Tracking the viral parasites cruising our waterways
2015-06-16
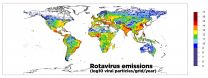
(Press-News.org) Humans aren't the only ones who like to cruise along the waterways, so do viruses. For the first time, a map of fecal viruses traveling our global waterways has been created using modeling methods to aid in assessing water quality worldwide.
"Many countries are at risk of serious public health hazards due to lack of basic sanitation," said Joan Rose, Homer Nowlin Chair in water research at Michigan State University. "With this map, however, we can assess where viruses are being discharged from untreated sewage and address how disease is being spread. With that, we can design a treatment and vaccination program that can help prevent sewage-associated diseases."
The study, conducted by Rose and an international team of researchers, focused on rotavirus, a pathogen found in human sewage, which is suspected of causing more than 450,000 deaths globally each year. Rotavirus severity rates are highest among young children under two. Because the disease spreads quickly - and via water - a deeper understanding of the transmission of rotavirus is key to combatting it.
The modeling approach used in the study was designed to better understand the global distribution of potential viruses in water sources. The model provided a grid that helped pinpoint "hotspots" where emission sources were greatest. According to Rose, those areas can now be selected for monitoring and control programs.
"The great advantage of a modeling approach is getting a better understanding of the situation in areas where no monitoring data exist, but where we do have model input available," she said.
The study, published in the journal Pathogens, directly addresses the Sustainability Development Goals outlined by the United Nations. SDGs are being developed to extend public health goals that were not achieved by the original Millennium Development Goals set by the UN in 2000, including cutting the proportion of the global population without access to safe sanitation in half by 2015.
"Achieving the SDGs is important for reducing waterborne diseases," Rose said. "Rotavirus epitomizes the danger of these diseases and represents the ongoing effects that sewage contamination of water has on global public health."
The study is part of the Global Water Pathogens Project, an initiative led by Rose that aims to obtain a better understanding of pathogens in sewage and surface water.
INFORMATION:
The international team of researchers contributing to this work were Nicholas Kiulia and Maureen Obara, MSU fisheries and wildlife department; Nynke Hofstra and Lucie Vermeulen, Environmental Systems Analysis Group, Wageningen University, (Netherlands); and Gertjan Medema, KWR Watercycle Research Institute, (Netherlands).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-16
Tropical Storm Bill was making landfall at 11 a.m. CDT on Matagorda Island, Texas on June 16 as NASA and NOAA satellites gathered data on the storm. At NASA a movie of Bill's landfall was created using data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite. The center of Bill is expected to move inland over south-central Texas during the afternoon and night of June 16.
On June 15 at 19:15 UTC (3:15 p.m. EDT) the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Bill approaching Texas and Louisiana. Powerful thunderstorms circled the center in fragmented ...
2015-06-16
Results from a new study led the Georgia Institute of Technology's School of Psychology and University of Minnesota's Carlson School of Management show that, compared to younger job seekers, older adults receive fewer job offers, search for weeks longer and are ultimately less likely to find re-employment after losing a job. The study is published by the journal Psychological Bulletin.
"There's very robust evidence that as an individual moves beyond age 50, they experience a large penalty toward how quickly they will find a job," says Professor Connie Wanberg, the Industrial ...
2015-06-16
CLEMSON, S.C. - Drowsy drivers take a heavy toll on the nation's highways. So finding a reliable way to test for fatigue to mitigate its potential damage could have a significant impact on highway safety.
U.S. statistics reveal drowsy drivers are five times more likely to be involved in an accident, or a near-crash incident, than alert drivers. Furthermore, drowsy or fatigued drivers are responsible for an estimated 56,000 crashes annually with more than 40,000 of them resulting in fatal and non-fatal injuries. Closer to home, there are more than 730 traffic accidents ...
2015-06-16
SEATTLE -- The world invested more than $200 billion to improve health in lower-income countries over the past 15 years.
Global health financing increased significantly after 2000, when the United Nations established the Millennium Development Goals, which included a strong focus on health. This trend in funding has only recently started to change, according to new research by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington. The article, "Sources and Focus of Health Development Assistance, 1990-2014," was published online June 16 ...
2015-06-16
New York - An immensely powerful yet invisible force pulls water from the earth to the top of the tallest redwood and delivers snow to the tops of the Himalayas. Yet despite the power of evaporating water, its potential to propel self-sufficient devices or produce electricity has remained largely untapped -- until now.
In the June 16 online issue of Nature Communications, Columbia University scientists report the development of two novel devices that derive power directly from evaporation - a floating, piston-driven engine that generates electricity causing a light to ...
2015-06-16
The urban mosquito that carries the dengue fever virus is hitching rides on river boats connecting the Amazonian town of Iquitos, Peru, with rural areas.
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases published a study by disease ecologists at Emory University, showing how the Aedes aegypti mosquito, which is normally associated with urban areas, is tapping human transportation networks to expand its range.
"The majority of large barges we surveyed were heavily infested," says Sarah Anne Guagliardo, who led the study as a PhD student in the lab of Uriel Kitron, chair of Emory's Department ...
2015-06-16
Plants are a ubiquitous and essential part of our lives. Estimates suggest there are hundreds of thousands of plant species known to science. How many species are there, really? How are they related? How many are threatened with extinction? Answering these questions in such an enormous clade of life is an important but daunting task for scientists.
Modern molecular techniques and, in particular, next-generation sequencing provide a powerful tool set to begin uncovering these answers. DNA regions can quickly be obtained and compared across species to infer relationships ...
2015-06-16
This news release is available in German.
They are thin, light-weight, flexible and can be produced cost- and energy-efficiently: printed microelectronic components made of synthetics. Flexible displays and touch screens, glowing films, RFID tags and solar cells represent a future market. In the context of an international cooperation project, physicists at the Technische Universität München (TUM) have now observed the creation of razor thin polymer electrodes during the printing process and successfully improved the electrical properties of the printed ...
2015-06-16
This news release is available in French. A multidisciplinary group of researchers from British Columbia has developed a participatory action research program to help address healthy body weight in children.
The SCOPE (Sustainable Childhood Obesity Prevention through Community Engagement) program has a simple message and was developed to engage communities to take action to prevent childhood obesity. The first phase of the SCOPE program was funded by Child Health BC, an initiative of BC Children's Hospital, and was carried out in communities in British Columbia. The ...
2015-06-16
Alexandria, VA - From the tiny microcosms of atomic theory and futuristic colonies on Mars to dinosaurs walking the Earth, science illustrators translate scientific findings and theories into something lifelike, accurate and aesthetically pleasing. The July cover story from EARTH Magazine, "Science Illustrators: Making the Invisible Visible," takes readers on a behind-the-scenes of how illustrators transform a scientific concept into an informed work of art.
Scientific illustrating is informed as much by researching the scientific literature as it is by the imagination. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tracking the viral parasites cruising our waterways



