Water used for hydraulic fracturing varies widely across United States
Study includes first nationwide map of water usage for hydraulic fracturing
2015-06-30
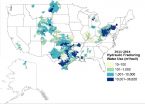
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, D.C. - The amount of water required to hydraulically fracture oil and gas wells varies widely across the country, according to the first national-scale analysis and map of hydraulic fracturing water usage detailed in a new study accepted for publication in Water Resources Research, a journal of the American Geophysical Union. The research found that water volumes for hydraulic fracturing averaged within watersheds across the United States range from as little as roughly 9,800 liters (2,600 gallons) to as much as 37 million liters (9.7 million gallons) per well.
In addition, from 2000 to 2014, median annual water volume estimates for hydraulic fracturing in horizontal wells had increased from about 670,000 liters (177,000 gallons) per oil and gas well to more than 15 million liters (4 million gallons) per oil well and 19 million liters (5.1 million gallons) per gas well. Meanwhile, median water use in vertical and directional wells remained below roughly 2.5 million liters (671,000 gallons) per well. For comparison, an Olympic-sized swimming pool holds about 660,000 gallons.
"One of the most important things we found was that the amount of water used per well varies quite a bit, even within a single oil and gas basin," said Tanya Gallegos, a scientist at the U.S. Geological Survey in Virginia, and the study's lead author. "This is important for land and resource managers, because a better understanding of the volumes of water injected for hydraulic fracturing could be a key to understanding the potential for some environmental impacts."
Horizontal wells are those that are first drilled vertically or directionally (at an angle from straight down) to reach the unconventional oil or gas reservoir and then laterally along the oil or gas-bearing rock layers. This is done to increase the contact area with the reservoir rock and stimulate greater oil or gas production than could be achieved through vertical wells alone, according to the study's authors.
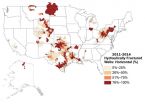
However, horizontal wells also generally require more water than vertical or directional wells. In fact, in 52 out of the 57 watersheds with the highest average water use for hydraulic fracturing, over 90 percent of the wells were horizontally drilled, according to the new study.
Although there has been an increase in the number of horizontal wells drilled since 2008, about 42 percent of new hydraulically fractured oil and gas wells completed in 2014 were still either vertical or directional. The ubiquity of the lower-water-use vertical and directional wells explains, in part, why the amount of water used per well is so variable across the United States, according to the study's authors.
The watersheds where the most water was used to hydraulically fracture wells on average coincided with parts of the following shale formations:
Eagle Ford (within watersheds located mainly in Texas)
Haynesville-Bossier (within watersheds located mainly in Texas & Louisiana)
Barnett (within watersheds located mainly in Texas)
Fayetteville (within watersheds located in Arkansas)
Woodford (within watersheds located mainly in Oklahoma)
Tuscaloosa (within watersheds located in Louisiana & Mississippi)
Marcellus & Utica (within watersheds located in parts of Ohio, Pennsylvania, West Virginia and within watersheds extending into southern New York)
Shale gas reservoirs are often hydraulically fractured using slick water, a fluid type that requires a lot of water. In contrast, tight oil formations like the Bakken (in parts of Montana and North Dakota) often use gel-based hydraulic fracturing treatment fluids, which generally contain lower amounts of water, according to the study's authors.
This research was carried out as part of a larger effort by the USGS to understand the resource requirements and potential environmental impacts of unconventional oil and gas development, the study's authors said. Prior publications include historical trends in the use of hydraulic fracturing from 1947-2010, as well as the chemistry of produced waters from hydraulically fractured wells, the authors said.
INFORMATION:
The American Geophysical Union is dedicated to advancing the Earth and space sciences for the benefit of humanity through its scholarly publications, conferences, and outreach programs. AGU is a not-for-profit, professional, scientific organization representing more than 60,000 members in 139 countries. Join the conversation on Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and our other social media channels.
More information about this study and other USGS energy research can be found at the USGS Energy Resources Program.
The following press release and accompanying images can be found at: http://news.agu.org/press-release/water-used-for-hydraulic-fracturing-varies-widely-across-united-states/
AGU Contact:
Leigh Cooper
+1 (202) 777-7324
lcooper@agu.org
U.S. Geological Survey Contact:
Anne Berry Wade
+1 (703) 648-4483
abwade@usgs.gov
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-30
A new report published in the July 2015 issue of The FASEB Journal suggests that a common molecule found in higher animals, including humans, affects brain structure. This molecule may play a significant role in how brain cells communicate, possibly shedding light on the underlying causes of certain brain disorders. The study, involving mice, shows that small changes in how sialic acid attaches to cell surfaces result in damaging effects on brain structure, poor motor skills, hyperactivity, and difficulty in learning.
"Sialic acid is part of the molecular language that ...
2015-06-30
It is well known that muscles need resistance (gravity) to maintain optimal health, and when they do not have this resistance, they deteriorate. A new report published in the July 2015 issue of The FASEB Journal, however, suggests that this might not be true for all muscles, offering hope that there may be ways to preserve muscle mass and strength for individuals in low-resistance environments, whether it be the microgravity of space, extended periods in a hospital bed, or a 9-5 job behind a desk.
"Maintaining muscle mass and good muscle repair is key to all areas of ...
2015-06-30
Here's more evidence that fish oil supplementation and antioxidants might be beneficial for at least some people facing Alzheimer's disease: A new report published in the July 2015 issue of The FASEB Journal describes the findings of a very small study in which people with mild clinical impairment, such as those in the very early stages of the disease, saw clearance of the hallmark amyloid-beta protein and reduced inflammation in neurological tissues. Although the findings involved just 12 patients over the course of 4 to 17 months, the findings suggest further clinical ...
2015-06-30
WASHINGTON - Cardiac arrest strikes almost 600,000 people each year, killing the vast majority of those individuals, says a new report from the Institute of Medicine. Every year in the U.S., approximately 395,000 cases of cardiac arrest occur outside of a hospital setting, in which less than 6 percent survive. Approximately 200,000 cardiac arrests occur each year in hospitals, and 24 percent of those patients survive. Estimates suggest that cardiac arrest is the third leading cause of death in the U.S. behind cancer and heart disease.
Following a cardiac arrest, each ...
2015-06-30
WASHINGTON, DC --June 30, 2015--Human urine contains factors that prevent a common culprit in urinary tract infections (UTIs), uropathogenic Escherichia coli bacteria, from properly attaching to bladder cells, a necessary step for infection. The research, published this week in mBio, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, reveals a weakness that could be exploited to develop more effective, non-antibiotic treatments for UTIs.
"There is a pressing, unmet need when it comes to developing new and better ways to treat UTIs," says Scott Hultgren, ...
2015-06-30
WASHINGTON, June 30 -- Hantaviruses use cholesterol in cell walls to gain access into cells and infect humans, according to laboratory research published this week in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Our work demonstrates that hantaviruses are extremely sensitive to the amount of cholesterol in the membranes of the cells they are trying to infect," said senior study author Kartik Chandran, Ph.D., an associate professor of microbiology and immunology, and Harold and Muriel Block Faculty Scholar in Virology, at the Albert ...
2015-06-30
From our nation's founding, the Fourth of July has been synonymous with fireworks.
While many grew up learning that fireworks can be dangerous to the eyes and hands if not handled properly, fireworks also produce air pollutants, including particulate matter, that are linked to short-term or long-term health effects.
NOAA scientist Dian Seidel and Abigail Birnbaum, a student intern at NOAA, have authored a new study appearing in the journal Atmospheric Environment that quantifies the surge in fine particulate matter -particles that are two and one half microns in diameter ...
2015-06-30
Tiny marine algae that play a critical role in supporting life on Earth may be better equipped to deal with future climate change than previously expected, research shows.
Scientists investigated the likely future impact of changing environmental conditions on ocean phytoplankton, a microscopic plant that forms the basis of all the oceans' food chains.
Phytoplankton is important for absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, while generating much of the oxygen needed to sustain life on Earth.
The study grew phytoplankton at the high carbon dioxide levels predicted ...
2015-06-30
Greenwich, CT, 30 June, 2015 - A new paper to be published in The Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery evaluates the effect that topical benzoyl peroxide (BPO), with chlorhexidine skin preparation, has on the presence of Propionibacterium acnes cultured at the time of shoulder surgery. The authors hypothesized that adding topical BPO, the active ingredient in Clearasil, to the pre-operative skin preparation would reduce the number of positive P. acnes cultures identified during surgery.
P. acnes infection is a significant problem after shoulder surgery. Residual P. ...
2015-06-30
New research has found that the number of plant species growing just next to restored streams can take up to 25 years to increase above those channelized during the timber floating era. This is according to doctoral student, Eliza Maher Hasselquist, and other researchers from Umeå University and the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU).
In the Vindel River catchment in northern Sweden, the main channel and most tributary streams were channelized from the 1850s to the 1950s to accommodate timber floating, which stopped in 1976. Boulders in the streams ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Water used for hydraulic fracturing varies widely across United States
Study includes first nationwide map of water usage for hydraulic fracturing



