INFORMATION:
The Arthur W. Page Center supported this work.
Most admired companies have room for social media improvement
2015-06-11
(Press-News.org) Not all of America's most admired companies are killing it on social media. In fact, some are almost flat lining, according to a team of researchers.
Several firms on Fortune Magazine's list of America's most admired companies are failing to achieve basic social media standards, let alone best practices, according to Marcia DiStaso, associate professor of public relations, Penn State.
"We were surprised that not all the companies had a Twitter account, for instance, and not every company had a Facebook page, or a YouTube page," said DiStaso. "There are top companies that don't have a Facebook page, but just used an entry from their Wikipedia page."
While 95 percent of the 417 most admired companies on the list had a Facebook page, 51 percent were basic Wikipedia-fed pages. For example, ExxonMobil and Berkshire Hathaway, two of the world's biggest companies, only have default Wikipedia page holders as their Facebook home.
On an industry basis, companies in the consumer packaged goods industry, such as Coca-Cola and Coach, did the best across all three major social media platforms -- Twitter, Facebook and YouTube.
"When you think about the social media platforms we looked at, it's easier to communicate your content and that content resonates easier if you're in the consumer packaged goods industry," said DiStaso. "Coca-Cola could post or send out a picture of a cute animal with a bottle of Coke which, as content, isn't as hard to deliver, and you usually also have very passionate followers who will like it."
The companies in the study had a better handle on Twitter and YouTube, according to the researchers, who reported their findings in a current issue of the Journal of Promotion Management. A total of 82 percent of the companies had a Twitter account and 72 percent had a YouTube account.
One industry that struggles particularly with social media is the health care industry. However, the researchers speculated that this may be because the industry is heavily regulated.
"All of the industries have room for improvement, which is what the study shows, but there's specifically some more room for improvement in the health care industry," said DiStaso. "Since we've done the study, we have seen some growth in how the health care industry has used social media, but there's a lot more opportunities."
Using social media effectively may help these companies do more than just sell products and services. Social media can establish personal connections between a company and its customers.
"What social media does for organizations is it really helps create brand supporters and connect with people in more ways," said DiStaso. "From a personal perspective it allows the public to really get to know the company before they become that brand advocate."
The study built on prior research that identified some best practices in each social media platform, said DiStaso, who worked with Tina McCorkindale, associate professor of communication, Appalachian State University and Alexa Agugliaro, former undergraduate student in public relations, Penn State. The best practices vary across the social media platforms, but include tactics such as providing details of how the account is being managed and including a link to the company website.
The researchers examined efforts across the three major social media platforms because not all platforms fit the mission of each company.
Fortune's most admired companies list is one of the most frequently cited sources of information about company reputation. To create the list, the magazine asks corporate executives, directors and securities analysts to identify the reputations of companies. The companies included in the study appeared on the 2012 version of the list.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Implantable antibiotic-laced sponges reduce sternal infections in cardiac surgery
2015-06-11
Beverly, MA, June 11, 2015 - Cardiac surgeons often "crack open" the flat bone that forms the middle front section of the chest, known as the sternum, in order to reach important structures. When a sternal wound infection (SWI) occurs, serious complications and even death may result. Implanting antibiotic-laden sponges between the sternal halves before closure has been adapted to prevent infections. While a recent report questioned this practice, a meta-analysis in The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, the official publication of the American Association for ...
Clear, strong stimulation may help prevent apathy for persons with dementia
2015-06-11
Nursing home residents with dementia are less likely to be apathetic if they live in an appropriately stimulating environment, according to nursing researchers.
Nearly half of all residents in nursing homes have dementia, according to a 2013 report by the Centers for Disease Control. Apathy is one of the most common neurobehavioral symptoms in dementia, with about 90 percent of older adults with dementia experiencing it. Those with mild dementia will decline more quickly into severe dementia if they also suffer from apathy, making it important to help them stay engaged. ...
Lehigh University researchers unveil engineering innovations at TechConnect 2015
2015-06-11
Lehigh University engineers, materials scientists and chemists will present their innovative breakthroughs to a national showcase of investors and industrial partners at the TechConnect 2015 World Innovation Conference and National Innovation Showcase in Washington on June 14-17.
Working at the junction of engineering and health, the Lehigh innovations include a nanoscale device that captures tumor cells in the blood, a bioengineered enzyme that scrubs microbial biofilms and the creation of a safe and efficient chemical reagent that is stable at room temperature.
These ...
Bright light after night shift may enhance alertness and cognitive performance
2015-06-11
DARIEN, Ill. -- A new study suggests that bright light at the end of a night shift may have potential as a countermeasure to improve driving performance, particularly for low light work environments and commutes that occur before dawn.
Results show that temperature, subjective alertness and psychomotor vigilance performance decreased significantly across the night. Bright light significantly suppressed melatonin, but did not improve subjective alertness or psychomotor vigilance performance. Sleep deprivation markedly increased incidents, accidents, and the average lane ...
New study links excessive iron in cells with AMD, other diseases
2015-06-11
LEXINGTON, Ky., June 12 -- In a new University of Kentucky study published today in Cell Reports, a leading scientific journal in cell biology, researchers describe a new molecular mechanism that contributes to age-related macular degeneration (AMD) due to accumulation of excessive iron within the cells of the retina.
Cells of the body use iron in dozens of normal metabolic processes. However, excessive iron or 'iron overload' can be very damaging to cells and tissues, and is implicated in numerous diseases, including AMD.
'The reason that cells die due to iron ...
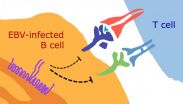
A viral protein that helps EBV-infected B cells to escape human killer T cells
2015-06-11
About 90% of adults worldwide are infected with Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV. The virus infects B cells (the white blood cells that make antibodies) and can contribute to B-cell-derived cancers, but in most people it remains dormant--a state scientists refer to as "latent infection"--for the rest of their lives. A study published on June 11th in PLOS Pathogens sheds new light on why the infected person's immune system cannot eliminate EBV, or the associated cancer risk.
Interested in the immune response against EBV, Andreas Moosmann, from the Helmholtz-Zentrum in Munich, ...
How the hawkmoth sees, hovers and tracks flowers in the dark
2015-06-11
It's difficult enough to see things in the dark, but what if you also had to hover in mid-air while tracking a flower moving in the wind? That's the challenge the hummingbird-sized hawkmoth (Manduca sexta) must overcome while feeding on the nectar of its favorite flowers.
Using high-speed infrared cameras and 3-D-printed robotic flowers, scientists have now learned how this insect juggles these complex sensing and control challenges - all while adjusting to changing light conditions. The work shows that the creatures can slow their brains to improve vision under low-light ...
Variations in atmospheric oxygen levels shaped Earth's climate through the ages
2015-06-11
ANN ARBOR--Variations in the amount of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere significantly altered global climate throughout the planet's history. Efforts to reconstruct past climates must include this previously overlooked factor, a new University of Michigan-led study concludes.
Oxygen currently comprises about 21 percent of Earth's atmosphere by volume but has varied between 10 percent and 35 percent over the past 541 million years.
In periods when oxygen levels declined, the resulting drop in atmospheric density led to increased surface evaporation, which in turn led to ...
Reactivating fault slip with fluid injection
2015-06-11
This news release is available in Japanese.
Water injected into an inactive fault can cause aseismic slip along the fault -- movement without detectable earthquakes -- that may then indirectly lead to micro-earthquakes. That's the result from a controlled experiment by Yves Guglielmi and colleagues, who observed these events in real time after injecting fluid into a natural fault near an underground experimental facility in southeastern France. Researchers are intensely interested in this type of induced seismicity, especially with a rise in earthquakes caused by ...
Genetic switch determines egg or sperm
2015-06-11
This news release is available in Japanese. New experiments in the Japanese rice fish show that the fox13 gene appears to be the switch that determines whether a germ cell becomes an egg or sperm cell. The finding could help researchers learn more about how the sexual fate of germ cells is determined during vertebrate development. Toshiya Nishimura and colleagues demonstrated that fox13, which is expressed in germ cells but not in the surrounding cells of the fish's reproductive organs, provides a molecular cue that prevents the start of sperm formation. When the researchers ...