(Press-News.org) Like most health professionals, David Olson has known for some time of the dangers posed by excessive stress. His latest research, though, is giving surprising new insight into how chronic stress in childhood can have an impact years after it occurred in women giving birth.
"Chronic stress is one of the better predictors of preterm birth," says Olson, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology in the University of Alberta's Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry. "In fact, if women are exposed to two or more adverse childhood experiences while growing up, their risk of preterm birth doubles."
Olson, along with Kathleen Hegadoren, a professor in the U of A's Faculty of Nursing, and graduate student Inge Christiaens, are the authors of a new study in the journal BMC Medicine linking chronic stress with preterm birth.
The World Health Organization estimates 15 million babies are born preterm each year. It is the leading cause of death for children under the age of five, and babies who survive are at much higher risk of developing a number of health conditions including chronic lung disease, cardiovascular disease and metabolic diseases such as Type 2 diabetes. They are also at increased risk for both cognitive and behavioural issues.
As part of the study, the researchers recruited more than 200 women who had given birth in Edmonton-area hospitals. One-third of the women had given birth preterm, with the remaining women having delivered at term. The women were asked to fill out a stress questionnaire, giving researchers insight into their early life experiences and the stresses that resulted from those experiences.
"All of the adverse childhood events that we asked about had to occur prior to the age of 18, and the average age of delivery in our study was 28 years. These adverse childhood events occurred, on average, 10 years or more before the women actually delivered," says Olson.
"Although not inevitable, childhood adversity can result in long-term impacts on health across the lifespan, including pregnancy outcomes," adds Hegadoren. "Prenatal care providers need to ask pregnant women about past and current experiences that may have affected their health. In doing that, they can help women understand a potential link between life experiences and preterm birth risk."
Though the research gives important new understanding about preterm birth, more answers are still needed. The researchers are now exploring how the body can "remember" traumatic events early in life in such a way that it affects health outcomes years later. Olson believes that a high burden of stressful experiences in childhood may cause changes in how genes are expressed in later life. He notes that earlier published studies involving preclinical models suggest that may be the case but that further human studies are needed.
Olson and Hegadoren hope to continue building upon the research to better predict which women will be at risk of preterm birth. They also hope to develop early interventions.
"If we know who is at risk, we can begin to treat them before the end of their pregnancy--and hopefully they'll
have improved pregnancy outcomes."
INFORMATION:
Research funding was provided by Alberta Innovates - Health Research and the Canada Research Chairs program.
Air pollution from wildfires may increase risk of cardiac arrests, and other sudden acute heart problems, researchers have found.
Lead author, Dr Anjali Haikerwal, Department of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine at Monash University, said while breathing wildfire smoke was linked to respiratory problems such as asthma - evidence of an association between wildfire smoke exposure and heart problems has been inconsistent.
In the new study, published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, researchers examined the association between exposure to tiny particulate ...
Researchers have discovered a new technique to enhance brain excitability that could improve physical performance in healthy individuals such as athletes and musicians.
The technique could also improve treatments for neurological and neuropsychological conditions such as stroke, depression and chronic pain.
The idea of stimulating different parts of the brain with electricity may sound futuristic, but these types of treatments have a remarkably long history. Early physicians and scientists such as Claudius Galen (the Roman physician) and Avicenna (the Persian physician) ...
A simple, lower-cost new method for DNA profiling of human hairs developed by the University of Adelaide should improve opportunities to link criminals to serious crimes.
The researchers have modified existing laboratory methods and been able to produce accurate DNA profiles from trace amounts at a much higher success rate.
"Technological advancements over the last 10 years have allowed police and forensic scientists to profile crime-scene DNA from ever smaller and more challenging samples collected from fingerprints, skin cells, saliva and hairs," says Associate Professor ...
Scientists, including SFU professor Peter Ruben, have found that sudden death caused by cardiac arrhythmia can be triggered by changes in body temperature. The study is published in the Journal of Physiology.
The soccer player who drops dead in the middle of a game, or the infant who dies during sleep is often a victim of arrhythmia. Sudden cardiac death has several causes, including inheritable mutations in our DNA affecting structure and function of proteins in the heart. Simon Fraser University professor Peter Ruben found when studying the proteins that underlie electrical ...
A recent study looks at why some children put on weight faster than others. The study's goal is to identify factors that can lead to obesity.
Assistant Professor Silje Steinsbekk and Professor Lars Wichstrøm at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's Department of Psychology are conducting the survey. "We've looked to see if physical activity, television time and appetite traits can explain why some children's body mass index (BMI) increases more than others' do," says Steinsbekk.
At the clinic, most parents have seen the percentile curves on the ...
PHOENIX, Ariz. -- July 15, 2015 -- Researchers at the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen) have identified a genetic mutation associated with the appearance of premature aging and severe loss of body fat in children.
TGen's Center for Rare Childhood Disorders found that the appearance of premature aging, a neonatal form of Progeroid syndrome, in a 3-year-old girl was caused by a mutation in the gene CAV1, according to a study published today in the scientific journal PLOS ONE.
The Center for Rare Childhood Disorders was established in 2010 to examine the ...
15 July, 2015, Hoffman Estates, IL - Sodium intake in the U.S. exceeds dietary recommendations and has been identified as a nutrient of public health concern in the Scientific Report of the 2015 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee1 due to its link to increased risk of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke2. While authorities continue to call for people to lower their sodium intake, much progress still needs to be made and multiple solutions are necessary to meet the recommended maximum intake of 2,300 milligrams per day for the general population and 1,500 milligrams ...
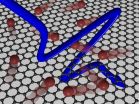
Mainz/Barcelona. A team of scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research (MPI-P) discovered that electrical conduction in graphene on the picosecond timescale - a picosecond being one thousandth of one billionth of a second - is governed by the same basic laws that describe the thermal properties of gases. This much simpler thermodynamic approach to the electrical conduction in graphene will allow scientists and engineers not only to better understand but also to improve the performance of graphene-based nanoelectronic devices.
The researchers found that ...
Researchers at Harvard University and the University of California, San Diego, have developed a new user-friendly resource to accompany the powerful gene editing tool called CRISPR/Cas9, which has been widely adopted to make precise, targeted changes in DNA. This breakthrough has the potential to facilitate new discoveries in gene therapies and basic genetics research. The research was published in the July 13 issue of Nature Methods.
The study describes an approach to simplify a laborious part of the gene editing process using the CRISPR/Cas9 system: choosing the best ...
Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) is becoming increasingly recognized as a very real and devastating problem in which impaired breathing is thought to play a critical role. Researchers believe breathing may be impaired during and after seizures, without the patient's knowledge.
By using electrical stimulation to activate the amygdala, a group of University of Iowa researchers has identified areas of the human brain in which breathing is controlled and, in some cases, impaired, providing an important insight into SUDEP.
Their study - which marks the first time ...