disease," said Kathleen E. Carey, MD, ...
2015-04-20
TORONTO, April 20, 2015--The design of inferior vena cava (IVC) filters for pulmonary embolism prophylaxis, once used almost exclusively for permanent implantation, has progressed to retrievable designs. However, complications can create scenarios in which the routine filter retrieval is either extremely difficult or impossible.
The use of advanced retrieval techniques, such as loop-snare, "sandwich," stiff wire or balloon realignment, forceps retrieval and excimer laser sheath can raise the overall success rate above 98%.
"Implementation of IVC filters is increasing ...
2015-04-20
TORONTO, April 20, 2015--Research comparing the accuracy of three MDCT slice thicknesses has found that 3-mm slices underestimated coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores at every level of calcification. The inaccuracies were caused by partial volume averaging errors.
"Our analysis proved this concept and showed that CAC can be more accurately measured with 0.5 or 1 mm using isotropic data acquisition obtained by a volume scanner at identical radiation dose ," said Farhood Saremi, MD, University of Southern California. "Coronary artery calcium can be more accurately measured ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pruning of blood vessels: Cells can fuse with themselves

