(Press-News.org) Forehead wrinkles that rapidly deepen and crow's feet that appear suddenly around the eyes might distress the average person, but the ability to quickly and realistically incorporate such details in a facial reconstruction is the key feature of a new performance capture method developed at Disney Research.
The method, which requires only a single video camera such as a webcam, is the first to both operate in real-time and to capture facial features in high resolution, including such details as wrinkles.
"This could open up a variety of new applications, from casual home users who wish to give their own likeness to a game character to commercial applications where, for example, a customer can apply and view virtual makeup," said Derek Bradley, research scientist at Disney Research. "In film production, our method would allow a director to assess an actor's performance transferred to a digital creature even as he is filming."
In addition to Bradley, the research team included Chen Cao and Kun Zhou of Zhejiang University as well as Thabo Beeler of Disney Research. The researchers will present their facial performance capture method at ACM SIGGRAPH 2015, the International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, in Los Angeles Aug. 9-13.
Capturing facial details has proven critical for conveying emotions or the state of mind of a character and audiences are sensitive to subtle characteristics of the face. Animators thus devote great care to tracking facial performances of actors so that they can create realistic virtual characters. Until now, these facial performance capture methods have been designed to either capture these details in high resolution offline, or to record less detail but at high speed.
The new method represents a substantial step towards the goal of attaining both high quality and high speed.
As with other real-time facial capture methods, the researchers begin by using generic, low-resolution face models as the basis for reconstruction. A face model is virtually fitted to the user by the system as the user changes expressions and contorts his or her face in front of a video camera.
The system then automatically calculates a personalized wrinkle probability map, based on the set of extreme expressions the user assumed to train the program. The wrinkles may not match the user's actual wrinkles exactly, but they exhibit a very similar appearance because of the way they are formed.
"By learning the relationship between local image appearance and local wrinkle formation, we can reconstruct plausible face wrinkles in real-time from a single camera," Beeler noted. Once trained, the online capture approach can be applied to any new user without additional training. The system is generic and can be used with most common types of real-time face trackers.
INFORMATION:
For more information on the method, and a video, please visit the project web page at http://www.disneyresearch.com/realtimeperformancecapture/.
About Disney Research
Disney Research is a network of research laboratories supporting The Walt Disney Company. Its purpose is to pursue scientific and technological innovation to advance the company's broad media and entertainment efforts. Vice Presidents Jessica Hodgins and Markus Gross manage Disney Research facilities in Los Angeles, Pittsburgh, Zürich, and Boston and work closely with the Pixar and ILM research groups in the San Francisco Bay Area. Research topics include computer graphics, animation, video processing, computer vision, robotics, wireless & mobile computing, human-computer interaction, displays, behavioral economics, and machine learning.
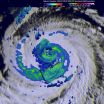
Heavy rain, towering thunderstorms, and a large area are things that NASA satellites observed as Typhoon Soudelor moves toward Taiwan on August 5, 2015.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Soudelor on August 5, 2015 at 01:45 UTC and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a visible image of the large storm in the Philippine Sea. The eye appeared to be cloud-filled as bands of thunderstorms spiraled into the center of the storm.
The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission core observatory, a satellite managed by both NASA and ...
A team of astronomers led by Caltech has discovered a giant swirling disk of gas 10 billion light-years away--a galaxy-in-the-making that is actively being fed cool primordial gas tracing back to the Big Bang. Using the Caltech-designed and -built Cosmic Web Imager (CWI) at Palomar Observatory, the researchers were able to image the protogalaxy and found that it is connected to a filament of the intergalactic medium, the cosmic web made of diffuse gas that crisscrosses between galaxies and extends throughout the universe.
The finding provides the strongest observational ...
Washington, DC, August 5, 2015 -- Potentially harmful bacteria can survive on endoscopes used to examine the interior of the digestive tract, despite a multi-step cleaning and disinfecting process, according to a study published in the August issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
Though endoscopes were cleaned in accordance with multi-society guidelines, viable microbes and residual contamination remained on surfaces after each stage of cleaning, ...
Dan's Wild Wild Science Journal
New paper shows global climate model errors are significantly less than thought
Scientists have matched the output of climate models to the way the Earth's temperature record is constructed in a new study in Geophysical Research Letters. Dan Satterfield explores how climate models are doing an even better job at predicting the Earth's temperature than was thought.
Eos.org
On the rebound: Modeling Earth's ever-changing shape
A new modeling tool easily computes the elastic response of changes in loading on Earth's surface to high resolution. ...
While undergoing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy induced weight loss and improvements in obesity-related disorders, long-term followup shows significant weight regain and a decrease in remission rates of diabetes and, to a lesser extent, other obesity-related disorders over time, according to a study published online by JAMA Surgery.
Obesity was recognized as a global epidemic by the World Health Organization 15 years ago and rates of obesity have since been increasing. Obesity is currently considered a severe health hazard and a risk factor for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, ...
In a small study, women who had Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery reached certain blood alcohol concentrations in half the number of drinks compared to women who didn't have the surgery, and reported a greater feeling of drunkenness, according to a study published online by JAMA Surgery.
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is the most common bariatric surgical procedure performed in the world. Although RYGB surgery causes a marked reduction in food intake and induces remission of food addiction, it is associated with an increased risk of developing alcohol use disorders. It ...
Telephone-based cognitive behavioral therapy was better at reducing worry, generalized anxiety disorder symptoms and depressive symptoms in older adults who live in rural areas, where access to mental health treatment may be limited, according to an article published online by JAMA Psychiatry.
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is one of the most common anxiety disorders in older adults and is associated with poor quality of life, increased health care utilization and impaired memory. Medications and psychotherapy are the primary treatments. Many older adults prefer psychotherapy ...
To lose weight, boost energy or soothe nerves, many consumers turn to dietary supplements. But some of these products contain undeclared substances. To protect consumers from taking something without their knowledge, scientists have developed a technique to determine what secret ingredients could be lurking in these supplements. They report their approach, which helped them find the active Viagra ingredient and other synthetic designer compounds in various products, in ACS' Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry.
Dietary supplements can appear to be a healthful option ...
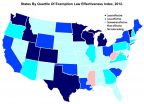
Athens, Ga. - Lax state vaccination laws contribute to lower immunization rates and increased outbreaks of preventable diseases--like whooping cough and measles--according to a new study from the University of Georgia.
Through their research, released in the August issue of the journal Health Affairs, study authors David Bradford and Anne Mandich found higher rates of pertussis, or whooping cough, in states that allowed philosophical exemptions and used a standardized exemption form.
Vaccination exemption rates have increased drastically in the past 10 years, according ...
Ottawa, ON (5 August 2015) - Canadian Science Publishing and the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology are pleased to announce the release of a special edition of Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences in recognition of the Museum's thirtieth anniversary on September 25, 2015.
The insatiable curiosity of the Royal Tyrrell Museum scientists has driven its research program for the past thirty years, and has positioned the Museum as a leader in furthering our understanding of the evolution of life on Earth. The Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, an NRC Research Press journal ...