(Press-News.org) BARCELONA-LUGANO, 1 July 2015 - Patients with the lowest body mass index (BMI) had the shortest overall survival in an analysis of bevacizumab studies in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) presented for the first time today at the ESMO 17th World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer 2015 in Barcelona.(1)
"There is good evidence that obesity increases the risk of getting colorectal cancer and that it increases the risk of colorectal cancer recurrence after curative therapy," said lead study author Dr Yousuf Zafar, associate professor of medicine at Duke Cancer Institute in Durham, North Carolina. "What we did not know prior to these results is whether there is a relationship between obesity and survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer."
He continued: "There is evidence that, at least in the US, obese patients may be at risk to receive lower doses of chemotherapy, so we hypothesised that obesity would be associated with worse survival in patients with colorectal cancer."
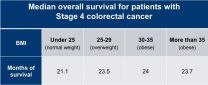
The current study analysed overall survival and progression-free survival according to four categories of BMI ( END
Patients with lowest BMI have shortest survival in pooled analysis of bev in mCRC
ESMO 17th World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer
2015-07-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Thin colorectal cancer patients have shorter survival than obese patients
2015-07-01
DURHAM, N.C. - Although being overweight with a high body-mass index (BMI) has long been associated with a higher risk for colorectal cancer, thinner patients might not fare as well after treatment for advanced cancer, according to a new study from Duke Medicine.
The study, which was presented today at the European Society for Medical Oncology World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer, found that patients with a low to healthy body weight lived an average of two-and-a-half months less than overweight and obese patients.
The results surprised researchers, who expected ...
Deuterium substitution improves therapeutic and metabolic profiles of medicines
2015-07-01
Lexington, Mass., July 1, 2015 - Substituting deuterium for certain hydrogen atoms in molecules has been shown to enhance the metabolic properties of a number of drugs and provides a promising approach to the discovery and development of innovative drug products. The deuterium chemistry approach has the potential to reduce the high failure rates of conventional drug development by building on the known pharmacology of existing compounds and leveraging their desirable therapeutic properties. Selective deuterium substitution as a means of ameliorating unwanted clinically ...
Experimental drug combined with standard chemo may shrink ovarian cancers
2015-07-01
Working in cell cultures and mice, researchers at Johns Hopkins have found that an experimental drug called fostamatinib combined with the chemotherapy drug paclitaxel may overcome ovarian cancer cells' resistance to paclitaxel.
Scientists elsewhere are already testing fostamatinib in people with lymphoma and idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura, an autoimmune disorder. Based on results of the current study described in a report online June 18 in the journal Cancer Cell, Johns Hopkins researchers say they are planning a phase I clinical trial to test the paclitaxel-fostamatinib ...
Producing spin-entangled electrons
2015-07-01
A team from the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science, along with collaborators from several Japanese institutions, have successfully produced pairs of spin-entangled electrons and demonstrated, for the first time, that these electrons remain entangled even when they are separated from one another on a chip. This research could contribute to the creation of futuristic quantum networks operating using quantum teleportation, which could allow information contained in quantum bits--qubits--to be shared between many elements on chip, a key requirement to scale up the power ...
Warts and all: How St. John's Wort can make you sick
2015-07-01
St John's Wort can produce the same adverse reactions as antidepressants, and serious side effects can occur when the two are taken together, according to new University of Adelaide research.
In a study published this month in the journal, Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, researchers compared the pattern of spontaneous reported adverse drug reactions to St John's Wort, a herbal treatment for depression, and fluoxetine, a commonly prescribed antidepressant. They found the adverse reactions were the same for people who took St John's Wort as it was ...
Europe, Siberia and in between: Caucasian populations of non-biting midges
2015-07-01
A research in the North Caucasus, conducted by a group of Russian scientists over three years, has revealed an intermediate distribution of Caucasian populations of non-biting midges between Europe and Siberia. Their observations also proved some interesting morphological distinctions between the studied populations and the previously researched ones from Europe and Siberia. Their results have been published in the open-access journal Comparative Cytogenetics.
The study on karyotypical and morphological peculiarities of Ch. bernensis is a part of the investigation of ...
Improving insulation materials, down to wetting crossed fibers
2015-07-01
Sandcastles are a prime example of how adding a small amount of liquid to a granular material changes its characteristics. But understanding the effect of a liquid wetting randomly oriented fibres in a fibrous medium remains a mystery. Relevant to the building industry, which uses glass wool, for instance, this phenomenon can be better understood by studying the behaviour of a liquid trapped between two parallel fibres. It can either remain in the shape of a drop or spread between the fibres into a long and thin column of liquid. Now, scientists have demonstrated that the ...
The bizarre mating habits of flatworms
2015-07-01
Failing to find a mating partner is a dent to the reproductive prospects of any animal, but in the flatworm species Macrostomum hystrix it might involve a real headache. Zoologists from the Universities of Basel and Bielefeld have discovered the extraordinary lengths to which this animal is willing to go in order to reproduce - including apparently injecting sperm directly into their own heads. The academic journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B has published their findings.
The absence of a mate usually spells disaster for sexually reproducing animals. However, some ...
Clues to inner atomic life from subtle light-emission shifts
2015-07-01
Atoms absorb and emit light of various wavelengths. Physicists have long known that there are some tiny changes, or shifts, in the light that gets absorbed or emitted, due to the properties of the atomic nucleus. Now, a team of scientists has elucidated the so-called hyperfine structure of cadmium atoms. Relying on a method called laser spectroscopy, they have measured variations in the energy transition within cadmium atom - Cd in the periodic table. They studied a chain of isotopes with an odd number of neutrons ranging from 59 in 107Cd to 75 in 123Cd. From these high-precision ...
Sleep deprivation could reduce intrusive memories of traumatic scenes
2015-07-01
A good night's sleep has long been recommended to those who have experienced a traumatic event. But an Oxford University-led study provides preliminary experimental work suggesting it could actually be the wrong thing to do.
The research, conducted in Oxford's Wellcome Trust-funded Sleep and Circadian Neuroscience Institute (SCNi) and published in the journal Sleep, showed that sleep deprivation might prevent people from consolidating memories of experimental trauma (emotional film clips in the study), reducing their tendency to experience flashbacks.
Dr Kate Porcheret, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Patients with lowest BMI have shortest survival in pooled analysis of bev in mCRCESMO 17th World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer