(Press-News.org) Sudden cardiac arrest kills an estimated 200,000 people a year in the United States, but many of those lives could be saved if ordinary bystanders simply performed CPR, a new study led by Duke Medicine shows.
The early application of cardio-pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) by an average person nearby, combined with defibrillation by firefighters or police before the arrival of emergency medical services (EMS), was the one intervention that substantially increased survival from cardiac arrest, according to findings reported by Duke researchers and colleagues in the July 21 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
"We were surprised to learn that survival increased only for those who received bystander-initiated CPR, compared with those who did not receive bystander-initiated CPR," said lead author Carolina Malta Hansen, M.D., of the Duke Clinical Research Institute. "Also, patients who received bystander or first-responder CPR and defibrillation were more likely to survive compared to those who received CPR and defibrillation once EMS arrived. This suggests that the very earliest intervention is crucial, and is something anyone can do. It saves lives."
Hansen and colleagues analyzed data from 4,961 cardiac arrest cases in 11 North Carolina counties from 2010-13. The data was gathered through a national registry set up to track cardiac arrests that occur outside of hospitals. The registry includes information about the responses of bystanders, first responders (firefighters, police officers, lifeguards and others on the scene ahead of the ambulance), and EMS. It also tracks how well people fared.
The four-year time frame coincided with a North Carolina campaign to encourage bystanders to perform chest-compression CPR -- no need for mouth-to-mouth resuscitation -- and to use an automated external defibrillator while awaiting an ambulance.
The campaign, called The HeartRescue Project, also worked to improve the use of portable defibrillators, which are increasingly available in public places and can be used by laypeople and first-responders to shock a heart back into rhythm.
Among the North Carolina counties included in the Duke study, survival with good neurologic recovery improved by 37 percent over those four years.
The project included public training programs in defibrillators and compression-only CPR at schools, hospitals and major events such as the N.C. State Fair, plus additional instruction for EMS and other emergency workers on optimal care for patients in cardiac arrest.
During the time covered in the study, Hansen said, 86.3 percent of patients received CPR before EMS arrived, with 45.7 percent initiated by bystanders and 40.6 percent by first-responders. Throughout the study period, a significant increase occurred in the proportion of patients receiving bystander-initiated CPR, from 39.3 percent in 2010 to 49.4 percent in 2013.
The proportion of patients who received bystander-initiated CPR and who also were defibrillated by first-responders increased from 14.1 percent in 2010, to 23.1 percent in 2013. Bystander CPR coupled with a first responder applying defibrillation was associated with improved patient survival compared to situations where patients waited to receive EMS-initiated CPR and defibrillation.
Of 1,648 defibrillated patients, 53.9 percent were defibrillated before arrival of the EMS - 6.9 percent by bystanders and 47 percent by first-responders. First-responder defibrillation increased significantly from 40.9 percent in 2010 52.1 percent in 2013.
"During the past decade, there has been a focus on increasing bystander CPR," said senior author Christopher Granger, M.D., a professor of cardiology and director of the Cardiac Care Unit?at Duke University Medical Center.
"Our findings show that survival can be improved by strengthening first-responder programs and encouraging more bystander CPR," Granger said. "This program shows that state and national programs to improve care of cardiac arrest, with a focus on the community and emergency medical response, can save more lives."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Hansen and Granger, study authors from Duke include Kristian Kragholm; Clark Tyson; Lisa Monk; Matthew E. Dupre; Emil L. Fosbøl; James G. Jollis; Benjamin Strauss; and Monique L. Anderson; along with David A. Pearson of Carolinas Medical Center; Brent Myers of Wake County EMS; Darrell Nelson of Wake Forest University; and Bryan McNally of Emory University.
The study received support from The HeartRescue Project, which is funded by Medtronic Philanthropy.
Two studies in the July 21 issue of JAMA find that use of interventions such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation and automated external defibrillators by bystanders and first responders have increased and were associated with improved survival and neurological outcomes for persons who experienced an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) is an increasing health concern worldwide, with poor prognoses. Shinji Nakahara, M.D., Ph.D., of the Kanagawa University of Human Services, Yokosuka, Japan, and colleagues examined the associations between ...
Although some previous studies have suggested an increased risk of bladder cancer with use of the diabetes drug pioglitazone, analyses that included nearly 200,000 patients found no statistically significant increased risk, however a small increased risk could not be excluded, according to a study in the July 21 issue of JAMA. Additional analyses with another large group found that use of pioglitazone was associated with an increase in the risk of prostate and pancreatic cancer, although further investigation is needed to assess whether the associations are causal or due ...
In a phase 2 trial that included nearly 1,000 adults, the AS03 and MF59 adjuvants (a component that improves immune response of inactivated influenza vaccines) increased the immune responses to two doses of an inactivated H7N9 influenza vaccine, with AS03-adjuvanted formulations inducing the highest amount of antibody response, according to a study in the July 21 issue of JAMA.
In March 2013 the first human infections with the avian influenza A(H7N9) virus were reported in China, and since that time hundreds of cases have been documented. While most infections are believed ...
Researchers have found an association between treatment with the antibiotic dicloxacillin and a decrease in international normalized ratio (INR; a measure of blood coagulation) levels among patients taking the vitamin K antagonists warfarin or phenprocoumon, according to a study in the July 21 issue of JAMA.
A challenge in the use of vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) is the potential for drug-drug interactions, resulting in insufficient or excessive anticoagulation. Solid data are lacking for most alleged interactions. In case reports, the commonly used antibiotic dicloxacillin ...
WASHINGTON, DC, July 21, 2015 - It's not unusual for two drivers to depart from the same location, head out to the same destination, drive more or less the same speed and nevertheless arrive at dramatically different times, with one driver taking significantly longer to arrive. While this can simply be bad luck, sometimes the reason isn't an obvious external event.
And if you are a world traveler, you've likely noticed the fact that transportation works like a charm in some countries, in the sense that you can plan your commute or trip via public bus with confidence. ...
The negative health effects of international air travel are well documented but now it seems that the common elderberry can provide some relief.
Associate Professor Evelin Tiralongo and Dr Shirley Wee from Griffith's Menzies Health Institute Queensland (MHIQ) have completed a clinical trial showing that an elderberry supplement can provide some protection from cold and flu-like symptoms following long-haul flights.
Intercontinental air travel can be stressful and affect a passenger's physical and psychological wellbeing. Whilst jet lag and fatigue remain the best known ...
WASHINGTON --Tamsulosin works no better than placebo on small kidney stones, but does improve passage of more large kidney stones than placebo does. The results of this large clinical trial evaluating tamsulosin versus placebo were published online Friday in Annals of Emergency Medicine ("Distal Ureteric Stones and Tamsulosin: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized, Multi-Center Trial (The DUST Trial)").
"Kidney stones bring more than a million Americans a year to emergency departments because they are excruciatingly painful," said lead study author Jeremy Furyk, ...
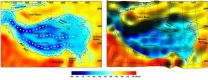
COLUMBUS, Ohio--Gravity data captured by satellite has allowed researchers to take a closer look at the geology deep beneath the Tibetan Plateau.
The analysis, published in the journal Nature Scientific Reports, offers some of the clearest views ever obtained of rock moving up to 50 miles below the plateau, in the lowest layer of Earth's crust.
There, the Indian tectonic plate presses continually northward into the Eurasian tectonic plate, giving rise to the highest mountains on Earth--and deadly earthquakes, such as the one that killed more than 9,000 people in Nepal ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- A microbe found in caves produces a compound that inhibits Pseudogymnoascus destructans, the fungus that causes white-nose syndrome in bats, researchers report in the journal Mycopathologia. The finding could lead to treatments that kill the fungus while minimizing disruption to cave ecosystems, the researchers say.
The yeast Candida albicans produces the compound: trans, trans-farnesol.
Candida species are already present in caves where bats hibernate and have been isolated from the bodies of healthy, hibernating bats, said University of Illinois ...
A clinical study funded by the National Institutes of Health has found that young, single black women in South Africa adhered to a daily pill regimen to prevent HIV infection--an HIV prevention strategy known as pre-exposure prophylaxis, or PrEP. This finding is the first strong indication that this population at substantial HIV risk could accept and reliably adhere to daily PrEP dosing. Men who have sex with men (MSM) and transgender women (TGW) in New York and Thailand also successfully adhered to daily dosing.
PrEP--which consists of a daily dose of two antiretrovirals, ...