NASA sees Tropical Storm Fred losing its punch
2015-09-02
(Press-News.org) Tropical Storm Fred is losing its punch. Satellite imagery shows that there are no strong thunderstorms developing in the tropical storm indicating that the storm is weakening.
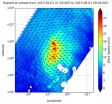
The RapidScat instrument that flies aboard the International Space Station measured Tropical Storm Fred's winds on September 1 at 4 a.m. EDT. RapidScat saw that the strongest winds tightly circled the center and were on the northern side of the storm, as strong as 24 and 27 meters per second (53.6 mph/ 86.4 kph and 60.4/97.2 kph).
On September 1 at 13:00 UTC (9 a.m. EDT) the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite saw Tropical Storm Fred moving past the Cape Verde Islands. At that time, the strongest thunderstorms were northwest of the center. By September 2, those strong thunderstorms were hard to find on NOAA's GOES- East satellite imagery taken at 10:45 a.m. EDT. Both the MODIS and the GOES images were created at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland
At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) on September 2 the center of Tropical Storm Fred was located near latitude 19.8 North, longitude 30.9 West. About 525 miles (845 km) west-northwest of the Cape Verde Islands. Fred is moving toward the west-northwest near 10 mph (17 kph), and this general motion is expected to continue over the next couple of days.
Satellite wind data indicate that the maximum sustained winds dropped to near 45 mph (75 kph) with higher gusts. Weakening is forecast during the next 48 hours. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1004 millibars.
Satellite imagery on September 2 showed that Fred had been without deep convection (strong uplift in the atmosphere that creates thunderstorms that make up a tropical cyclone) since about 11 p.m. on September 1. The National Hurricane Center noted that Fred just consists of a tight swirl of low- to mid-level clouds. NHC Forecaster Brown noted "If organized deep convection does not return very soon, which appears unlikely, Fred will become a post-tropical cyclone this afternoon. Strong westerly (wind) shear, marginal sea surface temperatures, and dry mid-level air should cause the circulation to gradually spin down during the next few days."
Fred is expected to become a post-tropical cyclone later in the day on Wednesday, September 2, 2015.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-09-02
GeoSpace
High water tables can be a boon to crop yields
A high water table - usually a bane to crop yields - can provide much-needed water during drought and to crops planted in coarse-grained soils, found a new study published online in Water Resources Research.
3-D maps illustrate formation of the Hangai Dome in central Mongolia
Scientists used 1.7 million seismic wave measurements from 227 earthquakes across East Asia to create animated 3-D images of subsurface rock formations under the Hangai Dome in central Mongolia as part of their recent study accepted in Geophysical ...
2015-09-02
A new study by WCS (Wildlife Conservation Society) has found that coral reef diversity 'hotspots' in the southwestern Indian Ocean rely more on the biomass of fish than where they are located, a conclusion that has major implications for management decisions to protect coral reef ecosystems.
Using data gathered over a 12-year period from nearly 270 coral reefs across the southwestern Indian Ocean, the WCS study found that the highest conservation priorities in the region should be reef systems where fish biomass exceeds 600 kilograms per hectare. This finding conflicts ...
2015-09-02
Can water ever be too clean? If the intent is to store it underground, the answer, surprisingly, is yes. In a new study, Stanford scientists have shown that recycled water percolating into underground storage aquifers in Southern California picked up trace amounts of arsenic because the water was too pure.
The research, published online in the journal Environmental Science & Technology, sheds light on a poorly understood aspect of groundwater recharge with purified recycled water, namely the potential mobilization of arsenic. Arsenic is a naturally occurring element that ...
2015-09-02
ATLANTA - Sept. 2, 2015 - The number of men with breast cancer who undergo surgery to remove the unaffected breast has risen sharply, according to a new report by American Cancer Society and Dana Farber Cancer Institute researchers. The report, appearing in JAMA Surgery, is the first to identify the trend, which mirrors a trend seen in U.S. women over the past two decades.
Breast cancer in men is rare, accounting for only about 1 percent of all cases in the United States. In women (particularly younger women), the use of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy (CPM) surgery ...
2015-09-02
Genes are not only important for regular memory performance, but also for the development of Alzheimer's disease. Researchers at the University of Basel now identified a specific group of genes that plays a central role in both processes. This group of molecules controls the concentration of calcium ions inside the cell. Their results appear in the current issue of the journal JAMA Psychiatry.
Intact memory capacity is crucial for everyday life. This fact becomes apparent once a memory disorder has developed. Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of age-associated ...
2015-09-02
WASHINGTON, DC, September 2, 2015 -- Social scientists have long argued documentary films are powerful tools for social change.
But a University of Iowa (UI) sociologist and his co-researchers are the first to use the Internet and social media to systematically show how a documentary film reshaped public perception and ultimately led to municipal bans on hydraulic fracking.
By measuring an uptick in online searches as well as social media chatter and mass media coverage, Ion Bogdan Vasi, an associate professor of sociology at the UI and corresponding author of a new ...
2015-09-02
A new study of more than 300 women suggests that exposure to certain phthalates -- substances commonly used in food packaging, personal-care and other everyday products -- could be associated with miscarriage, mostly between 5 and 13 weeks of pregnancy. The research, appearing in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology, is the first epidemiological study on non-work-related exposure to phthalates to provide evidence for the possible link among a general population.
Out of concern over the potential health effects of phthalates, the U.S. has banned six of these ...
2015-09-02
Scientific experiments examining what happens to the faulty channel protein that causes cystic fibrosis during inflammation have yielded unexpected and exciting results. The study, conducted by Sara Bitam and her colleagues at INSERM in France, has just passed peer review on open science publishing platform F1000Research.
Cystic fibrosis is a life-limiting auto¬somal recessive monogenic disorder that affects 1 in every 2000 - 3500 newborns in the EU and US per year. It is caused by mutations in the gene that encodes the CFTR protein, an epithelial ion channel involved ...
2015-09-02
Gum disease is a common condition among adults that occurs when bacteria form biofilms or plaques on teeth, and consequently the gums become inflamed. Some severe cases, called periodontitis, call for antibiotics. But now scientists have discovered that wild blueberry extract could help prevent dental plaque formation. Their report in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry could lead to a new therapy for periodontitis and a reduced need for antibiotics.
Many people have had some degree of gum inflammation, or gingivitis, caused by dental plaque. The gums get ...
2015-09-02
NASHVILLE, Tenn. - In the popular mind, mass extinctions are associated with catastrophic events, like giant meteorite impacts and volcanic super-eruptions.
But the world's first known mass extinction, which took place about 540 million years ago, now appears to have had a more subtle cause: evolution itself.
"People have been slow to recognize that biological organisms can also drive mass extinction," said Simon Darroch, assistant professor of earth and environmental sciences at Vanderbilt University. "But our comparative study of several communities of Ediacarans, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA sees Tropical Storm Fred losing its punch


