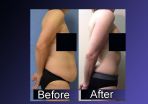
(Press-News.org) ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill., June 1, 2015 - An increase in the number of weight loss surgeries in the U.S. is beginning to have a ripple effect in plastic surgery, according to new data released today by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). Procedures specifically associated with massive weight loss, including tummy tucks, thigh lifts, breast lifts and upper arm lifts, grew at their fastest rate in four years in 2014, according to the report. That follows a similar increase in the growth of weight loss surgeries.
"We think there is a correlation between the two types of procedures, and we expect that trend to continue," said ASPS President Scot Glasberg, MD, and private-practice plastic surgeon based in Manhattan, New York. "Post-massive weight loss patients are the number one growth area I have seen in my practice, and I'm sure that's the case in many doctor's offices across the country."
In 2013, 179,000 Americans underwent weight loss surgery, averaging nearly 500 procedures every day. According to the American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, it's the most since 2009 and the third highest number on record. Since then, plastic surgeries related to weight loss are up across the board, as well.
Thigh lifts and upper arm lifts had their biggest single-year increase in five years in 2014, both up nine percent. Tummy tucks inched up four percent and breast lift procedures posted a ten percent increase, the largest single-year gain since 2009, when the ASPS began tracking procedures performed specifically on massive weight loss patients.
"You can't attribute that to anything other than the fact that there are more massive weight loss patients out there looking to take care of the problems that they now have after their weight loss surgery," said Dr. Glasberg. "On the one hand they are thrilled to have lost so much weight, but they are trading one dilemma for another."
Those who experience massive weight loss are often left with excessive amounts of sagging skin, particularly in the thighs, under the arms, around the abdomen and in the breasts. The excess skin can not only be unsightly and uncomfortable, in many cases it can be painful.
"It was hard for me to exercise. I couldn't do aerobics or even run because the excess skin was so bad, and no amount of compression would change that," said Jan O'Daniel of Pickerington, Ohio. Six years ago O'Daniel underwent bariatric surgery and dropped more than 130 pounds, but no matter how much weight she lost, she still didn't like what she saw. "I carried a lot of weight in my abdomen and felt like my stomach was just as big. Even though I knew it wasn't, even though I knew my clothing size had gone down six sizes, I still focused on my belly and it absolutely drove me nuts."
"That's not uncommon," said O'Daniel's plastic surgeon Jason Lichten, MD, of Lancaster, Ohio. "These patients have the tremendous psychological burden of looking into the mirror and seeing all of this extra skin that's hanging off of them, and no matter how much weight they lose, a lot of them still see themselves as heavy because of it."
In 2014, nearly 45,000 patients who experienced massive weight loss also opted to undergo plastic surgery to reshape their bodies. While those numbers represent the biggest single-year increase in nearly a half decade, it's still only a fraction of patients who may benefit from it.
"Going forward, we'd like to be a part of the process from the outset, when patients are first starting to consider weight loss surgery," said Dr. Glasberg. "A lot of times patients think weight loss surgery is the answer to their issues, when in reality it may only be one step in the process."
Dr. Lichten agrees. "If plastic surgeons can get involved with patients earlier, we can not only give them a more realistic idea of what to expect from a physical standpoint, but we can help them devise a plan for any follow up procedures after their weight loss," he said.
That's something O'Daniel wishes she'd done. She was so focused on losing the weight, she didn't realize there could be follow up surgeries. "I didn't realize plastic surgery was an option," she said. "I thought it was out of reach for me from an affordability standpoint, but it wasn't. I'm glad I did it, because it changed my life."
INFORMATION:
About ASPS
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) is the world's largest organization of board- certified plastic surgeons. Representing more than 7,000 Member Surgeons, the Society is recognized as a leading authority and information source on aesthetic and reconstructive plastic surgery. ASPS comprises more than 94 percent of all board-certified plastic surgeons in the United States. Founded in 1931, the Society represents physicians certified by The American Board of Plastic Surgery or The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada. ASPS advances quality care to plastic surgery patients by encouraging high standards of training, ethics, physician practice and research in plastic surgery. You can learn more and visit the American Society of Plastic Surgeons at PlasticSurgery.org or Facebook.com/PlasticSurgeryASPS or Twitter.com/ASPS_News.
Boston - A new study by Boston University and Boston Medical Center (BMC) researchers reveals that U.S. states with stronger alcohol policies have lower rates of youth overall drinking and binge drinking. The study's results, published in the journal Pediatrics, further suggest that the link is largely a result of policies intended mostly for adults and their effects on reducing adult binge drinking.
The first-of-its kind study, led by a multi-disciplinary research team at BMC and the BU School of Public Health (BUSPH), reviewed data on 29 youth-specific and adult policies ...
EVANSTON, Ill. --- Why do some people immediately burst into laughter after a humorous moment, while others can barely crack a smile? New research examining emotional reactivity suggests one of the answers may lie in a person's DNA.
In a new study linking a gene to positive emotional expressions such as smiling and laughing, researchers demonstrated that people with a certain genetic variant -- those with short alleles of the gene 5-HTTLPR -- smiled or laughed more while watching cartoons or subtly amusing film clips than people with long alleles.
Previous research ...
VANCOUVER, Wash.--Washington State University researchers have found that the more hunter-gatherers smoke cannabis, the less they are infected by intestinal worms. The link suggests that they may unconsciously be, in effect, smoking medical marijuana.
Ed Hagen, a WSU Vancouver anthropologist, explored cannabis use among the Aka foragers to see if people away from the cultural and media influences of Western civilization might use plant toxins medicinally.
"In the same way we have a taste for salt, we might have a taste for psychoactive plant toxins, because these things ...
Cancer Research UK scientists have discovered how giving a class of drugs called AKT inhibitors in combination with radiotherapy might boost its effectiveness across a wide range of cancers, according to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation today*.
Tumours often grow so quickly that some of the cells do not have access to the body's blood supply, causing them to become oxygen-starved. This rapid growth usually sends signals to the cells to die, but in cancers with faults in a gene called p53 -- present in at least half of all cancers -- this signal ...
A debate at this year's Euroanaesthesia meeting in Berlin will focus on whether laughing gas (nitrous oxide) should be banned from the operating room. The debate coincides with an article on the "Current place of nitrous oxide in clinical practice" published in the European Journal of Anaesthesiology, that concludes there is "no clinically relevant evidence for the withdrawal of nitrous oxide from the armamentarium of anaesthesia practice or procedural sedation." The article has been prepared by a special taskforce of the European Society of Anaesthesiology (ESA), which ...
New research presented at this year's Euroanaesthesia conference in Berlin shows that American patients undergoing orthopaedic surgery* receive more treatments for pain and that their experience of pain differs in some aspects to orthopaedic patients internationally. The study is by Drs Winfried Meissner and Ruth Zaslansky, University Hospital Jena, Germany, and Dr C. Richard Chapman Utah, Pain Research Center, Salt Lake City, USA. All researchers are part of the international PAIN OUT** research group.
Poorly controlled pain after surgery is a major problem internationally ...
Research presented at this year's Euroanaesthesia exploring the protective effect of various heart medications that patients are taking before undergoing coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery concludes that statins reduce the risk of death by two thirds, or 67 percent, while no consistent effects were seen for other medications. The study is reported by Assistant Professor Dr. Robert Sanders, Anesthesiology & Critical care Trials & Interdisciplinary Outcomes Network (ACTION), Department of Anesthesiology, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WN, USA, and Drs. Puja Myles ...
In a head-to-head clinical trial comparing standard chemotherapy with the immunotherapy drug nivolumab, researchers found that people with squamous-non-small cell lung cancer who received nivolumab lived, on average, 3.2 months longer than those receiving chemotherapy. Squamous non-small cell lung cancer accounts for 25 to 30 percent of all lung malignancies.
Results of the trial, reported in the May 31 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine and presented at the American Society for Clinical Oncology 2015 annual meeting, also showed that after a year, the nivolumab ...
Using high-precision genetic tests to differentiate the thousands of bacteria that make up the human microbiome, researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center suggest that they have found a possible -- and potentially surprising -- root cause of the increased frequency of certain eye infections among contact lens wearers.
In a study report on their work to be presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Microbiology on May 31 in New Orleans, NYU Langone researchers say they have identified a diverse set of microorganisms in the eyes of daily contact lens wearers ...
CHICAGO, IL, MAY 31, 2015 -- Treating advanced melanoma patients with either a combination of the immunotherapy drugs nivolumab (Opdivo™) and ipilimumab (Yervoy™) or nivolumab alone significantly increases progression-free survival (PFS) over using ipilimumab alone, according to new findings from researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) simultaneously presented today at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) annual meeting and published online in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM). Examining specific characteristics of each ...