NASA sees Typhoon Nangka knocking on Japan's door
2015-07-16
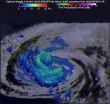
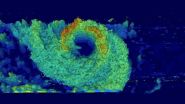
(Press-News.org) Typhoon Nangka was knocking on Japan's door when NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead early on July 16. Satellite imagery showed that Nangka's northern quadrant began spreading over southeastern Japan. The GPM core satellite spotted towering thunderstorms in Nangka's western side.
NASA/JAXA's Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) core observatory satellite passed above Typhoon Nangka on July 15, 2015 at 1621 UTC (12:21 p.m. EDT) as the weakening typhoon approached the Japanese island of Shikoku. GPM's Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) instrument revealed that the highest thunderstorm tops in Nangka's western eye wall were then reaching heights of about 12 km (7.4 miles).
On July 16 at 2:05 UTC (July 15 at 10:05 p.m. EDT) the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Typhoon Nangka affecting southeastern Japan. The MODIS image showed that Nangka maintained its eye and that eye was surrounded by thick, spiraling bands of thunderstorms out to about 150 nautical miles from the center making the storm over 300 nautical miles wide.
By 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Typhoon Nangka had moved to just 142 nautical miles southeast of Iwakuni, Japan, centered near 32.9 North and 134.4 East. Nangka's maximum sustained winds were down to 65 knots (75 mph/120 kph) making it a minimal category 1 typhoon. Nangka was moving to the north at 10 knots (11.5 mph/18.5 kph).
Nangka is moving north and is approaching a landfall in mainland Japan. The storm is expected to move north over Japan and rapidly weaken as it veers northeast.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-07-16
A physical education program that brings commercial-grade fitness equipment to under-resourced schools, along with a curriculum based on boosting confidence and making participation more enjoyable, dramatically increases students' performance on California's standardized physical fitness test, a UCLA study has found.
Publishing in the July issue of the Journal of Education and Training Studies, Anastasia Loukaitou-Sideris, a professor of urban planning and associate dean in the UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs, reported that the UCLA Health Sound Body Sound Mind curriculum ...
2015-07-16
Light becomes trapped as it orbits within tiny granules of a crystalline material that has increasingly intrigued physicists, a team led by University of California, San Diego, physics professor Michael Fogler has found.
Hexagonal boron nitride, stacked layers of boron and nitrogen atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, has recently been found to bend electromagnetic energy in unusual and potentially useful ways.
Last year Fogler and colleagues demonstrated that light could be stored within nanoscale granules of hexagonal boron nitride. Now Fogler's research group ...
2015-07-16
Washington, DC, July 16, 2015 - Fewer than one in six (4/30) healthcare workers (HCW) followed all CDC recommendations for the removal of personal protective equipment (PPE) after patient care, according to a brief report published in the July issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
In this study undertaken by researchers from the University of Wisconsin, a trained observer watched healthcare personnel entering and exiting patient rooms specified as ...
2015-07-16
INDIANAPOLIS -- Potentially fatal blood clots account for thousands of emergency room visits each year and often those patients are admitted to the hospital, treated with an injectable anticoagulant and monitored for a few days. In companion studies published July 15 in Academic Emergency Medicine, an alternative approach was found to be more effective, less costly and allowed patients to go home the same day.
Researchers at the Indiana University School of Medicine treated 106 low-risk patients diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism at two metropolitan ...
2015-07-16
To arrange for an interview with a researcher, please contact the Communications staff member identified at the end of each tip. For more information on ORNL and its research and development activities, please refer to one of our media contacts. If you have a general media-related question or comment, you can send it to news@ornl.gov.
ENERGY - Samsung savings ...
Although variable refrigerant flow heat pumps are known to have advantages, higher initial costs and difficulty in quantifying those benefits serve as deterrents to their widespread use. ORNL's flexible research ...
2015-07-16
A new report from the World Health Organisation urges the global community to accelerate action against rabies and other neglected zoonotic diseases.
The WHO report - 'The Control of Neglected Zoonotic Diseases: from advocacy to action' - says rabies can be eliminated through existing knowledge and tools. It urges accelerated action by the global community.
The study says that achieving a world free from dog-mediated human rabies in just 15 years is possible because of existing management tools - but only if there is increased investment.
The Global Alliance for ...
2015-07-16
Shooting a firearm requires coordinating many actions that depend upon core cognitive abilities, including the critical ability to stop just before pulling the trigger. People who have difficulty inhibiting responses are more likely to shoot unarmed civilians in simulated scenarios, but response inhibition training can help to reduce these shooting errors, according to new research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Our findings indicate that shooting abilities can be predicted, in part, by cognitive abilities, ...
2015-07-16
A new pilot study in Parkinson's disease suggests a new era of clinical research which removes the barrier of distance for both scientists and volunteers. The research, which appears in the journal Digital Health, could also enable researchers to leverage the rapid growth in personal genetic testing to better diagnose, and potentially treat, a wide range of diseases.
"These findings demonstrate that remote recruitment and conduct of research visits is feasible and well-received by participants," said Ray Dorsey, M.D., M.B.A., a neurologist at the University of Rochester ...
2015-07-16
July 16, 2015 - Did you belong to community, sports, or other clubs in your teens? If so, you might be more likely to survive into your late seventies, suggests a study in Psychosomatic Medicine: Journal of Biobehavioral Medicine, the official journal of the American Psychosomatic Society. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
People who were club members at age 18 are at lower risk of death by age 78, according to the report by Ian Deary, PhD, and colleagues of University of Edinburgh. The study adds to a growing body of evidence suggesting that social participation ...
2015-07-16
Cannabis -- marijuana, hashish -- was used as a go-to medical remedy by societies around the world for centuries. But the therapeutic use of marijuana was banned in most countries in the 1930s and '40s due to a growing awareness of the dangers of addiction. The significant medical benefits of marijuana in alleviating symptoms of such diseases as Parkinson's, cancer, and multiple sclerosis have only recently been reinvestigated.
A new study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research by Tel Aviv University and Hebrew University researchers explores another promising ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA sees Typhoon Nangka knocking on Japan's door