(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C. -- May 26, 2015 -- A new study has demonstrated that a protein called Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) is critical for the Ebola virus to infect a host. The study, published in the May/June issue of mBio, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, suggests that drugs that block NPC1 could be used to treat this deadly disease.
"The science behind the concept of blocking the interaction between NPC1 and the virus is solid. Now, it is just a matter of powering through and identifying drugs that can inhibit NPC1 and moving them forward," said John Dye, Jr., PhD, co-principal investigator of the study and Viral Immunology Branch Chief, US Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID), Frederick, Maryland.
Currently, there are no FDA approved treatments for Ebola, and all of the therapies in the drug pipeline focus on attacking the virus. Targeting NPC1 is the first host-based therapeutic approach.
"Our work also illustrates the value of studying rare diseases like Niemann-Pick type C, which occurs in individuals who lack the NPC1 protein. That research has provided a body of knowledge that scientists could immediately apply to Ebola once it became known that Ebola exploits NPC1 for infection," said Steven Walkley, DVM, PhD, director of the Rose F. Kennedy Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Research Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City. Kartik Chandran, PhD, associate professor of microbiology & immunology at Einstein, was also co-principal investigator of the study. Drs. Chandran and Dye were members of the team that originally identified NPC1 as the Ebola receptor.
Previous in vitro studies have demonstrated that Ebola enters host cells by binding directly to NPC1, and that blocking the ability of the virus to engage NPC1 prevents Ebola infection
To test whether this was also true in vivo, investigators exposed three types of mice to Ebola: wild-type mice (normal mice), mice that were genetically engineered to be completely deficient in NPC1 (NPC1-/-), and mice engineered to have both a normal and a mutant NPC1 allele (NPC+/-).
While wild-type mice had high viral loads and died from Ebola infection by day nine, mice that were 100% deficient in NPC1 were completely free of the virus. "NPC1 is absolutely essential for in vivo pathogenesis, and if you can disrupt this, there are no signs of Ebola virus replication or pathogenesis," said Andrew Herbert, PhD, senior research scientist in the Viral Immunology Branch at USAMRIID.
NPC1+/- mice initially developed high levels of Ebola viremia, but these levels quickly decreased as the host immune response effectively cleared the virus. "The underlying story of an Ebola infection is that your immune system and the virus are in a race. If you can do anything to control the amount of virus that is in the system, keep it below a certain threshold, your immune system in many cases will win that race," said Dr. Dye.
The researchers also tested the efficacy of three NPC1 inhibitors in mice exposed to Ebola. Only two of the drugs provided minimal protection, but the researchers are not discouraged because it is unclear exactly how these inhibitors work. "We were not able to achieve great protection, but if we can disrupt NPC1 function more directly or more efficiently, targeting NPC1 should be a viable option for developing therapeutics against Ebola and other filoviruses," said Dr. Herbert.
Five filoviruses, including Ebola and Marburg viruses, are currently associated with severe disease in humans, "Every filovirus that we have evaluated so far requires NPC1, so if this works, we will have potentially found a silver bullet against all filoviruses," said Dr. Dye.
INFORMATION:
The American Society for Microbiology is the largest single life science society, composed of over 39,000 scientists and health professionals. ASM's mission is to advance the microbiological sciences as a vehicle for understanding life processes and to apply and communicate this knowledge for the improvement of health and environmental and economic well-being worldwide.
An international team including scientists from Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University and the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID) has identified the molecular "lock" that the deadly Ebola virus must pick to gain entry to cells. The findings, made in mice, suggest that drugs blocking entry to this lock could protect against Ebola infection. The study was published in today's edition of the online journal mBio.
The researchers found that the Ebola virus can't infect cells unless it first attaches to a host protein called ...
By unlocking the secrets of a bizarre virus that survives in nearly boiling acid, scientists at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have found a blueprint for battling human disease using DNA clad in near-indestructible armor.
"What's interesting and unusual is being able to see how proteins and DNA can be put together in a way that's absolutely stable under the harshest conditions imaginable," said Edward H. Egelman, PhD, of the UVA Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics. "We've discovered what appears to be a basic mechanism of resistance - to ...
Mitsuyoshi Nakao, Director of the Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics in Kumamoto University and Associate Professor Noriko Saitoh revealed that a cluster of defined, non-coding RNAs are mechanistically involved in endocrine therapy resistance in human breast cancer cells. Furthermore, resveratrol, a kind of polyphenol, was found to repress these RNAs and inhibit the proliferative activity of breast cancer cells which had acquired resistance. The work was published in Nature Communications on April 29th, 2015.
Breast cancer is one of the most common types ...
This news release is available in French.
Commuting length, distance, and means are stress factors that can lead to burnout, says Annie Barreck of the University of Montreal's School of Industrial Relations. "A correlation exists between commuting stress factors and the likelihood of suffering from burnout. But their importance varies according to the individual, the conditions in which their trips take place, and the place where the individual works," she explained. Barreck will present her research today at the 83rd congress of the Association francophone pour ...
In a new national survey of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, Health Union found a severe impact on quality of life, employment, and ability to afford treatment. The autoimmune condition attacks the body, resulting in joint inflammation, pain, stiffness, and swelling, but may also harm other organs. About 1.3 million Americans or about one percent of the global population have RA.
Ninety-four percent of respondents with RA said they cannot do as much as they were able before acquiring the disease. Additionally, 67% said others do not understand the severity of their ...
Protected areas are the cornerstone to prevent species extinctions. The Convention on Biological Diversity have set a target to protect 17% of all terrestrial land by 2020.
Many of the international recommendations concerning protection goals are provided for single countries to take action individually. Researchers in the University of Helsinki, Finland, stress the importance of international collaborations in the protected area expansion process.
"It has been shown that working at the country level is less efficient than promoting transnational collaborations. As ...
New UK research has challenged the assumption that people with rheumatoid arthritis always take their medication as prescribed.
Researchers from the Arthritis Research UK Centre for Epidemiology at The University of Manchester found that 40% of patients scored low on an adherence questionnaire at least once during their time in a recent study, indicating that they might not be taking their expensive biological therapies as regularly as prescribed.
Their research is published online in the journal Rheumatology.
The findings have prompted Arthritis Research UK's head ...
Cough treatments could change dramatically after the herpes virus helped researchers discover that the respiratory tract links to two different parts of the nervous system.
A research team led by The University of Queensland's Dr Stuart Mazzone made the important breakthrough after setting out to learn more about the triggers behind excessive coughing.
"Different physical sensations arise from the upper and lower respiratory tracts in people with respiratory diseases," said Dr Mazzone, from the School of Biomedical Sciences.
"The irritating sensations from the upper ...
Polymer solar cells are a hot area of research due to both their strong future potential and the significant challenges they pose. It is believed that thanks to lower production costs, they could become a viable alternative to conventional solar cells with silicon substrates when they achieve a power conversion efficiency--a measure that indicates how much electricity they can generate from a given amount of sunlight--of between 10 and 15 percent. Now, using carefully designed materials and an "inverted" architecture, a team of scientists has achieved efficiency of 10 percent, ...
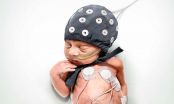
Giant strides have been taken in the early care of very premature infants in postnatal intensive care units during the past two decades. Doctors can now support the function of especially the lungs, heart and the circulatory system so as to guarantee the survival of most of even extremely premature infants.
Despite a good start, many of these may still have lifelong problems with brain function, such as attention deficit disorders or difficulty with visual function. For this reason, the primary focus of developing care for premature infants has been on securing brain ...