The missing link
Fossil remains of an Old World lizard discovered in the New World overturn long-held hypothesis of lizard evolution
2015-08-26
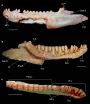
(Press-News.org) University of Alberta paleontologists have discovered a new species of lizard, named Gueragama sulamericana, in the municipality of Cruzeiro do Oeste in Southern Brazil in the rock outcrops of a Late Cretaceous desert, dated approximately 80 million years ago.
"The roughly 1700 species of iguanas are almost without exception restricted to the New World, primarily the Southern United States down to the tip of South America," says Michael Caldwell, biological sciences professor from the University of Alberta and one of the study's authors. Oddly however, iguanas closest relatives, including chameleons and bearded dragons, are all Old World. As one of the most diverse groups of extant lizards, spanning from acrodontan iguanians (meaning the teeth are fused to the top of their jaws) dominating the Old World to non-acrodontans in the New World, this new lizard species is the first acrodontan found in South America, suggesting both groups of ancient iguanians achieved a worldwide distribution before the final break up of Pangaea.
A terrestrial Noah's Arc
"This fossil is an 80 million year old specimen of an acrodontan in the New World," explains Caldwell. "It's a missing link in the sense of the paleobiogeography and possibly the origins of the group, so it's pretty good evidence to suggest that back in the lower part of the Cretaceous, the southern part of Pangaea was still a kind of single continental chunk."
Distributions of plants and animals from the Late Cretaceous reflect the ancestry of Pangaea when it was whole. "This Gueragama sulamericana fossil indicates that the group is old, that it's probably Southern Pangaean in its origin, and that after the break up, the acrodontans and chameleon group dominated in the Old World, and the iguanid side arose out of this acrodontan lineage that was left alone on South America," says Caldwell. "South America remained isolated until about 5 million years ago. That's when it bumps into North America, and we see this exchange of organism north and south. It was kind of like a floating Noah's Arc for a very long time, about 100 million years. This is an Old World lizard in the new world at a time when we weren't expecting to find it. It answers a few questions about iguanid lizards and their origin."
The University of Alberta is a world leader in paleontology. This study was a collaboration between the University of Alberta and scientists in Brazil. Caldwell says of the collaboration, "It's providing an opportunity for our students and research groups to expand our expertise and interests into an ever-increasing diversity of organisms within this group of animals called snakes and lizards."
The lead author of the paper is Caldwell's PhD student, Tiago Simoes, a Vanier scholar. "As with many other scientific findings, this one raises a number of questions we haven't previously considered," says Simoes. "This finding raises a number of biogeographic and faunal turnover questions of great interest to both paleontologists and herpetologists that we hope to answer in the future."
In terms of next steps, Caldwell notes "Each answer only rattles the questions harder. The evolution of the group is much older than has been previously thought, which means we can push an acrodontan to 80 million years in South America. We now need to focus on much older units of of rock if we're going to find the next step in the process."
The findings, "A stem acrodontan lizard in the Cretaceous of Brazil revises early lizard evolution in Gondwana," were published in the journal Nature Communications, one of the world's top multidisciplinary scientific journals.
INFORMATION:
The University of Alberta Faculty of Science is a research and teaching powerhouse dedicated to shaping the future by pushing the boundaries of knowledge in the classroom, laboratory, and field. Through exceptional teaching, learning, and research experiences, we competitively position our students, staff, and faculty for current and future success.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-26
The humble dust collecting in the average American household harbors a teeming menagerie of bacteria and fungi, and as researchers from the University of Colorado Boulder and North Carolina State University have discovered, it may be able to predict not only the geographic region of a given home, but the gender ratio of the occupants and the presence of a pet as well.
The new findings, which were published today in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, highlight the impressive amount of microbial diversity in the average household and the degree to which these ...
2015-08-26
Dutch research shows that trained detectives of specialized observation teams are much better at registering details of a drug deal than ordinary civilians. Previous legal-psychological research revealed no relevant differences in observation skills between police professionals and civilians. The findings have been published in Legal and Criminological Psychology.
Judges and juries often assume that police officers' statements are more reliable than those of regular eyewitnesses. Because of this assumption, police officers' statements typically carry more weight in legal ...
2015-08-26
Only one in five gay and bisexual teen boys have been tested for HIV
HIV infections are on the rise for young men who have sex with men
Text messages, online program can identify nearby confidential testing sites
Testing in schools would 'normalize' the process.
CHICAGO --- Young men who have sex with men have the highest risk for HIV infection, but only one in five has ever been tested for HIV, a much lower rate than testing for non-adolescents, reports a new national Northwestern Medicine study conducted in partnership with the Center for Innovative Public ...
2015-08-26
On the coral reef, knowing who's your friend and who's your enemy can sometimes be a little complicated.
Take seaweed, for instance. Normally it's the enemy of coral, secreting toxic chemicals, blocking the sunlight, and damaging coral with its rough surfaces. But when hordes of hungry crown-of-thorns sea stars invade the reef, everything changes, reports a study to be published August 25 in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Seaweeds appear to protect coral from the marauding sea stars, giving new meaning to the proverb: "The enemy of my enemy is my friend." ...
2015-08-26
Lecithin is an ingredient that you've probably never heard of, but one that plays a vital role in the production of chocolate and many other foods. It's never been clear how this ingredient works on a molecular level, and confectioners have relied on observational methods - essentially trial and error - to perfect their recipes.
Now, scientists have shown how the field of molecular dynamics (simulation on a molecular level) could be a valuable tool in understanding chocolate conching - the part of the chocolate-making process where aromatic sensation, texture and 'mouthfeel' ...
2015-08-26
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels are the most common cause of death in Europe, resulting in over four million deaths a year (45% of all deaths) according to the latest available figures published today (Wednesday) in the European Heart Journal [1].
Although deaths from cardiovascular disease (CVD) are declining in most of Europe, there are large inequalities between European countries, with higher death rates seen in Eastern Europe. These high death rates correspond to the lower life expectancy also found in these countries, indicating the impact of CVD on inequalities ...
2015-08-26
Doctors in Togo, West Africa have seen a 10% drop in tuberculosis death rates after redesigning diagnosis and treatment services in one of the country's health districts.
The full results are published in BMJ Quality Improvement Reports today - an open access forum to help clinicians share improvement ideas.
Tuberculosis (TB) is the second leading cause of death among infectious diseases worldwide, killing nearly 2 million people each year, mostly in less developed countries.
Even though there have been improvements in tuberculosis control over the past two decades, ...
2015-08-26
For the first time, UK physicians have demonstrated that antiviral-based therapies have the potential to protect humans from the deadly Ebola virus. The report, published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases journal, describes a case-series of eight British health-care workers who were evacuated to the Royal Free Hospital in London, UK after possible accidental exposure to Ebola virus in Sierra Leone between January and March 2015.
Four of the health-care workers were considered to have been at significant risk of exposure to Ebola from needlestick injuries and were given ...
2015-08-26
A new study from The Journal of Neuroscience shows that humans and rhesus monkeys have very similar abilities in recognizing objects "at a glance," validating the use of this animal model in the study of human visual perception. In the study, published August 26, humans and monkeys not only demonstrated similar ease in recognizing objects in varied positions and landscapes, but both species also tended to make the same errors.
For the study, researchers from MIT compared the performance of two rhesus macaque monkeys and 638 adult human subjects on a large set of object ...
2015-08-26
Baltimore, Md., August 25, 2015 - Malawi has a population of 16 million, yet, only one inpatient rehabilitation center for individuals with stroke, spinal cord injury, and similar conditions. With just 40 beds, the Kachere Rehabilitation Center in Blantyre, Malawi's second largest city, provides services to the entire country. Because there is little funding for rehabilitation in the country, there is essentially no rehabilitation and follow-up services for patients after they return to their families, homes, and communities.
Leslie B. Glickman, PT, PhD, an assistant ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The missing link
Fossil remains of an Old World lizard discovered in the New World overturn long-held hypothesis of lizard evolution



