(Press-News.org) A team working with Roland Fischer, Professor of Inorganic and Metal-Organic Chemistry at the Technical University Munich (TUM) has developed a highly efficient supercapacitor. The basis of the energy storage device is a novel, powerful and also sustainable graphene hybrid material that has comparable performance data to currently utilized batteries.
Usually, energy storage is associated with batteries and accumulators that provide energy for electronic devices. However, in laptops, cameras, cellphones or vehicles, so-called supercapacitors are increasingly installed these days.
Unlike batteries they can quickly store large amounts of energy and put it out just as fast. If, for instance, a train brakes when entering the station, supercapacitors are storing the energy and provide it again when the train needs a lot of energy very quickly while starting up.
However, one problem with supercapacitors to date was their lack of energy density. While lithium accumulators reach an energy density of up to 265 Kilowatt hours (KW/h), supercapacitors thus far have only been delivering a tenth thereof.
Sustainable material provides high performance
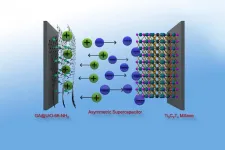
The team working with TUM chemist Roland Fischer has now developed a novel, powerful as well as sustainable graphene hybrid material for supercapacitors. It serves as the positive electrode in the energy storage device. The researchers are combining it with a proven negative electrode based on titan and carbon.
The new energy storage device does not only attain an energy density of up to 73 Wh/kg, which is roughly equivalent to the energy density of an nickel metal hydride battery, but also performs much better than most other supercapacitors at a power density of 16 kW/kg. The secret of the new supercapacitor is the combination of different materials - hence, chemists refer to the supercapacitor as "asymmetrical."
Hybrid materials: Nature is the role model
The researchers are betting on a new strategy to overcome the performance limits of standard materials - they utilize hybrid materials. "Nature is full of highly complex, evolutionarily optimized hybrid materials - bones and teeth are examples. Their mechanical properties, such as hardness and elasticity were optimized through the combination of various materials by nature," says Roland Fischer.
The abstract idea of combining basic materials was transferred to supercapacitors by the research team. As a basis, they used the novel positive electrode of the storage unit with chemically modified graphene and combined it with a nano-structured metal organic framework, a so-called MOF.
Powerful and stable
Decisive for the performance of graphene hybrids are on the one hand a large specific surface and controllable pore sizes and on the other hand a high electrical conductivity. "The high performance capabilities of the material is based on the combination of the microporous MOFs with the conductive graphene acid," explains first author Jayaramulu Kolleboyina, a former guest scientist working with Roland Fischer.
A large surface is important for good supercapacitors. It allows for the collection of a respectively large number of charge carriers within the material - this is the basic principle for the storage of electrical energy.
Through skillful material design, the researchers achieved the feat of linking the graphene acid with the MOFs. The resulting hybrid MOFs have a very large inner surface of up to 900 square meters per gram and are highly performant as positive electrodes in a supercapacitor.
Long stability
However, that is not the only advantage of the new material. To achieve a chemically stable hybrid, one needs strong chemical bonds between the components. The bonds are apparently the same as those between amino acids in proteins, according to Fischer: "In fact, we have connected the graphene acid with a MOF-amino acid, which creates a type of peptide bond."
The stable connection between the nano-structured components has huge advantages in terms of long term stability: The more stable the bonds, the more charging and discharging cycles are possible without significant performance impairment.
For comparison: A classic lithium accumulator has a useful life of around 5,000 cycles. The new cell developed by the TUM researchers retains close to 90 percent capacity even after 10,000 cycles.
International network of experts
Fischer emphasizes how important the unfettered international cooperation the researchers controlled themselves was when it came to the development of the new supercapacitor. Accordingly, Jayaramulu Kolleboyina built the team. He was a guest scientist from India invited by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation and who by now is the head of the chemistry department at the newly established Indian Institute of Technology in Jammu.
"Our team also networked with electro-chemistry and battery research experts in Barcelona as well as graphene derivate experts from the Czech Republic," reports Fischer. "Furthermore, we have integrated partners from the USA and Australia. This wonderful, international co-operation promises much for the future."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) within the cluster of excellence e-conversion, the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, the Indian Institute of Technology Jammu, the Queensland University of Technology and the Australian Research Council (ARC). Further funding came from the European Regional Development Fund provided by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic.
Publication:
Jayaramulu Kolleboyina, Michael Horn, Andreas Schneemann, Aristides Bakandritsos, Vaclav Ranc, Martin Petr, Vitalie Stavila, Chandrabhas Narayana, B?a?ej Scheibe, Št?pán Kment, Michal Otyepka, Nunzio Motta, Deepak Dubal, Radek Zboril und Roland A. Fischer
Covalent Graphene-MOF Hybrids for High Performance Asymmetric Supercapacitors
Advanced Materials, 4.12.2020 - DOI: 10.1002/adma.202004560
Forgive Asiatic black bear if they're not impressed with their popular giant panda neighbors.
For decades, conservationists have preached that panda popularity, and the resulting support for their habitat, automatically benefits other animals in the mountainous ranges. That logic extends across the world, as animals regarded as cute, noble or otherwise appealing drum up support to protect where they live.
Yet in Biological Conservation, scientists take a closer look at how other animals under the panda "umbrella" fare and find several species have every reason to be ticked at panda-centric ...
HOUSTON -- Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have discovered that a protein called NF-kappa B-inducing kinase (NIK) is essential for the shift in metabolic activity that occurs with T cell activation, making it a critical factor in regulating the anti-tumor immune response.
The preclinical research, published today in Nature Immunology, suggests that elevating NIK activity in T cells may be a promising strategy to enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapy, including adoptive cellular therapies and immune checkpoint blockade.
In a preclinical melanoma model, the researchers evaluated melanoma-specific T cells engineered to express higher levels of NIK. Compared to controls, ...
HOUSTON -- Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center who profiled more than 45,000 individual cells from patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis (PC), a specific form of metastatic gastric cancer, defined the extensive cellular heterogeneity and identified two distinct subtypes correlated with patient survival.
Based on their findings, published today in Nature Medicine, the researchers developed and validated a gene expression signature capable of predicting patient survival better than other clinical features. If validated in prospective studies, this tool may be useful in stratifying ...
EUGENE, Ore. -- Jan. 4, 2021 -- Phosphorous, calcium and charcoal in spotty patches of fertile soil in the Amazon rainforest suggest that natural processes such as fires and river flooding, not the ingenuity of indigenous populations, created rare sites suitable for agriculture, according to new research.
The presence of pre-Columbian artifacts and signs of plant domestication uncovered in the region's fertile soil, commonly called Amazonian dark earth, had been thought to mean that agricultural practices, including controlled burning, by indigenous people had boosted soil nutrients.
However, radiocarbon dating ...
What The Study Did: Denmark was one of the first countries to enforce lockdown to reduce the spread of COVID-19 and subsequent gradual reopening, whereas Sweden has had few restrictions, largely limited to public recommendations. Researchers assessed public mobility and social media attention associated with COVID-19 spread and societal interventions from February to June in Denmark and Sweden.
Authors: Isabell Brikell, Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
What The Study Did: Researchers used health insurance data from Taiwan to investigate the risk of substance use disorder among patients with autism spectrum disorder and its associations with risk of death.
Authors: Chih-Sung Liang, M.D., of the National Defense Medical Center, and Mu-Hong Chen, M.D., Ph.D., of the Taipei Veterans General Hospital in Taipei, Taiwan, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.5371)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
Bitterling fishes (Subfamily: Acheilognathinae) spawn in the gills of living freshwater mussels obligately depending on the mussels for reproduction. On the Matsuyama Plain, Japan, populations of unionid mussels--Pronodularia japanensis, Nodularia douglasiae, and Sinanodonta lauta--have decreased rapidly over the past 30 years. Simultaneously, the population of a native bitterling fish, Tanakia lanceolata, which depends on the three unionids as a breeding substrate, has decreased. Furthermore, a congeneric bitterling, Tanakia limbata, has been artificially introduced, and hybridisation and genetic introgression occur between them. Here, we surveyed the reproduction and occurrence of hybridisation between native and invasive species ...
Improving solar cell design is integral for improving energy consumption. Scientists have lately focused on making solar cells more efficient, flexible, and portable to enable their integration into everyday applications. Consequently, novel lightweight and flexible thin film solar cells have been developed. It is, however, not easy to combine efficiency with flexibility. For a material (usually a semiconductor) to be efficient, it must have a small "band gap"--the energy required to excite charge carriers for electrical conduction--and should absorb and convert a large portion of the sunlight into electricity. Till date, no such efficient absorber suitable for thin film solar cells has been developed.
Typically, charge carriers in a semiconductor are ...
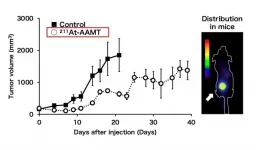
Osaka, Japan - A cancer-specific L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) is highly expressed in cancer tissues. Inhibiting the function of LAT1 has been known to have anti-tumor effects, but there has been limited progress in the development of radionuclide therapy agents targeting LAT1. Now, a multidisciplinary research team at Osaka University has established a targeted alpha-therapy with a novel drug targeting LAT1.
The researchers first produced the alpha-ray emitter 211Astatine, no easy task given that Astatine (At) is the rarest naturally occurring element on Earth. Targeted alpha-therapy selectively delivers α-emitters to tumors; the advantage over conventional β-therapy is that alpha ...
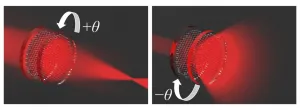
The odd, wavy pattern that results from viewing certain phone or computer screens through polarized glasses has led researchers to take a step toward thinner, lighter-weight lenses. Called moiré, the pattern is made by laying one material with opaque and translucent parts at an angle over another material of similar contrast.
A team of researchers from Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, TUAT, in Japan have demonstrated that moiré metalenses--tiny, patterned lenses composed of artificial "meta" atoms--can tune focal length along a wider range than previously seen. They published their results on November ...