NASA's Aqua satellite sees Typhoon Halola elongating
2015-07-15
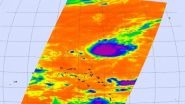
(Press-News.org) NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Typhoon Halola in the northwestern Pacific Ocean and captured temperature data on the storm. Satellite data showed that wind shear is affecting the stubborn storm.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Halola on July 14 at 20:20 UTC (4:20 p.m. EDT/1:20 p.m. PDT) infrared data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that also flies aboard Aqua showed cloud top temperatures were as cold as -63F/-52C. Cloud top temperatures that cold have the ability to drop heavy rainfall.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that animated enhanced infrared satellite imagery continued to show the storm has become elongated. Clouds and showers have been pushed to the northeast of the center due to moderate to high (20-25 knot) southwesterly vertical wind shear. However, the storm is expected to retain typhoon status, despite the wind shear.
On July 15 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Typhoon Halola's maximum sustained winds were near 75 knots (86 mph/138.9 kph). It was centered near 17.8 North latitude and 168.0 East longitude about 149 nautical miles (171.5 miles/275.9 km) southeast of Wake Island. Halola is moving to the west-northwestward at 15 knots (17.2 mph/27.8 kph).
Halola is expected to maintain typhoon intensity and continue moving in a west-northwesterly direction over the next several days, over the open waters of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-07-15
High school students who take part in pre-college programs that focus on science are much more likely to pursue higher education and, eventually, careers in science, technology, engineering and medicine - the STEM disciplines.
In a paper published in the Journal of Higher Education Outreach and Engagement, Michigan State University researchers from the National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, the Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics and the College of Education used an MSU program as a case study for why these programs are key to training tomorrow's generation ...
2015-07-15
PHILADELPHIA, PA - July 15, 2015 - Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) remains under-recognized in hospitalized patients, despite being associated with cardiovascular complications and sudden death. A multi-disciplinary group of researchers and physicians at Thomas Jefferson University and Hospitals have created a clinical pathway, or screening process, to identify the disorder in higher-risk, hospitalized patients and recently published the results in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.
"The results showed that our screening process identified sleep disordered breathing ...
2015-07-15
New York, NY, July 15, 2015--Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) have found that key parts of the human brain network that give us the power to control and redirect our attention--a core cognitive ability--may be unique to humans. The research, which was published in the July 13 online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggests that the network may have evolved in response to increasingly complex social cues.
"The human brain is powerful, but even it cannot make sense of the entire sum of stimuli that bombard our senses," ...
2015-07-15
ROSEMONT, Ill.--Patients who received rehabilitation instructions via video teleconference, or "telerehabilitation," following total knee replacement (TKR) surgery had comparable outcomes to patients who received in-person physical therapy, according to a study appearing in the July 15 issue of The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (JBJS).
"This study is the first to provide strong evidence for use of telerehabilitation as an alternative to conventional face-to-face care following total knee replacement surgery," said Hélène Moffet, PhD, lead study author, physical ...
2015-07-15
JUPITER, FL, July 15, 2015 - As early as 1943, when autism was first described by psychiatrist Leo Kanner, reports were made that some, but not all, children with autism spectrum disorder have relatively enlarged heads. But even today, more than half a century later, the exact cause of this early abnormal growth of the head and brain has remained unclear.
Now, scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have uncovered how mutations in a specific autism risk gene alter the basic trajectory of early brain development in animal models.
The ...
2015-07-15
Montreal, July 15, 2015 - A Canadian research team at the IRCM in Montreal, led by molecular virologist Eric A. Cohen, PhD, made a significant discovery on how HIV escapes the body's antiviral responses. The team uncovered how an HIV viral protein known as Vpu tricks the immune system by using its own regulatory process to evade the host's first line of defence. This breakthrough was published yesterday in the scientific journal PLOS Pathogens and will be presented at the upcoming IAS 2015 conference in Vancouver. The findings pave the way for future HIV prevention or cure ...
2015-07-15
BOSTON - New research led by investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) provides the first direct evidence linking traumatic brain injury to Alzheimer's disease and chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) -- and offers the potential for early intervention to prevent the development of these debilitating neurodegenerative diseases. TBI can result from repetitive contact sport injuries or from exposure to military blasts, and is one of the most significant risk factors for both Alzheimer's disease and CTE.
In a study published today in the online edition ...
2015-07-15
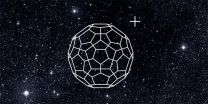
Scientists at the University of Basel were able to identify for the first time a molecule responsible for the absorption of starlight in space: the positively charged Buckminsterfullerene, or so-called football molecule. Their results have been published in the current issue of Nature.
Almost 100 years ago, astronomers discovered that the spectrum of star light arrived on earth with dark gaps, so-called interstellar bands. Ever since, researchers have been trying to find out which type of matter in space absorbs the light and is responsible for these "diffuse interstellar ...
2015-07-15
About 1 in 88 children has an autism spectrum disorder. This represents a 78% increase in the incidence of autism spectrum disorder since 2002 (although some of the increase may be due to improved diagnostic capabilities). Individuals with an autism spectrum disorder may have poor nutrition because they often exhibit selective eating patterns as well as sensory sensitivity that predispose them to restrict their diets.
The July 2015 issue of Advances in Nutrition, the international review journal of the American Society for Nutrition, features "Nutritional Status of ...
2015-07-15
GeoSpace
Greenland's fjords are far deeper than previously thought, and glaciers will melt faster, researchers find
West Greenland's fjords are vastly deeper than rudimentary models have shown and intruding ocean water can badly undercut glacier faces. A new study in Geophysical Research Letters explores how this process will raise sea levels faster than expected.
Eos.org
A University-Government Partnership for Oceanographic Research
After 44 years of coordinating the U.S. academic research fleet and facilities, the University-National Oceanographic Laboratory System ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA's Aqua satellite sees Typhoon Halola elongating