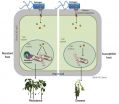
Douglas study on neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb
Towards a better understanding of the mechanisms of depression
2015-05-21
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in French.
Montreal, May 21, 2015 - A new study published by the team of Naguib Mechawar, Ph.D., a researcher at the Douglas Institute (CIUSSS de l'Ouest-de-l'île-de-Montréal) and Associate Professor in the Department of Psychiatry at McGill University, suggests that the integration of new neurons in the adult brain is a phenomenon more generally compromised in the brains of depressed patients.
This new work confirms that neurogenesis in the human olfactory bulb is a marginal phenomenon in adults. These findings shed light on the special features of the human brain.
We already knew about the existence of neurogenesis in the adult brain, the process through which new neurons are produced and integrated throughout the course of life, mainly in two brain regions, the hippocampus and the olfactory bulb (OB). So far, however, this knowledge has relied mainly on studies in rodents. In humans, although neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus is no longer a matter of debate, the presence of neurogenesis in the OB has remained controversial.
The Douglas-Bell Canada Brain Bank
The work of the doctoral candidate Marissa Maheu on Naguib Mechawar's team breaks new ground. Based on post-mortem brain samples from the Douglas-Bell Canada Brain Bank, it shows the presence of only a few immature cells within each olfactory tract, which is the migration path to the OB. However, the comparison of brain tissue from healthy people with samples from depressed, suicidal individuals, suggests that migration and maturation of these cells is affected in depressed patients.
"While previous evidence from animals and humans has suggested that neuronal proliferation or survival might be altered in depression, this is the first evidence implicating changes in neuronal maturation and migration in the disorder," explains Dr. Mechawar.
Given that the phenomenon of neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus has already been implicated in depression, these new data, published in the journal Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, is an important step towards understanding depression.
INFORMATION:
This work was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and the Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé (FRQS).
For information and interviews:
Florence Meney
Media Relations
Communications and Public Affairs
Douglas Mental Health University Institute
Tel.: 514-761-6131, ext. 2769
About the Douglas Institute - http://www.douglas.qc.ca
The Douglas is a world-class institute affiliated with McGill University and the World Health Organization. It treats people suffering from mental illness and offers them both hope and healing. Its teams of specialists and researchers are constantly increasing scientific knowledge, integrating this knowledge into patient care, and sharing it with the community in order to educate the public and eliminate prejudices surrounding mental health.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-05-21
Alexandria, VA - In the years following the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster, forest fires billowed plumes of contaminated smoke, carrying radioactive particles throughout Europe on the wind. Now, researchers fear that a shift to a hotter, drier climate in Eastern Europe could increase the frequency of these fires.
Researchers from the University of South Carolina in Columbia used satellite imagery of fires in the 2000s and field measurements of radioisotope levels to model changes in the distribution of radiation over the region. The researchers found that fires likely ...
2015-05-21
Researchers have developed a model to assess how dams affect the viability of sea-run fish species that need to pass dams as they use both fresh and marine waters during their lifetimes. NOAA's Northeast Fisheries Science Center (NEFSC) and Greater Atlantic Regional Fisheries Office (GARFO) have partnered on this project to test how varying passage efficiency at dams related to survival rates for these species.
Using a model of endangered Atlantic salmon in Maine's Penobscot River as a case study, NOAA researchers found that abundance, distribution and number of fish ...
2015-05-21
Hamilton, ON (May 21, 2015) - Scientists at McMaster University have discovered how to make adult sensory neurons from human patients simply by having them roll up their sleeve and providing a blood sample.
Specifically, stem cell scientists at McMaster can now directly convert adult human blood cells to both central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) neurons as well as neurons in the peripheral nervous system (rest of the body) that are responsible for pain, temperature and itch perception. This means that how a person's nervous system cells react and respond to ...
2015-05-21
One of the reasons pluripotent stem cells are so popular in medical research is that they can be differentiated into any cell type. However, typical differentiation protocols lead to a heterogeneous population from which the desired type must be purified. Normally, antibodies that react to surface receptors unique to the desired cell are used for this purpose. However, in many cases the purification levels remain poor and the cells can be damaged. New RNA technology produced at CiRA may avoid these problems.
Professor Hirohide Saito at the Dept. of Reprogramming Science ...
2015-05-21
Receptors carrying built-in decoys are the latest discovery in the evolutionary battle between plants and pathogens. The decoy domains within the receptor detect pathogens and raise the cell's alarm when there is an infection.
Plants display component parts of their immune system on receptors to trick pathogens into binding with them, which then triggers defence mechanisms. The discovery comes from Professor Jonathan Jones' group at The Sainsbury Laboratory, published in the high-impact journal Cell with a companion paper on a similar discovery from the Deslandes group ...
2015-05-21
Almost 90 per cent of men with advanced prostate cancer carry genetic mutations in their tumours that could be targeted by either existing or new cancer drugs, a landmark new study reveals.
Scientists in the UK and the US have created a comprehensive map of the genetic mutations within lethal prostate cancers that have spread around the body, in a paper being hailed as the disease's 'Rosetta Stone'.
Researchers say that doctors could now start testing for these 'clinically actionable' mutations and give patients with advanced prostate cancer existing drugs or drug combinations ...
2015-05-21
May 21, 2015 - A University of Wyoming faculty member led a research team that discovered a certain type of soil bacteria can use their social behavior of outer membrane exchange (OME) to repair damaged cells and improve the fitness of the bacteria population as a whole.
Daniel Wall, a UW associate professor in the Department of Molecular Biology, and others were able to show that damaged sustained by the outer membrane (OM) of a myxobacteria cell population was repaired by a healthy population using the process of OME. The research revealed that these social organisms ...
2015-05-21
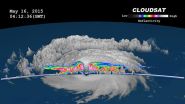
When Dolphin was a typhoon on May 16, NASA's CloudSat satellite completed a stunning eye overpass of Typhoon Dolphin in the West Pacific at 0412 UTC (12:12 a.m. EDT). By May 22, Dolphin's remnants were moving through the Northern Pacific.
NASA's CloudSat satellite sends pulses of microwave energy through the clouds, and some of the energy in the pulses is reflected back to the spacecraft. The time delay between when the pulse is sent and when the reflected energy is received back at the spacecraft is mapped into a distance of the cloud from the surface of the Earth, and ...
2015-05-21
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Last year, researchers at the University of Missouri published a study on genetic diversity in American black bears in Missouri, Arkansas and Oklahoma and determined that conservation management is needed to maintain healthy populations in the region. Now, those scientists have expanded the study to include black bears throughout North America. They discovered that black bears in Alaska are more closely related to bears in the eastern regions of the U.S. and Canada than those located in western regions. Details from the study revealed ancient movement patterns ...
2015-05-21
(PARIS, FRANCE) - Stent thrombosis following urgent angioplasty for acute heart attack occurred in less than 1% of patients in a large, "real-world" registry, regardless of whether the antithrombotic treatment used during the procedure was bivalirudin, heparin alone, or a GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor (typically in combination with heparin).*
However, patients who experienced a stent thrombosis between days 2 and 30, regardless of drug regimen, were more likely to die within one year than were patients who developed stent thrombosis within the first 24 hours of their procedure.
"What ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Douglas study on neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb
Towards a better understanding of the mechanisms of depression