(Press-News.org) A novel strategy of blocking the growth of blood vessels with antibodies should result in improved treatment of cancerous tumors.
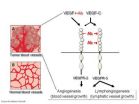
The growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature is called angiogenesis. In adults, angiogenesis occurs only during wound healing and menstrual cycling, but is abundant and harmful in cancerous tumors and the old-age eye disease frequently leading to blindness called age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Without the formation of new blood vessels, tumors cannot grow beyond a small size due to lack of oxygen and nutrients. Inhibition of angiogenesis is used in the treatment of cancer and AMD, but not all cancer patients respond, while others become refractory to therapy.
Academy professor Kari Alitalo and co-workers at the University of Helsinki, Finland, have previously shown that antibodies directed towards vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-3, found on the surface of endothelial cells lining vessels, can inhibit lymphatic metastasis by 50-70% in preclinical tumor models. Furthermore, antibodies that inhibited the growth factor VEGF-C from binding to the VEGFR-3 suppressed angiogenesis. However, the trouble with this type of inhibitors is that they work poorly in high growth factor concentrations, when the growth factor easily outcompetes the inhibitor. Also the delivery of drugs into tumors is hampered by erratic blood flow and high tumor pressure, which may prevent sufficient amounts of the inhibitor from reaching its target within the tumor.
The novel type of VEGFR-3 blocking antibody has an unprecedented mechanism of action, which was effective even at very high concentrations of the VEGF-C growth factor. Importantly, the authors showed that combined use of antibodies blocking growth factor binding VEGFR-3 dimerization provided not only an additive, but rather a synergistic inhibition.
"The new dimerization inhibitor unveils a biologically meaningful rationale for suppressing angiogenesis in tumors that could outperform traditional competitive inhibitors of angiogenesis in tumor therapy. These findings should translate into improved anti-angiogenic and anti-lymphangiogenic tumor therapies", says Professor Alitalo.
INFORMATION:
A double block of blood vessels to starve cancerous tumors
2010-12-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ACP commends Congress for preserving patient access by stopping scheduled Medicare SGR cuts
2010-12-10
(Washington) – The American College of Physicians (ACP) today commended Congress for taking bipartisan action to preserve access for patients enrolled in Medicare and TriCare by stabilizing physician payments through 2011. The College noted, though, that the incoming 112th Congress will need to enact legislation to provide longer-term stability in payments and lead to repeal of the Sustainable Growth Rate (SGR) formula.
The legislation, passed unanimously by the Senate yesterday and passed by an overwhelming majority in the House of Representatives today, will avert ...
Ice-age reptile extinctions provide a glimpse of likely responses to human-caused climate change
2010-12-10
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---A wave of reptile extinctions on the Greek islands over the past 15,000 years may offer a preview of the way plants and animals will respond as the world rapidly warms due to human-caused climate change, according to a University of Michigan ecologist and his colleagues.
The Greek island extinctions also highlight the critical importance of preserving habitat corridors that will enable plants and animals to migrate in response to climate change, thereby maximizing their chances of survival.
As the climate warmed at the tail end of the last ice age, ...
Blood-thinning treatment standards changing for heart patients, new research shows
2010-12-10
CINCINNATI—Researchers at the University of Cincinnati (UC) and Massachusetts General Hospital have found that warfarin, a known anticoagulation (blood-thinning) drug, may not be as beneficial to some patients with atrial fibrillation as previously thought.
These findings were published online this week ahead of print in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Warfarin is commonly prescribed to prevent blood clotting, particularly for patients with atrial fibrillation—a type of abnormal heart rhythm.
Mark Eckman, MD, professor of medicine at ...
Medicine: Alzheimer's and heart attacks share the same genes
2010-12-10
Alzheimer and heart attacks have been found to share common genetic basis. The research leads the way to the first genetic test on developing the risk of the diseases even at a young age. According to Federico Licastro, an immunologist at the University of Bologna who coordinated the study published in the scientific journal, Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, a test is now ready. "They are already selling it in America", he says, citing the case of a private firm in New Mexico (USA) that collaborated on the study. "But the tests could easily be also conducted wherever, using ...
National team of scientists peers into the future of stem cell biology
2010-12-10
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– Remarkable progress in understanding how stem cell biology works has been reported by a team of leading scientists, directed by experts at UC Santa Barbara. Their research has been published in the journal Cell Stem Cell.
Stem cell biology is making waves around the world with great hope for the eventual repair of parts of the body. While many scientists see these breakthroughs as viable, there are hurdles that must be overcome, including the worrisome potential for introducing cancer when making a repair to an organ.
Significant interdisciplinary ...
Immune system changes linked to inflammatory bowel disease revealed
2010-12-10
Scientists at the Virginia Bioinformatics Institute at Virginia Tech have discovered some of the key molecular events in the immune system that contribute to inflammatory bowel disease. The results, which help researchers move one step further in their efforts to develop new drugs to treat inflammatory and immune-mediated diseases, are reported in the November 2010 edition (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21068720) of the journal Mucosal Immunology from the Nature Publishing Group.
Inflammatory bowel disease starts when the gut initiates an abnormal immune response ...
Researchers discover how natural drug fights inflammation
2010-12-10
Researchers at the Virginia Bioinformatics Institute at Virginia Tech have discovered how abscisic acid, a natural plant hormone with known beneficial properties for the treatment of disease, helps fight inflammation. The results (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/210882970), which are published in the November 2010 Journal of Biological Chemistry, reveal important new drug targets for the development of treatments for inflammatory and immune-mediated diseases.
The scientists had reported some of the key molecular events in the immune system of mice that contribute to ...
World's smallest battery created at CINT nanotechnology center
2010-12-10
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — A benchtop version of the world's smallest battery — its anode a single nanowire one seven-thousandth the thickness of a human hair —has been created by a team led by Sandia National Laboratories researcher Jianyu Huang.
To better study the anode's characteristics, the tiny rechargeable, lithium-based battery was formed inside a transmission electron microscope (TEM) at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies (CINT), a Department of Energy research facility jointly operated by Sandia and Los Alamos national laboratories.
Says Huang of the work, ...
Fahrenheit -459: Neutron stars and string theory in a lab
2010-12-10
DURHAM, N.C. – Using lasers to contain some ultra-chilled atoms, a team of scientists has measured the viscosity or stickiness of a gas often considered to be the sixth state of matter. The measurements verify that this gas can be used as a "scale model" of exotic matter, such as super-high temperature superconductors, the nuclear matter of neutron stars, and even the state of matter created microseconds after the Big Bang.
The results may also allow experimental tests of string theory in the future.
Duke physicist John Thomas made the viscosity measurements using an ...
Bering Sea chill yields fatter plankton, pollock diet changes
2010-12-10
Despite a 30-year warming trend, the last three years in the Bering Sea have been the coldest on record. A University of Alaska Fairbanks scientist says that the cold temperatures have helped produce larger zooplankton in the Bering Sea, which may affect the way Walleye pollock feed.
Alexei Pinchuk, research professional at the UAF Seward Marine Center, has spent the last three years gathering zooplankton samples in the Bering Sea. He and his colleagues have been looking at how changes in temperature in the Bering Sea affect resident zooplankton and, in turn, how those ...