INFORMATION:
The work was done by RIKEN in collaboration with The University of Tokyo and the National Institute of Material Science, who prepared the nanosheets used in the material.
New hydrogel stretches and contracts like a heat-driven muscle
2015-08-10
(Press-News.org) In research published in Nature Materials, a team led by scientists from the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science in Japan has developed a new hydrogel that works like an artificial muscle--quickly stretching and contracting in response to changing temperature. They have also managed to use the polymer to build an L-shaped object that slowly walks forward as the temperature is repeatedly raised and lowered.
Hydrogels are polymers that can maintain large quantities of water within their networks. Because of this, they can swell and shrink in response to changes in the environment such as voltage, heat, and acidity. In this sense they are actually similar to the plant cells, which are able to change shape as the amount of water within them changes in response to environmental conditions.
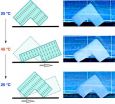
However, most hydrogels do this very slowly, and must absorb and excrete water to either expand or shrink in volume. The unique property of the hydrogel developed by the RIKEN team is that it acts like an artificial muscle, which does not contract equally in all directions. Rather, they contract in one dimension while expanding in another, meaning that they can change shape repeatedly without absorbing or excreting water.
The secret to the new hydrogel's property is electrostatic charge. Using a method that they published earlier this year, the team arranged metal-oxide nanosheets into a single plane within a material by using a magnetic field and then fixed them in place using a procedure called light-triggered in-situ vinyl polymerization, which essentially uses light to congeal a substance into a hydrogel. The nanosheets ended up stuck within the polymer, aligned in a single plane. Due to electrostatic forces, the sheets create electrostatic resistance in one direction but not in the other.
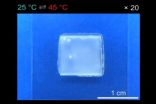
According to author Yasuhiro Ishida, "We originally designed this material to be stretchable in one direction, but we also found that at a temperature called the lower critical solution temperature, which we calculated to be 32 degrees Celsius, the polymer rapidly changed shape, stretching in length. Intriguingly, the gel did not change in volume. The substance underwent the change in shape in air and in a liquid environment, showing that it doesn't require the uptake of water. So in other words, it will work even in a normal air environment."
The team members were intrigued to find, additionally, that the process was very fast, taking just one second, with the rate of deformation, at about 70% per second, being higher than what has been seen in other hydrogels.
As a demonstration of how the polymer could be put to practical use, the group designed an L-shaped piece of polymer that can actually walk, in a water environment, as the legs lengthen and contract in response to changing temperature.
The group now plans to conduct further studies to create substances that can be used in practical applications. According to Ishida, "We are now planning further work to improve the properties of the substance. One idea we have is to use a hydrogel like this to make artificial muscles that could automatically open and close radiator systems as temperatures rise and fall. This could be used, for example, to prevent a device from overheating."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study suggests altered brain development among former NFL players
2015-08-10
(Boston)-- Former National Football League (NFL) players who started playing tackle football before the age of 12 were found to have a higher risk of altered brain development compared to those who started playing at a later age. The study is the first to demonstrate a link between early exposure to repetitive head impacts and later life structural brain changes.
Led by researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) and Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), the study appears online in the Journal of Neurotrauma.
The researchers examined 40 former NFL players ...
Portable ultra-broadband lasers could be key to next-generation sensors
2015-08-10
The invisible chemicals around and within us can tell many complicated stories. By sensing them, security agents can uncover explosive threats. By monitoring them in our breath, doctors can diagnose serious illnesses. And by detecting them on distant planets, astronomers may find signs of life.
These chemicals sometimes reveal their secrets when probed with mid-infrared wavelength lasers. Nearly all chemicals, including explosives, industrial, and pollutants, strongly absorb light in the mid-infrared wavelength region, which is often called the "fingerprint region" for ...
A small, modular, efficient fusion plant
2015-08-10
CAMBRIDGE, Mass.--It's an old joke that many fusion scientists have grown tired of hearing: Practical nuclear fusion power plants are just 30 years away -- and always will be.
But now, finally, the joke may no longer be true: Advances in magnet technology have enabled researchers at MIT to propose a new design for a practical compact tokamak fusion reactor -- and it's one that might be realized in as little as a decade, they say. The era of practical fusion power, which could offer a nearly inexhaustible energy resource, may be coming near.
Using these new commercially ...
Atomic-level defense secrets revealed
2015-08-10
EAST LANSING, Mich. (July 10,2015) - Just as nations around the globe carefully guard their defense secrets, so do plants.
New research in the current issue of Nature, however, has revealed the molecular secrets of plants' defense mechanisms at the atomic level. The study, led by Michigan State University and Van Andel Research Institute, focuses on the plant hormone jasmonate and its interaction with three key proteins. The findings could help scientists develop dream crops that are better equipped to fend off pests, diseases and future challenges created by fluctuating ...
Women having a baby by IVF are at increased risk of reflux disease after birth
2015-08-10
(Vienna, 6 August, 2015) Women who give birth to babies conceived by in-vitro fertilisation (IVF) are at increased risk of experiencing long-term symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD), according to the results of a study published in the UEG Journal.1 Researchers in Turkey compared two groups of women who had given birth to their first child at least 1 year earlier and found that those who had had IVF were three-times more likely to be diagnosed with GORD than those who had conceived naturally. No differences in GORD prevalence were reported between the women ...
Stepping up the sexy
2015-08-10
Queen's University professor Nikolaus Troje (Psychology, Biology, School of Computing) believes that it is the consistency of the whole appearance rather than the attractiveness of the parts.
"Most previous work on attractiveness focused on the effect of isolated features." says Dr. Troje. "The current study demonstrates how important it is that these features fit together well."
Participants were shown schematic point-light displays that depict a person using 15 moving dots. The representation conveyed both the individual characteristics of a person's movements and their ...
Slowing down muscle loss in heart failure patients
2015-08-10
Patients in advanced states of myocardial insufficiency generally lose their muscle mass and muscle strength. Indeed a fact that until now has negatively impacted the clinical course of the disease and that has resulted in poor prognoses for patients. Such pathological muscle loss impacts the skeletal muscles in particular. The responsible molecular signaling pathways have not yet been fully understood. One cause of this degenerative process lies in the system that regulates the blood pressure and salt/water supply in the body - the so-called renin-angiotensin-aldosterone ...
Parents' math anxiety can undermine children's math achievement
2015-08-10
If the thought of a math test makes you break out in a cold sweat, Mom or Dad may be partly to blame, according to new research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
A team of researchers led by University of Chicago psychological scientists Sian Beilock and Susan Levine found that children of math-anxious parents learned less math over the school year and were more likely to be math-anxious themselves--but only when these parents provided frequent help on the child's math homework.
Lead study author Erin A. Maloney ...
Study examines how and why states adopt drunk driving laws
2015-08-10
How do states decide what laws to adopt to prevent alcohol-impaired driving and keep their roads safe?
A new study by public health researchers at NYU's Steinhardt School of Culture, Education, and Human Development finds that the severity of the problem within the state is not the most important predictor of whether states adopt new laws to restrict drunk driving - nor is the political makeup of the state government. Instead, the two strongest predictors of states adopting their first drunk driving laws were having a large population of young people and a neighboring ...
Developing a better flu vaccine
2015-08-10
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health researchers say they have developed a method that could make a nasal spray flu vaccine effective for those under two and over 49 - two groups for which the vaccine is not approved.
By studying the weakened flu virus that is the basis for the nasal spray vaccine in cells from human nasal and sinus cavities, the researchers say they have determined that the virus can be weakened (for young children) or strengthened (in older people) enough to create an appropriate immune response in people of all ages.
A report on the findings ...