(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Birmingham have identified an important new way in which our immune systems are regulated, and hope that understanding it will help tackle the debilitating effects of type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and other serious diseases.
The team discovered a novel pathway that regulates the movement of pathogenic immune cells from the blood into tissue during an inflammatory response.
A healthy, efficient immune system ordinarily works to damp down inflammation and carefully regulate the magnitude of the response to infection and disease. In diseases such as diabetes and arthritis, as well as when we age, our immune system becomes less stringently regulated and this can lead to an exaggerated inflammatory response - allowing inappropriate access of immune cells to vulnerable tissues. The new study shows that beneficial effects of the new pathway are lost in these diseases, as well as during normal ageing.
The study, published in Nature Medicine, details how a key molecule regulates this aspect of our immune response. Importantly, the team were then able to show how the addition of this molecule to immune cells from patients with diabetes and arthritis could regain control of the movement of their immune cells, thereby reversing the pathogenic changes seen in these diseases.
Professor Ed Rainger, from the University of Birmingham, explained, "Our immune system becomes progressively less effective over the years and this can become harmful leading to disease. Being able to understand the link between ageing and pathology will help us to reduce the risk of ill health associated with increasing age."
"Our discovery of this new pathway is very exciting. Not only does it reveal new ways in which our bodies control inflammation, it also indicates that we may be able design new drugs to reverse the disease and age specific loss of this pathway."
"The fact that the new pathway is relevant to both diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, which are quite different diseases, implies a broad applicability to many chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. This is an area of research we are keen to follow, and will be working with doctors from other specialities to determine whether this is the case and whether new therapies might be more broadly applicable"
The global healthcare landscape is undergoing a significant shift, with some populations experiencing a sharp increase in life expectancy. However, an ageing population comes with a rise in the prevalence of debilitating diseases, which in turn passes on a significant burden to the patients, their families and their health service providers.
Professor Rainger added, 'The link between the decline of this pathway and normal ageing is also very interesting, as this is a natural process. It means that patients with diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis may have accelerated decline of this pathway so that individuals as young as 20 have the immune function of 70 year olds. If we can identify patients at risk of developing this disease we may be able to artificially restore some vigour to their immune systems and reduce the burden of disease for the individual patient as well as their families and the NHS.''
The next step is to use the findings in clinical studies that will investigate the viability of treatments and therapies targeting this pathway.
Professor Peter Weissberg, Medical Director at the British Heart Foundation, said: "This is a superb piece of research that appears to have identified a new way to regulate chronic inflammation. It helps to explain why autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis become more common with age."
"It remains to be seen whether these findings will have any direct relevance to cardiovascular disease. However, coronary heart disease tends to be more common in people with chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, so if this research leads to better treatments for these conditions, it might be expected that this will lead to fewer heart attacks in these patients."
INFORMATION:
A University of Texas at Austin scientist, working with an international research team, has developed the most precise sequence map yet of U.S. cotton and will soon create an even more detailed map for navigating the complex cotton genome. The finding may help lead to an inexpensive version of American cotton that rivals the quality of luxurious Egyptian cotton and helps develop crops that use less water and fewer pesticides for a cotton that is easier on the skin and easier on the land.
Z. Jeffrey Chen and his collaborators, Tianzhen Zhang and Wangzhen Guo at Nanjing ...
Using the latest genome sequencing techniques, a research team led by scientists from UC San Francisco (UCSF), Baylor College of Medicine, and Texas Children's Hospital has identified a new autoimmune syndrome characterized by a combination of severe lung disease and arthritis that currently has no therapy.
The hereditary disorder, which appears in early childhood, had never been diagnosed as a single syndrome. The new research revealed that it is caused by mutations in a single gene that disrupt how proteins are shuttled around within cells. Patients with the newly ...
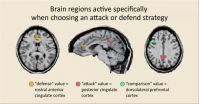
We often make quick strategic decisions to attack an opponent or defend our position, yet how we make them is not well understood. Now, researchers at the RIKEN Brain Science Institute in Japan have pinpointed specific brain regions related to this process by examining neural activity in people playing shogi, a Japanese form of chess. Published in Nature Neuroscience, the study shows that two different regions within the cingulate cortex--one toward the front of the brain and the other toward the back--separately encode the values of defensive and offensive strategies.
Like ...
Large amounts of methane - whether as free gas or as solid gas hydrates - can be found in the sea floor along the ocean shores. When the hydrates dissolve or when the gas finds pathways in the sea floor to ascend, the methane can be released into the water and rise to the surface. Once emitted into the atmosphere, it acts as a very potent greenhouse gas twenty times stronger than carbon dioxide. Fortunately, marine bacteria exist that consume part of the methane before it reaches the water surface. Geomicrobiologists and oceanographers from Switzerland, Germany, Great Britain ...
New apps developed for children come online every day and many of them are marketed or labeled as "educational" - but how can we tell which of these thousands of apps will actually help children learn? A comprehensive new report published in Psychological Science in the Public Interest, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, integrates research from scientific disciplines like psychological science, linguistics, and neuroscience to provide an evidence-based guide that parents, educators, and app designers alike can use to evaluate the quality of so-called ...
HANOVER, N.H. - Although the media often portray the Arctic as a new "Great Game" ripe for conflict, a group of international Arctic experts co-chaired by Dartmouth College released recommendations today aimed at preserving the polar north as an area for political and military cooperation, sustainable development and scientific research.
The report, which addresses the priorities of the Arctic Council, an intergovernmental forum of the eight nations that border the polar region, resulted from meetings at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace in Washington, ...
Only three wolves seem to remain in Isle Royale National Park. Researchers from Michigan Technological University observed the wolves during their annual Winter Study, and the lone group, at an unprecedented low, is a sharp decline from nine wolves observed last winter.
The study's report, released today, marks the project's 57th year of observing wolves and moose in Isle Royale. It is the longest running predator-prey study in the world. This year, along with the three resident wolves, scientists estimated 1,250 moose on the island and observed two visiting wolves, ...
Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators have found the probable mechanism underlying a previously described biomarker associated with the risk of developing serious diseases ranging from cancer to cardiovascular disease and the risk of serious complications. In a paper published in the American Journal of Hematology, the research team reports finding that higher levels of a measure routinely taken as part of the complete blood count - the extent of variation in the size of red blood cells - is caused by reduced clearance of aging cells from the bloodstream. Hundreds ...
When you take a medication for, say, high cholesterol, do you know that pill is really what the label says it is? Depending upon the type of medicine and where you live, the threat of falsified medications (also referred to as counterfeit, fraudulent, and substandard) can be quite real, yet the full scope and prevalence of the problem is poorly understood, say researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine in a new report published April 20 in the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene.
Counterfeit medicines have traditionally been defined ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- While the female baboon's big red bottom may be an eyesore to some, it has an aphrodisiac effect on her mates. Biologists have long thought that baboon males prefer females with bigger backsides as the mark of a good mother, but new research suggests it isn't so simple.
A study of wild baboons in southern Kenya reveals that the size of a female's swollen rump doesn't matter as much as previously thought.
The study appears online in the journal Animal Behaviour.
Baboons breed throughout the year, and mating occurs during times when a female's behind ...