(Press-News.org) People infected with the hepatitis C virus are at risk for liver damage, but the results of a new Johns Hopkins study now show the infection may also spell heart trouble.
The findings, described online July 27 in The Journal of Infectious Diseases, emerged from a larger ongoing study of men who have sex with men, many but not all of whom were infected with HIV and followed over time to track risk of infection and disease progression. A subset of the participants had both HIV and hepatitis C, two infections that often occur together.
Even though people infected with HIV are already known to have an elevated risk for heart disease, researchers emphasize their results offer strong evidence that hepatitis C can spark cardiovascular damage independent of HIV.
Specifically, the research found that study participants chronically infected with hepatitis C were more likely to harbor abnormal fat-and-calcium plaques inside their arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis and a common forerunner of heart attacks and strokes.
"We have strong reason to believe that infection with hepatitis C fuels cardiovascular disease, independent of HIV and sets the stage for subsequent cardiovascular trouble," says study principal investigator Eric Seaberg, Ph.D., assistant professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. "We believe our findings are relevant to anyone infected with hepatitis C regardless of HIV status."
Investigators emphasize they don't know exactly how infection with the hepatitis C virus precipitates the growth of artery-clogging plaque but that their evidence is strong enough to warrant vigilant monitoring for cardiac symptoms among people infected with the virus.
"People infected with hepatitis C are already followed regularly for signs of liver disease, but our findings suggest clinicians who care for them should also assess their overall cardiac risk profile regularly," says study author Wendy Post, M.D., M.S., professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and a cardiologist at the Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center for the Prevention of Heart Disease.
Post says that at a minimum patients with hepatitis C would benefit from an annual cardiac evaluation that includes cholesterol and glucose testing, a blood pressure check and assessment of lifestyle habits.
The study involved 994 men 40 to 70 years old without overt heart disease who were followed across several institutions in Baltimore, Washington, D.C., Pittsburgh, Los Angeles and Chicago. Of the 994, 613 were infected with HIV, 70 were infected with both viruses and 17 were only infected with hepatitis C. Participants underwent cardiac CT scans to detect and measure the amount of fat and calcium deposits inside the vessels of their hearts. Those infected with hepatitis C, regardless of HIV status, had, on average, 30 percent more disease-fueling calcified plaque in their arteries, the main driver of heart attack and stroke risk. People infected with either HIV or hepatitis C, on average, had 42 percent more noncalcified fatty buildup, a type of plaque believed to confer the greatest cardiac risk.
In addition, those who had higher levels of circulating hepatitis C virus in their blood were 50 percent more likely to have clogged arteries, compared with men without hepatitis C. Higher virus levels in the blood signal that the infection is not well controlled by drugs or the immune system. Poorly controlled infection, the investigators add, may lead to more inflammation throughout the body, which can fuel blood vessel damage and thus contribute to heart disease.
Treating hepatitis C infection promptly can ward off long-term liver damage, but researchers say their findings now raise another critical question: whether a new class of medications that help 90 percent of patients clear the virus within a few short months could also halt the formation of plaque and reduce cardiac risk in the long run.
More than 2.7 million people in the United States are infected with the hepatitis C virus, according to estimates from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
INFORMATION:
Other Johns Hopkins investigators involved in the study included Rebeccah McKibben, Sabina Haberlen, Todd Brown and Chloe Thio. Investigators from other institutions included Matthew Budoff, Mallory Witt, Lawrence Kingsley and Frank Palella.
The work was by funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute under grant number RO1 HL095129, with additional support from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (grant UL1 TR 001079) and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Conflict of interest disclosure: Johns Hopkins investigator Todd Brown, M.D., is a consultant for the following pharmaceutical companies: Gilead Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Abbvie, EMD Serono and ViiV Healthcare. These relationships are managed by Johns Hopkins in accordance with its policy on interaction with industry.
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Media Relations and Public Affairs
Media contacts:
Ekaterina Pesheva, epeshev1@jhmi.edu, (410) 502-9433
Stephanie Desmon, sdesmon1@jhu.edu, (410) 955-7619
New research from Monash University shows that children are being exposed to thousands of alcohol adverts when watching sport TV, questioning the effectiveness of advertising regulations designed to protect children.
The study, published in the international journal PLOS ONE, found that 87 per cent of all alcohol adverts during the daytime were in sport TV when hundreds of thousands of children were watching. A clause in Australia's advertising regulations allowing alcohol advertising in live sport programming during the day when children are watching appears to be responsible ...
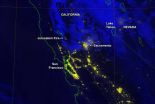
From its orbit around the Earth, the NASA-NOAA Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite or Suomi NPP satellite, captured a night-time image of California's Jerusalem Fire.
InciWeb is an interagency all-risk incident information management system that coordinates with federal, state and local agencies to manage wildfires. According to Inciweb, this fire is burning on lands managed by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management within the Berryessa Snow Mountain National Monument. It is being managed by the Sonoma-Lake-Napa Unit of the California Department of Forestry ...
MADISON, Wis. -- Human learning is a complex, sometimes mysterious process. Most of us have had experiences where we have struggled to learn something new, but also times when we've picked something up nearly effortlessly.
What if a fusion of computer science and psychology could help us understand more about how people learn, making it possible to design ideal lessons?
That long-range goal is moving toward reality thanks to an effort led by professors in the University of Wisconsin-Madison departments of computer sciences, psychology and educational psychology. Their ...
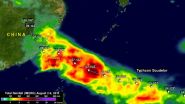
Typhoon Soudelor dropped over two feet of rainfall when it made landfall in China in early August, and soaked Taiwan. NASA estimated that rainfall using data from the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission.
Soudelor formed in the middle of the Pacific Ocean well east of Guam on July 20, 2015. Soudelor became more powerful with peak intensity of about 155 knots (178 mph) reached on August 3, 2015 when the super typhoon was well east of Taiwan over the open waters of the Pacific Ocean.
Soudelor's winds died down a little but rebounded to with over 100 knots (115 ...
Swine housing has been a hot topic in recent years, not only in the United States, but in many countries, such as Denmark. Due to genetic advancements in recent years, the average litter size in Denmark is 16.6 total born piglets. With increased number of piglets, determining the optimal housing system for both the piglet and sow is critical.
In Denmark, gestation crates were banned in new buildings in 1999 and from all existing units in 2013. As of January 1, 2015, sows are required to be loose housed from time of weaning until seven days before expected parturition ...
August 6, 2015 - According to the Association for Pet Obesity Prevention in 2014, approximately 53% and 58% of dogs and cats, respectively, in the United States were overweight and obese. These numbers have steadily increased since 2010. However, most pet owners (? 90%) do not realize and cannot identify that their pets are overweight/obese.
What can we do about this growing problem? Pet food companies and nutritionists are searching for ingredients, like prebiotics and probiotics, to combat these conditions. But, could the problem have another solution?
Dr. Aulus Carciofi, ...
The signs that an abused child might later commit crimes might not be obvious -- that boisterous playground behavior from a third-grade boy, for example, or the 10-year-old girl who seems a little anxious or withdrawn.
But new research from the University of Washington suggests that troubling behaviors exhibited by abused children can be predictors of later criminal activity, and that those indicators differ between boys and girls.
The study, published Aug. 11 in the Journal of Interpersonal Violence, found that elementary-aged boys who show "externalizing" behaviors ...
It is a paradox: Patients with advanced congestive heart failure lose skeletal muscle mass, but their heart muscles become enlarged to provide the body with an adequate supply of blood and thus with oxygen. It has long been known that the protein angiotensin II plays a villainous role in this process, but the exact mechanism has remained unclear. Now, after seven years of fitting the pieces of this puzzle together, the biologist Dr. Philipp Du Bois and the cardiologist PD Dr. Jens Fielitz of the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), a joint cooperation between ...
DURHAM, N.H. -- When the sun hurls a billion tons of high-energy particles and magnetic fields into space at speeds of more than a million miles per hour and the "space weather" conditions are right, the resulting geomagnetic storm at Earth can wreak havoc on communication and navigation systems, electrical power grids, and pose radiation hazards to astronauts and airline passengers and crew.
Being able to predict when those conditions are right is a key scientific goal, and researchers from the University of New Hampshire's Space Science Center (SSC) are now adding ...
Findings from a pair of new studies could speed up the development of a universally accurate diagnostic test for human herpes simplex viruses (HSV), according to researchers at Johns Hopkins and Harvard universities and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The work may also lead to the development of a vaccine that protects against the virus.
Depending on the strain and other factors, HSV can cause cold sores -- classically associated with HSV1 -- or genital herpes -- classically HSV2 -- with the latter being the more serious of the two diseases, particularly because ...