(Press-News.org) Time is critical when it comes to stroke, and early treatment is associated with better outcomes. According to the Screening with MRI for Accurate and Rapid stroke Treatment (SMART) study, small changes in quality improvement procedures enabled clinicians to use MRI scans to diagnose stroke patients before giving acute treatment, within 60 minutes of hospital arrival. MRI scans provide detailed images but take longer to complete than CT scans, which are commonly used in most centers. The findings, published in Neurology, were supported in part by the National Institutes of Health's National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS).
"By making small changes to our processes, we were able to scan suspected stroke patients with MRI and appropriately treat patients within a goal time of 60 minutes. This is an important finding for hospitals, healthcare providers and the public," said Amie Hsia, M.D., medical director of the Comprehensive Stroke Center at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington D.C., and senior author of the study. "Not only does MRI provide more precise and complete information than the traditionally used CT scan, now we've also demonstrated that it is feasible to use from a time perspective."
National guidelines suggest that stroke patients should receive treatment within 60 minutes of arriving at the hospital. The majority of hospitals rely on rapid CT scans to determine if an individual is eligible for intravenous tPA, the only FDA-approved treatment for ischemic strokes, those caused by blood clots in the brain. If a CT scan shows the patient is having a bleeding, or hemorrhagic, type of stroke, tPA cannot be used as treatment. For many years CT scans were the only imaging tool available in most hospitals, but now MRIs are becoming more widely available.
Clinicians at MedStar Washington Hospital Center and Suburban Hospital, Bethesda, Maryland, routinely work with physician-scientists from NIH and have access to their cutting-edge medical protocols and technologies. The two hospitals use MRI instead of CT scans to screen stroke patients. Although MRI scans can take up to 15 minutes longer than CT scans, they provide clinicians with more detailed information about what is happening in a patient's brain. Using MRI, clinicians can see early changes taking place during the stroke. In this way, they can see what tissue is at risk and identify blocked blood vessels or subtle bleeding that cannot be picked up by CT.
To reduce the door to treatment time, multidisciplinary teams at both hospitals carefully examined the existing processes to identify time-consuming bottlenecks or duplicative methods. By using "lean process interventions," they found a number of steps that could be eliminated or changed. For example, at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, a lengthy MRI screening form was simplified to three questions; at Suburban Hospital, tPA was put into the medication cart in the MRI suite so that it could be given immediately to patients after scanning instead of returning them to the Emergency Department for treatment.
Once the changes were implemented, Dr. Hsia's team examined whether they had an impact on treatment times for patients. The results indicated that door to treatment time was reduced from 93 to 55 minutes, a difference of 40 percent. Over a two year period, the percentage of patients treated within 60 minutes increased from 13 to 61.5 percent. Further analysis revealed that these changes were due to faster MRI start times.
"There was no difference in the patient characteristics. It was clear the improvements were due to the changes we made in the processes at these two hospitals," said Dr. Hsia.
"A number of the changes that Dr. Hsia's team assessed were not specific for MRI scans, but were related to general procedures of getting patients ready for imaging as quickly as possible. This suggests that these findings are relevant even in hospitals that do not have emergency access to MRI scanners," said Walter Koroshetz, M.D., acting director of NINDS. "We will persist in evaluating best practices for acute stroke care to ensure that the greatest number of patients receive treatment as early as possible following stroke."
Dr. Hsia and her colleagues will continue to monitor the door to treatment times, to ensure they are sustainable. In addition, they plan to continue to evaluate best practices for acute stroke care and look for other improvements to further decrease door-to-treatment times for patients.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the NINDS.
References:
Shah et al. "SMART: Screening with MRI for Accurate and Rapid Stroke Treatment," Neurology, May 13, 2015.
The NINDS is the nation's leading funder of research on the brain and nervous system. The mission of NINDS is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
PHOENIX, Ariz. -- May 13, 2015 -- A study led by the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen) has for the first time matched dozens of infantile diseases and syndromes involving muscle weakness and stiff joints to their likely genetic origins.
The study, in association with the University of British Columbia and BC Children's Hospital Vancouver, was published this month (May) in the American Journal of Medical Genetics. The study's goal is to better enable physicians and geneticists to advance new treatments that might help these children.
"It's amazing to us ...
Washington, D.C., May 13, 2015 -- Using efficiency principles borrowed from "lean" manufacturing processes, two Washington-area hospitals have gotten a life-saving drug to stroke patients significantly quicker, while also obtaining better diagnostic information using MRI. That's according to a new study published online ahead of print in the May 13 issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
National benchmarks call for getting stroke patients from the door of the emergency room to injection with the clot-busting drug known as ...
MISSOULA -- The amount of time and effort songbirds spend warming their eggs directly correlates to their own survival probability and that of their eggs, according to a study by University of Montana researchers that will appear in an upcoming issue of The American Naturalist.
The amount of care parents provide their young varies greatly across the animal kingdom, particularly among songbird species, who spend anywhere from 20 percent to nearly 100 percent of daylight hours warming eggs in their nests. A team of researchers led by Thomas Martin, senior scientist and ...
Cats may hold vital clues about the health benefits of vitamin D, a study suggests.
Researchers found that higher levels of vitamin D are linked to better survival chances for hospitalised pet cats.
Cats could prove useful for investigating the complex link between vitamin D and a range of health problems that also affect people, the researchers say.
The findings may also help vets to give owners better advice about their pets' prognosis, according to researchers at the University of Edinburgh's Royal (Dick) School of Veterinary Studies.
Researchers examined blood ...
Eighty percent of a population of Burmese long-tailed macaques on an island in southern Thailand use stone and shell tools to crack open seafood, and do so using 17 different action patterns, according to a study published May 13, 2015 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Amanda Tan from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, and colleagues, under an 8 year field project led by Michael D Gumert, also from NTU.
The authors of the study explored variation in how Burmese long-tailed macaques used percussive stone and shell tools to hammer coastal foods on Piak Nam ...
Investigators at the Stanford University School of Medicine have identified a pattern of gene activity that could help scientists create a blood test for quickly and accurately detecting whether patients are experiencing a deadly immune-system panic attack.
Sepsis is a whole-body inflammation syndrome set off when the immune system wildly overreacts to the presence of infectious pathogens. It is the leading cause of hospital deaths in the United States, accounting for nearly half of the total number, and is tied to the early deaths of at least 750,000 Americans each year. ...
The potato leafhopper is a tiny insect--barely half the size of a grain of rice--with a bright lime green color that helps it blend in against plant leaves. Despite its unassuming appearance, this little pest causes big headaches for farmers across the eastern half of the United States. By feeding voraciously on many crops, including potatoes, green beans and alfalfa, the migratory potato leafhopper causes untold millions of dollars in damage every year.
Now, a study by entomologists at the University of Maryland and Queens College at the City University of New York ...
Alcohol drunk by a mouse in early pregnancy changes the way genes function in the brains of the offspring, shows the recent study conducted at the University of Helsinki. The early exposure was also later apparent in the brain structure of the adult offspring. The timing of the exposure corresponds to the human gestational weeks 3-6 in terms of fetal development.
In addition, the exposure to alcohol was found to cause similar changes to gene function in other tissues of the infant mice. These results suggest that alcohol causes permanent changes to gene regulation in ...
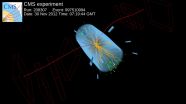
Two experiments at the Large Hadron Collider at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) in Geneva, Switzerland, have combined their results and observed a previously unseen subatomic process.
As published in the journal Nature this week, a joint analysis by the CMS and LHCb collaborations has established a new and extremely rare decay of the Bs particle (a heavy composite particle consisting of a bottom antiquark and a strange quark) into two muons. Theorists had predicted that this decay would only occur about four times out of a billion, and that is roughly ...
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) -- or, simply, prostate enlargement -- is one of the most common diseases of aging among men in the United States. In fact, by the time they hit 80 or above, upwards of 90 percent of all men in the U.S. experience some degree of prostate enlargement. And of those, 40 percent require medical treatment.
Despite the fact that the disease impacts so many people and carries with it a huge price tag -- estimated at tens of billions of dollars per year in medical expenses and lost wages, among other costs -- the factors that contribute to BPH ...