Atmospheric oxygen levels may have influenced past climate
2015-06-11
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in Japanese.
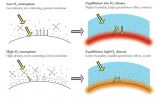
Variations in the percentage of atmospheric oxygen may have influenced climate in the past 500 million years, according to new calculations by Christopher Poulsen and colleagues. Since oxygen isn't a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide, it typically hasn't been included in studies of past climate change. But the proportion of atmospheric oxygen has varied between 10 percent and 35 percent over the past 500 million years, and Poulsen and colleagues have developed a model to show how those fluctuations might impact climate. In general, the percentage of oxygen contributes to the atmosphere's mass and density, which in turn influences how the atmosphere absorbs and scatters incoming solar radiation. When oxygen concentrations are low and the atmosphere is less dense, the changes to solar radiation scattering can lead to higher temperatures and precipitation, the researchers note. They applied their model to data from the Cenomanian time period, about 100 to 94 million years ago -- one of the warmest periods in the past 100 million years and a time of very low atmospheric oxygen concentration. By accounting for the climatic effects of oxygen, the researchers' model was able to predict the Cenomanian's temperatures more consistently than models that use carbon dioxide data alone. Daniel Peppe and Dana Royer discuss the results in a related Perspective.
INFORMATION:
Article #20: "Long-term climate forcing by atmospheric oxygen concentrations," by C.J. Poulsen; C. Tabor at University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, MI; J.D. White at Baylor University in Waco, TX.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-11
This news release is available in Japanese.
How do nocturnal insects forage so successfully in the twilight and darkness? A new study by Simon Sponberg and colleagues suggests that the vision of the hawkmoth, Manduca sexta, which hovers in place while it feeds on nectar at dawn and dusk, is finely attuned to the swaying of flowers in the breeze. These findings imply that both the sight and flight of the hawkmoth likely evolved to match the movements of flowers -- their only source of food -- perfectly, helping to explain how the nimble insects are able ...
2015-06-11
A new study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine found that synchronized physiological interactions between remote brain regions have genetic underpinnings.
The research was performed at Stanford but was made possible by collaborations with the Seattle-based Allen Institute for Brain Science and the IMAGEN Consortium, a multicenter European project, said the study's senior author, Michael Greicius, M.D., an associate professor of neurology and neurological sciences.
The study will be published June 11 in Science.
An emerging consensus among ...
2015-06-11
This news release is available in German.
It has been hypothesized that globalization of human-mediated dispersal of species may break down biogeographic boundaries. However, empirical tests had been lacking until recently. An international research team has now discovered a comprehensive biogeographic reorganization for 175 species of alien gastropods across 56 countries. The data shows that homogenization is indeed happening. Geographic barriers to dispersal have fallen down but climate still limits how species colonize new areas. The study was published in the ...
2015-06-11
Investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard have added another piece to the puzzle of how a small group of individuals known as elite controllers are able to control HIV infection without drug treatment. In their paper published in the open-access journal PLOS Pathogens, the research team reports finding that dendritic cells of elite controllers are better able to detect the presence of HIV - paradoxically through a greater susceptibility to HIV infection - which enables them to stimulate the generation of T cells ...
2015-06-11
The concept sounds like the stuff of science fiction: take a pill, and suddenly new tissues grow to replace damaged ones.
Researchers at Case Western Reserve and UT Southwestern Medical Center this week announced that they have taken significant steps toward turning this once-improbable idea into a vivid reality. In a study published in the June 12 edition of Science, they detail how a new drug repaired damage to the colon, liver and bone marrow in animal models -- even going so far as to save the lives of mice who otherwise would have died in a bone marrow transplantation ...
2015-06-11
This news release is available in Japanese.
Researchers in Japan have found, for the first time in vertebrates, a genetic switch that determines whether germ cells become sperm or eggs. The gene is named foxl3, and has been identified using a small fish called medaka (Oryzias latipes). In medaka without this gene's functionality, surprisingly, sperm are produced in the ovaries of females. The sperm that are produced function normally, and have been confirmed to produce normal offspring. These results will be announced in the journal Science through Science Express ...
2015-06-11
EDMONTON, Canada, June 11 -- In this summer's much anticipated blockbuster Jurassic World, actor Chris Pratt joins forces with a pack of swift and lethal velociraptors. 'Velociraptor belongs to a group of predatory dinosaurs called the deinonychosaurs, or simply the 'raptors',' says University of Alberta paleontologist Scott Persons. 'Raptors are characterized by particularly nasty feet. Their big toes each bore an enlarged and wickedly hooked talon, which makes raptors well suited for Hollywood fight scenes.'
Persons and University of Alberta alumnus Lida Xing are part ...
2015-06-11
A NASA mission led by UCLA professor Christopher Russell has released new images of the dwarf planet Ceres, the largest asteroid between Mars and Jupiter.
The photos were produced by the spacecraft Dawn, which is now observing Ceres from 2,700 miles above its surface; NASA has also produced a one-minute video animation that sheds new light on this mysterious and heavily cratered world.
'Everything we learn from Ceres will be absolutely new,' said Christopher Russell, a UCLA professor of space physics and planetary science, and the Dawn mission's principal investigator. ...
2015-06-11
Philadelphia, June 11 -- The Maillard reaction is a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that results in browned foods like seared steaks and toasted bread. When proteins and sugars are mixed together and heated, new chemical compounds are formed. Some are responsible for new flavors and some, according to a new study published in the Journal of Dairy Science®, may protect us against cardiovascular disease.
Researchers at the R&D Center, Seoul Dairy Cooperative, the College of Life Science & Biotechnology, Korea University, and the BK21 Plus Graduate ...
2015-06-11
People with autism are often described as "seeing the world differently." They tend to show superior perception for details, like, for example, the autistic artist Stephen Wiltshire's highly accurate representations of cityscapes drawn from memory. Now, researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on June 11 show that those differences in perceptual skill are present very early in infancy, before the onset of clinical symptoms of autism.
The researchers say that the findings may shift scientists' view of autism by suggesting that changes in perception ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Atmospheric oxygen levels may have influenced past climate