Slowdown after Ice Age sounds a warning for Great Barrier Reef's future
2015-05-05
(Press-News.org) Environmental factors similar to those affecting the present day Great Barrier Reef have been linked to a major slowdown in its growth eight thousand years ago, research led by the University of Sydney, Australia shows.
"Poor water quality, increased sediments and nutrients - conditions increasingly being faced by the modern day reef - caused a delay in the Reef's growth of between seven hundred and two thousand years duration," said Belinda Dechnik, from the University of Sydney's School of Geosciences and lead author of an article published in Marine Geology in May.
"It took hundreds more years then we would have expected to establish itself and even longer to attain the complex level of biodiversity that much of the Reef has become famous for."
"While that may appear inconsequential in the 700,000 year history of the Reef even a decade of such delayed growth would have a rapid impact on today's Reef and the experiences of the estimated two million people who visit it every year," Dechnik said.
The research was conducted at the University's research station at One Tree Island on the Reef.
The researchers sampled 15 reef cores from the Southern Great Barrier Reef. The cores were radiocarbon dated to establish their ages. Species of reef corals were also identified to establish any coral community changes over the past eight thousand years.
The findings show that when the Great Barrier Reef started its current regrowth, following the sea level rise when the ice sheets last melted eight thousand years ago, it was acutely sensitive to the turbulent conditions.
The increase in sediments and nutrients following the flooding of the pre-existing reefs is likely to have been responsible for the poor water quality.
"Not only was there a lag in reef growth of up to two thousand years following the flooding of the previous reef platforms but the reef communities that grew there were much less complex than those inhabiting those areas of the reef today. It took another two to three thousand years for the rich diversity that we see in those reef areas today to become established."
The researchers believe the findings have important implications for the future health of the Great Barrier Reef, as port expansions and high nutrient runoff is expected to increase over the coming decades, particularly in Gladstone, adjacent to where the reefs that were studied are located.
INFORMATION:
This research was done in collaboration with the University of Granada and Queen's University, Belfast.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-05-05
Why does a species not adapt to an ever-wider range of conditions, gradually expanding its geographical range? In their paper published on May 5 in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences), Jitka Polechova and Nick Barton at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (IST Austria) seek to answer this question, which lies at the interface between ecology and evolution. The theory presented by Polechova and Barton suggests that any natural population is liable to form sharp margins.
J.B.S. Haldane, one of the founders of population genetics, studied ...
2015-05-05
In cooperation with a Swiss research team, geographers of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have developed a novel measuring system relying on two different physical methods that promises to enhance forecasting of avalanches and spring floods. The method combines GPS and radar to measure snow properties also on the slopes.
Accurate forecasting of avalanches, and the risk of flooding in Alpine catchment areas during the spring thaw, primarily requires time-resolved data on snow volumes and the levels of liquid water in the snow cover. A research group led ...
2015-05-05
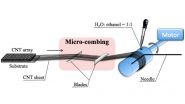
Researchers from North Carolina State University and China's Suzhou Institute of Nano-Science and Nano-Biotics have developed an inexpensive technique called "microcombing" to align carbon nanotubes (CNTs), which can be used to create large, pure CNT films that are stronger than any previous such films. The technique also improves the electrical conductivity that makes these films attractive for use in electronic and aerospace applications.
"It's a simple process and can create a lightweight CNT film, or 'bucky paper,' that is a meter wide and twice as strong as previous ...
2015-05-05
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative condition that strikes at the heart of what makes us human: the ability to think, to feel, to remember and to communicate with those around us. The tragedy is compounded by the fact that there is currently no cure, no treatment, and no diagnostic method capable of identifying Alzheimer's at its early stages.
A ground-breaking study has now, for the first time anywhere, characterized early-stage changes that occur inside individual, Alzheimer's-affected cells in the intact brain. Remarkably, the study indicates that even ...
2015-05-05
How many websites have you clicked on recently that haven't converted their format to mobile, frustrating your efforts to get the information you need in an effective and timely way?
Now researchers from Northwestern University have unearthed some provocative facts on how consumers utilize their mobile devices to buy groceries. With the global market for smartphones predicted to reach two billion by 2016, their findings should convince retailers planning marketing strategies and advertising campaigns that they need to pay attention to mobile.
In "On the Go: How Mobile ...
2015-05-05
PITTSBURGH (May 5, 2015) ... For decades, robots have advanced the efficiency of human activity. Typically, however, robots are formed from bulky, stiff materials and require connections to external power sources; these features limit their dexterity and mobility. But what if a new material would allow for development of a "soft robot" that could reconfigure its own shape and move using its own internally generated power?
By developing a new computational model, researchers at the University of Pittsburgh's Swanson School of Engineering have designed a synthetic polymer ...
2015-05-05
Treating gum disease reduced symptoms of prostate inflammation, called prostatitis, report researchers from Case Western Reserve University School of Dental Medicine and the Departments of Urology and Pathology at University Hospitals Case Medical Center.
Previous studies have found a link between gum disease and prostatitis, a disease that inflames the gland that produces semen. Inflammation can make urination difficult.
"This study shows that if we treat the gum disease, it can improve the symptoms of prostatitis and the quality of life for those who have the disease," ...
2015-05-05
Although the use of cannabis as a medical drug is currently booming (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2012; 109: 495-501), we should not forget that leisure time consumption--for example, smoking weed--can cause acute and chronic harms. These include panic attacks, impaired coordination of movement, and nausea, as Eva Hoch and colleagues show in a topical review article in Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2015; 112: 271-8). The symptoms depend on a patient's age, the amount of the drug consumed, and the frequency of drug use. It also matters in which form the ...
2015-05-05
(Winston-Salem, N.C. - May 5, 2015) - Researchers from Wake Forest University and the University of Utah are the first to successfully fabricate halide organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite field-effect transistors and measure their electrical characteristics at room temperature.
"We designed the structure of these field-effect transistors that allowed us to achieve electrostatic gating of these materials and determine directly their electrical properties," said lead author, Oana Jurchescu, an assistant professor of physics at Wake Forest. "Then we fabricated these transistors ...
2015-05-05
This news release is available in German.
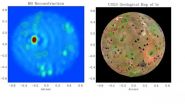
With the first detailed observations of a lava lake on a moon of Jupiter, the Large Binocular Telescope Observatory in Arizona places itself as the forerunner of the next generation of Extremely Large Telescopes. The applied high-resolution imaging methods were developed by an international research team including scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Bonn and the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Heidelberg.
Io, the innermost of the four moons of Jupiter discovered by Galileo in January ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Slowdown after Ice Age sounds a warning for Great Barrier Reef's future