(Press-News.org) Scientists have identified a gene - FOXC1 - that, if switched on, causes more aggressive cancer in a fifth of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) patients, according to a Cancer Research UK study* published in the journal Cancer Cell, today.
The FOXC1 gene is normally switched on during embryonic development and is needed to turn cells into specialised tissues, like the eyes, kidney, brain and bone.
But this new research found that in certain patients with AML - a type of blood cancer that affects white blood cells and the bone marrow - this gene was wrongly switched on inside the patient's cancer cells.
When it is switched on in blood cell tissue, FOXC1 stunts the development of blood cells and stops them maturing into normal specialised blood cells.
This triggers the cancer to be more aggressive, as young cells are able to replicate more than mature cells - causing cancer cells to grow faster and become more difficult to treat.
Around 2,900 people are diagnosed with AML each year in the UK. Of these, around 20 per cent would have had the FOXC1 gene wrongly switched on in their cancer.
Dr Tim Somervaille, lead author from the Cancer Research UK Manchester Institute at The University of Manchester, said: "This is an important finding which helps us understand how acute myeloid leukaemia develops and why some cases of AML are more aggressive than others. Here, instead of being faulty or mutated, this normal gene is turned on in the wrong place at the wrong time which makes the cancer grow more rapidly.
"There are certain situations where this gene is necessary, as in the development of the eye and skeleton before birth. But when it's switched on in the wrong tissue, it causes more aggressive forms of leukaemia."
Nell Barrie, senior science communication manager at Cancer Research UK, said: "It's essential that we continue to research basic biology to further understand how cells become cancerous. In this study, identifying a specific gene behind more aggressive forms of acute myeloid leukaemia could give clues for new ways to personalise treatments for select patients. The better we understand the nuts and bolts of each cancer, the sooner we can find new ways to stop it."
INFORMATION:
For more information on acute myeloid leukaemia visit our website or call our Cancer Research UK nurses on 0808 800 4040.
For media enquiries contact Stephanie McClellan in the Cancer Research UK press office on 020 3469 5314 or, out of hours, on 07050 264 059.
Notes to editor:
Somerville et al. Frequent derepression of the mesenchymal transcription factor gene FOXC1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell
This study was funded by Cancer Research UK with additional funding from the charity Bloodwise, which recently changed its name from Leukaemia & Lymphoma Research.
About Cancer Research UK
Cancer Research UK is the world's leading cancer charity dedicated to saving lives through research.
Cancer Research UK's pioneering work into the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cancer has helped save millions of lives.
Cancer Research UK receives no government funding for its life-saving research. Every step it makes towards beating cancer relies on every pound donated.
Cancer Research UK has been at the heart of the progress that has already seen survival in the UK double in the last forty years.
Today, 2 in 4 people survive their cancer for at least 10 years. Cancer Research UK's ambition is to accelerate progress so that 3 in 4 people will survive their cancer for at least 10 years within the next 20 years.
Cancer Research UK supports research into all aspects of cancer through the work of over 4,000 scientists, doctors and nurses.
Together with its partners and supporters, Cancer Research UK's vision is to bring forward the day when all cancers are cured.
For further information about Cancer Research UK's work or to find out how to support the charity, please call 0300 123 1022 or visit http://www.cancerresearchuk.org. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook.
(BOSTON) - Stem cell therapies are often limited by low survival of transplanted stem cells and the lack of precise control over their differentiation into the terminal cell types needed to repair or replace injured tissues. Now, a team led by Wyss Institute Core Faculty member David Mooney, Ph.D., has developed a new strategy - embedding stem cells into porous, transplantable hydrogels - that has experimentally improved bone repair by boosting the survival rate of transplanted stem cells and influencing their cell differentiation.
Mooney - who is also the Robert P. Pinkas ...
(Boston)--A panel of experts and researchers have developed a new classification system for gout, the most common form of inflammatory arthritis. This new system standardizes the classification of this condition using a variety of evidence-based criteria.
Led by a researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) and institutions from around the world, the study is a joint publication appearing in two journals simultaneously, Annals of Rheumatologic Disease and Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Gout is characterized by the deposition of a specific type of crystal in ...
GAINESVILLE, Fla. -- Larger and private colleges and universities seem to attract hookah cafes and lounges, but smoke-free policies decrease these odds, according to findings published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine this month.
That may bode well for the long-term health of college-age students.
Waterpipe smoking, more commonly known as hookah, boasts enticing flavors and a healthier reputation, increasing its popularity among college students. It is estimated that more than 10 percent of U.S. college students are current users.
However, recent evidence ...
MADISON, Wis. -- Hydrogen could be the ideal fuel: Whether used to make electricity in a fuel cell or burned to make heat, the only byproduct is water; there is no climate-altering carbon dioxide.
Like gasoline, hydrogen could also be used to store energy.
Hydrogen is usually produced by separating water with electrical power. And although the water supply is essentially limitless, a major roadblock to a future "hydrogen economy" is the need for platinum or other expensive noble metals in the water-splitting devices.
Noble metals resist oxidation and include many ...
Societies are failing women, children and adolescents, particularly in the poorest communities around the world, and urgent action is needed to save lives and improve health, say global health experts.
In a special supplement published today by The BMJ, public health experts from around the globe highlight the critical actions and investments that will have the greatest impact on the health and well-being of women, children and adolescents.
The 15 papers in this special supplement outline the current evidence, identify successes as well as critical gaps in progress, ...
Montreal, September 14, 2015 - Using extensive genetic data compiled by the UK10K project, an international team of researchers led by Dr. Brent Richards of the Lady Davis Institute at the Jewish General Hospital has identified a genetic variant near the gene EN1 as having the strongest effect on bone mineral density (BMD) and fracture identified to date. The findings are published in the forthcoming issue of the prestigious journal Nature.
"EN1 has never before been linked to osteoporosis in humans, so this opens up a brand new pathway to pursue in developing drugs to ...
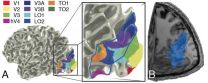
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- A study three years ago sparked a medical mystery when it revealed a part of the brain not found in any present-day anatomy textbooks.
Recently, Indiana University computational neuroscientist Franco Pestilli and an international research team published an article in the journal Cerebral Cortex that suggests this missing part of the brain may play an important role in how we understand the world -- despite getting "lost" for more than a century.
A long flat bundle of nerves called the vertical occipital fasciculus, or VOF, the structure appeared ...
Researchers at Cardiff University have devised a way of increasing the yield of biodiesel by using the waste left over from its production process.
Using simple catalysis, the researchers have been able to recycle a non-desired by-product produced when biodiesel is formed from vegetable oil, and convert this into an ingredient to produce even more biodiesel.
It is believed this new process will have significant environmental benefits by improving the yield of biodiesel in a sustainable way that doesn't require the use of additional fossil fuels, and could potentially ...
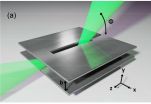
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Terahertz radiation could one day provide the backbone for wireless systems that can deliver data up to one hundred times faster than today's cellular or Wi-Fi networks. But there remain many technical challenges to be solved before terahertz wireless is ready for prime time.
Researchers from Brown University have taken a major step toward addressing one of those challenges. They've developed what they believe to be the first system for multiplexing terahertz waves. Multiplexers are devices that enable separate streams of data to ...
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- Vitamin D insufficiency among the elderly is highly correlated with accelerated cognitive decline and impaired performance, particularly in domains such as memory loss that are associated with Alzheimer's disease and dementia, researchers with the UC Davis Alzheimer's Disease Center and Rutgers University have found. The effect is "substantial," with individuals with low vitamin D declining at a rate three times faster than those with adequate vitamin D levels.
The researchers said their findings amplify the importance of identifying vitamin D ...