(Press-News.org) Move over, Katniss Everdeen. For archerfish, the odds are ever in their favor, according to new research from Wake Forest University.
The sharp-shooting fish's ability to spit water to hit food targets has been well documented, but a new study published online in the journal Zoology showed for the first time that there is little difference in the amount of force of their water jets based on target distance. And, when given the choice, the fish preferred closer targets.
The study was co-authored by Wake Forest researchers Morgan Burnette, a biology graduate student, and Miriam Ashley-Ross, associate professor of biology, whose work focuses on the mechanics of animal behavior in a variety of animal species.
"The force of their jets of water isn't decreasing by much when they shoot at a distant target," Burnette said, "but the fish consistently chose closer targets to ensure a food payoff because, ultimately, it's about whether the fish is going to eat or not that day."
Described as nature's sharpshooters or water pistols, archerfish inhabit the mangroves of southeast Asia and northern Australia. When the fish spot small insects on overhead branches and leaves, they spit a stream of water from their mouths that can dislodge that insect, causing it to fall onto the water's surface. Due to the complex structure of the vegetation in their environment, the distance a shot would have to travel to a potential target may vary considerably. A shooter also must compete with other archerfish for the fallen prey.
The first step toward this goal was to understand how, or even if, the forces from the water jet were different, depending on how far away the fish's target was. Last year, another research group demonstrated that the fish could alter how the stream travels to and hits a target, based on the distance to that target. This finding implied that forces to distant targets could be similar to forces delivered to closer targets, and Burnette and Ashley-Ross set out to test this idea.
"I'm really interested in how animals are taking information from their environment and changing or using that information in some behavior," Burnette said.
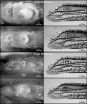
From the archerfish in their lab, they measured the force at impact and also used high-speed video cameras to capture the impact of the water jet at 500 frames per second.
What Burnette found was that even when the target is relatively far away from the fish (up to six times the body length of the animal), the forces on the target showed little reduction with respect to a closer target. In another part of the study, they gave the fish a choice: shoot down a close target or a more distant target, and see which one the fish would choose first.
"It was really interesting that the fish would consistently choose targets that were closer even though we had shown that the forces didn't change very much with distance," Burnette said. "Choosing a closer target, then, reduces the amount of time that a bystander has to respond to get the dislodged insect."
Ashley-Ross said that to simply characterize the archerfish as nature's squirt gun isn't quite accurate, because the fish behavior is a lot more complicated than that. Previous studies have compared the calculations the fish are making to what a baseball outfielder is doing, she said, which is figuring out where the ball is going to drop and where they need to be to intercept.
"It's the same exact type of spatial calculation," she said "This study gives us one more window into the complexity of animal experience. Our bias is to think that fish are just dumb and don't have a whole lot going on and that's not true. The fish are making very sophisticated calculations in their inscrutable little fish minds."
INFORMATION:
A new study says that global warming has measurably worsened the ongoing California drought. While scientists largely agree that natural weather variations have caused a lack of rain, an emerging consensus says that rising temperatures may be making things worse by driving moisture from plants and soil into the air. The new study is the first to estimate how much worse: as much as a quarter. The findings suggest that within a few decades, continually increasing temperatures and resulting moisture losses will push California into even more persistent aridity. The study appears ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Formula One racing teams may have a lesson to teach business leaders: Innovation can be overrated.
That's the conclusion from academic researchers who pored over data from 49 teams over the course of 30 years of Formula One racing. They found that the teams that innovated the most - especially those that made the most radical changes in their cars - weren't usually the most successful on the race course.
Moreover, radical innovations were the least successful at exactly the times when many business leaders would be most likely to try them: when there ...
A research team at York has adapted the astonishing capacity of animals such as newts to regenerate lost tissues and organs caused when they have a limb severed.
The research, which is funded by a £190,158 award from the medical research charity Arthritis Research UK, is published in Nature Scientific Reports.
The scientists, led by Dr Paul Genever in the Arthritis Research UK Tissue Engineering Centre in the University's Department of Biology, have developed a technique to rejuvenate cells from older people with osteoarthritis to repair worn or damaged cartilage ...
Physicists suggest a new way to look for dark matter: They beleive that dark matter particles annihilate into so-called dark radiation when they collide. If true, then we should be able to detect the signals from this radiation.
The majority of the mass in the Universe remains unknown. Despite knowing very little about this dark matter, its overall abundance is precisely measured. In other words: Physicists know it is out there, but they have not yet detected it.
It is definitely worth looking for, argues Ian Shoemaker, former postdoctoral researcher at Centre ...
Putnam Valley, NY. (Aug. 19, 2015) - A team of researchers in South Korea has successfully transplanted mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) derived from human amniotic membranes of the placenta (AMSCs) into laboratory mice modeled with oxygen-induced retinopathy (a murine model used to mimic eye disease). The treatment aimed at suppressing abnormal angiogenesis (blood vessel growth) which is recognized as the cause of many eye diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration. The researchers reported that the AMSCs successfully migrated to the retinas ...
National Institutes of Health (NIH) scientists and colleagues report that an experimental vaccine given six weeks before exposure to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) fully protects rhesus macaques from disease. The vaccine also generated potentially protective MERS-CoV antibodies in blood drawn from vaccinated camels. A study detailing the synthetic DNA vaccine appears in the Aug. 19 Science Translational Medicine. MERS-CoV, which causes pneumonia deep in the lungs, emerged in 2012 and has sickened more than 1,400 people and killed 500, mostly in ...
Summary: In 2011, the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society issued a guideline recommending that neonates undergoing cardiac surgery for repair of congenital heart disease be placed on continuous encephalographic (EEG) monitoring after surgery to detect seizures. These recommendations followed reports that seizures are common in this population, may not be detected clinically, and are associated with adverse neurocognitive outcomes. Yet, in a discussion at the 2014 Annual Meeting of The American Association for Thoracic Surgery, 80% to 90% of the audience was not following ...
KINGSTON - Queen's University researcher Martin Duncan has co-authored a study that solves the mystery of how gas giants such as Jupiter and Saturn formed in the early solar system.
In a paper published this week in the journal Nature, Dr. Duncan, along with co-authors Harold Levison and Katherine Kretke (Southwest Research Institute), explain how the cores of gas giants formed through the accumulation of small, centimetre- to metre-sized, "pebbles.
"As far as we know, this is the first model to reproduce the structure of the outer solar system - two gas giants, two ...
There are fewer smokers in the current generation of adolescents. Current figures show about 25 per cent of teens smoke, down dramatically from 40 per cent in 1987.
But are those who pick up the habit doing so because they have a negative self-image? Does the typical teenaged smoker try to balance out this unhealthy habit with more exercise? And if so, then why would an adolescent smoke, yet still participate in recommended levels of physical activity?
A recent study, conducted in part at Concordia University and published in Preventive Medicine Reports, sought to answer ...
Female fish in the Bahamas have developed ways of showing males that "No means no."
In an example of a co-evolutionary arms race between male and female fish, North Carolina State University researchers show that female mosquitofish have developed differently sized and shaped genital openings in response to the presence of predators and - in a somewhat surprising finding - to block mating attempts by males from different populations.
"Genital openings are much smaller in females that live with the threat of predators and are larger and more oval shaped in females ...