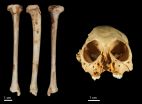
(Press-News.org) ALLENDALE, Mich. -- An international team of scientists, including a Grand Valley State University professor and alumni, recently discovered a species of monkey fossil the team has dated to be more than one million years old.
The discovery was made after the team recovered a fossil tibia (shin bone) belonging to the species of extinct monkey Antillothrix bernensis from an underwater cave in Altagracia Province, Dominican Republic. The species was roughly the size of a small cat, dwelled in trees, and lived largely on a diet of fruits and leaves.
"We know that there is a diverse extinct fauna on the Caribbean Islands, but dating the material has been difficult," said Melissa Tallman, assistant professor of biomedical sciences who was involved in the discovery and analysis of the fossil. "Antillothrix bernensis is one of two species of extinct primate on Hispaniola. Previously discovered primate material has all been dated to within the last 10,000 years. This new material is morphologically consistent with the previously collected material, but is dated to 1.3 million years ago."
The fossil was embedded in a limestone rock that was dated using the Uranium-series technique.
"When the limestone rocks are formed, uranium gets trapped in them and decays by natural radioactive processes to form thorium and lead," Tallman said. "Scientists know the rate at which uranium decays and by measuring the amount of uranium, thorium and lead present in the rocks today, one can calculate the age of the rocks."
Tallman, along with Andrea Morrow, '14, used three-dimensional geometric morphometrics to confirm that the fossil tibia did belong to Antillothrix bernensis. This process helped them reconstruct how the small primate might have moved about in its environment and allowed the comparison of relatively young examples of Antillothrix bones to the newly discovered million-year-old specimens.
Tallman said since the days of Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, scientists have long been puzzled over the age of primate fossils from this region.
"Many times when a long-lived species is discovered, there is a shift in its morphology over time," Tallman said. "For these primates, at least in the tibia, they remained remarkably stable morphologically. They obviously adapted to their island environment in such a way that was flexible enough that it allowed them to persist for more than one million years. They were likely still around when humans first colonized the Greater Antillean Islands."
INFORMATION:
The full study, "1.32 ± 0.11 Ma age for underwater remains constrain antiquity and longevity of the Dominican primate Antillothrix bernensis," can be read via the Journal of Human Evolution.
This discovery was made possible by the collaboration between the Dominican Speleological Society, the Museo del Hombre Dominicano in Santo Domingo, and Brooklyn College, CUNY. Cave divers, Cristian Pittaro, Phillip Lehman, Dave Pratt, and Victoria Alexandrova were responsible for this incredible find within Padre Nuestro Cave.
As climate change accelerates ice melt in the Arctic, polar bears may find caribou and snow geese replacing seals as an important food source, shows a recent study published in the journal PLOS ONE. The research, by Linda Gormezano and Robert Rockwell at the American Museum of Natural History, is based on new computations incorporating caloric energy from terrestrial food sources and indicates that the bears' extended stays on land may not be as grim as previously suggested.
"Polar bears are opportunists and have been documented consuming various types and combinations ...
Natural wonders like tumbling waterfalls, jutting rock faces and banks of wildflowers have long drawn visitors to America's national parks and inspired efforts to protect their beauty.
According to a study published Sept. 4 in Park Science, visitors also value and seek to protect a different kind of threatened natural resource in the parks: dark nighttime skies.
Almost 90 percent of visitors to Maine's Acadia National Park interviewed for the study agreed or strongly agreed with the statements, "Viewing the night sky is important to me" and "The National Park Service ...
(Boston)--Patients with spinal stenosis (SS) experienced good short term benefit, lasting from weeks to months, after receiving epidural steroid injections (ESI).
These findings, which appear in a letter in the journal Pain Medicine, contradict a previously published New England Journal Medicine (NEJM) study that found epidural steroid injections were not helpful in spinal stenosis cases.
It has been one year since the publication of "A Randomized Trial of Epidural Glucocorticoid Steroid Injections for Spinal Stenosis." This was a large scale clinical trial evaluating ...
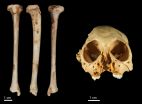
An international team of scientists have dated a species of fossil monkey found across the Caribbean to just over 1 million years old.
The discovery was made after the researchers recovered a fossil tibia (shin bone) belonging to the species of extinct monkey Antillothrix bernensis from an underwater cave in Altagracia Province, Dominican Republic. The fossil was embedded in a limestone rock that was dated using the Uranium-series technique.
In a paper published this week in the well renowned international journal, the Journal of Human Evolution, the team use three-dimensional ...
Tropical Storm Kevin's center was several hundred miles south-southwest of Baja California when NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and saw some associated high clouds streaming over the peninsula.
The MODIS and the AIRS instruments aboard Aqua captured visible and infrared images of Kevin on September 3 at 20:50 UTC (4:50 p.m. EDT). The visible image from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument provided look at Kevin's clouds. MODIS showed a somewhat elongated tropical storm with a fragmented band of thunderstorms wrapping into the low-level ...
Scientists studying how a heat-loving microbe transfers its DNA from one generation to the next say it could further our understanding of an extraordinary superbug.
Sulfolobus is part of the Archaea kingdom - a single-cell organism similar to bacteria - which was isolated in hot springs on the island of Hokkaido, Japan.
Some Archaea live ordinary lives in mundane environments such as lakes, seas and insect and mammal intestinal tracts, while others live extraordinary lives pushed to extremes in incredibly harsh habitats such as deep sea hydrothermal vents, volcanic ...
"Objects of granular media, such as a sandcastle, consist of millions or billions of grains. The computation time needed to produce photorealistic images amounts to hundreds to thousands of processor hours," Professor Carsten Dachsbacher of the Institute for Visualization and Data Analysis of KIT explains. Materials, such as sand, salt or sugar, consist of randomly oriented grains that are visible at a closer look only. Image synthesis, the so-called rendering, is very difficult, as the paths of millions of light rays through the grains have to be simulated. "In addition, ...
Nowadays, internet auctions play an important role in online trading. No matter whether you want to buy a hedge trimmer or an antique pocket watch - unlike purchases by a click at a fixed price, online auctions provide the atmosphere of a competition for the auction object. Whoever perceives the competition of real contenders, e.g. by avatars or photos on the screen, wishes to stay in the race - and increases his bid. This is a result of a KIT study with more than 450 test persons.
Online auctions combine shopping with entertainment, fun, and excitement. This is the ...
Action to prevent tooth decay in children, such as supervised tooth brushing and fluoride varnish schemes, are not just beneficial to children's oral health but could also result in cost savings to the NHS of hundreds of pounds per child, so says a leading dental health researcher.
Professor Elizabeth Kay, Foundation Dean of the Peninsula Dental School from Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, has carried out the first economic evaluation of public health measures to reduce tooth decay in children at high risk, in association with the National ...
When a jogger sets out on his evening run, the active movements of his arms and legs are accompanied by involuntary changes in the position of the head relative to the rest of the body. Yet the jogger does not experience feelings of dizziness like those induced in the passive riders of a rollercoaster, who have no control over the abrupt dips and swoops to which they are exposed. The reason for the difference lies in the vestibular organ (VO) located in the inner ear, which controls balance and posture. The VO senses ongoing self-motion and ensures that, while running, ...