(Press-News.org) SYRACUSE, N.Y. - There's no doubt the Earth's temperatures are going up. According to a December report by the World Meteorological Organization, 2020 is on track to be one of the three hottest years on record, already within the warmest decade to date. During the year's hottest months, many people rely on electricity-generated cooling systems to remain comfortable. But the power plants that keep air conditioners pushing out cold air could soon be in a vicious cycle in a warming world-not able to keep up with growing demands on hotter days and driving up greenhouse gas emissions to dangerous levels.
Ethan Coffel, assistant professor of geography and the environment in the Maxwell School, explores this power and climate struggle in the research paper, "Thermal power generation is disadvantaged in a thermal world." The work published in the scientific journal Environmental Research Letters. Professor Coffel answered five questions about the new findings and how warming temperatures will impact every part of our power infrastructure.
Q: Can you describe your research?
A: We show that the thermal power plants that currently generate most of our electricity are already having to reduce their electricity output on hot days due to cooling limitations. On the hottest days, power plant capacity can be reduced by more than 10 percent because the air and water that are used to cool the plants is too warm. This lost generation capacity is a problem because these hot days are when electricity is most needed to run air conditioners.
As global warming makes heat waves more frequent, intense and long, the negative effects of heat on power plants will become more pronounced. With 2 degrees Celsius of global warming-the upper target agreed to in the 2015 Paris Accord-power plant outages on hot days could nearly double from today's level.
Q: In conducting your research, in what ways or specific examples did you find climate change impacting human systems?
A: Our work demonstrates a harmful interaction between human adaptation and infrastructure vulnerability in a warming world. As hot days become more frequent, more people will want air conditioners to protect themselves from unpleasant and dangerous heat. But, these air conditioners need electricity, which further increases the greenhouse gas emissions that drive global warming! And further, more A/C will increase electricity demand at the same time as heat is reducing the output of power plants, potentially straining the electricity grid in some places.
Q: What does your research reveal or uncover about future global electricity production?
A: We find that thermal power generation will be disadvantaged in a warmer world. By the middle of the century, we find that 100-200 additional average-sized global power plants could be required to make up for the electricity generation capacity lost due to heat. Transitioning the electricity sector to renewables-especially wind and solar-will not only reduce the greenhouse gas emissions that cause climate change, but will also reduce the negative impacts of global warming on our power infrastructure.
Q: So much attention is put on governments, companies, cities, etc. and their contributions to global warming. Are there smaller things individuals and families can and should focus on?
A: While individual steps are no substitute for strong national policy action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, there are many things individuals can do, both large and small. Some big steps people can take are installing solar panels on their homes, replacing gas or oil furnaces with electric heat pumps, replacing an old vehicle with an electric car, or replacing a gas stove with an electric model. These infrastructure investments can significantly reduce someone's individual emissions (and keep those emissions low for years to come).
Smaller steps include flying just a bit less, driving a bit less or eating a bit less meat. These individual actions are important because they encourage others around you to take climate-friendly steps to reduce their emissions too.
Q: What should policymakers be doing now to prepare for warming threats and its impact to our electricity supply? What options would you suggest?
A: To meet the Paris Accord target of 1.5-2 degrees Celsius of global warming, global greenhouse gas emissions need to reach net zero by mid-century. Achieving this goal would require extremely large investments in renewable energy, electric vehicles and changes to land management. These changes are starting to happen, but not nearly fast enough.
We are very fortunate that major progress has been made to reduce the cost of wind and solar power-these zero-carbon electricity sources are now often cheaper than fossil fuels. So making the transition away from coal, oil and gas not only makes climate sense, but also economic sense. However, we are already feeling the impacts of global warming.
Governments should be preparing for the large increases in electricity demand that will come with increased temperatures and A/C use, and ensuring that electricity supplies are sufficient to meet this rising power demand, even after accounting for the reduced power output of thermal power plants on hot days.
INFORMATION:
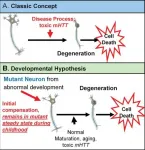
Amsterdam, NL, January 6, 2021 - There is growing evidence to support the hypothesis that there is a neurodevelopmental component to the late-onset neurodegeneration occurring in the brain of huntingtin gene (HTT gene) mutation carriers, and that this increased susceptibility to brain cell death begins during childhood. Experts discuss the evidence that the HTT gene mutation affects brain and body growth based on a unique study of children at risk for HD, the Kids-HD study, in a review paper and accompanying research article published in the Journal of Huntington's Disease.
The classic concept is that Huntington's disease is caused by toxic mutant huntingtin (mHTT) acting over time on mature brain cells. However, there is growing evidence for an alternative ...
Engineers at the University of Maryland (UMD) have created a new shape-changing or "morphing" 3D printing nozzle that was featured as a Frontispiece in the January 5th issue of the journal Advanced Materials Technologies.
The team's morphing nozzle offers researchers new means for 3D printing "fiber-filled composites" - materials made up of short fibers that boost special properties over traditional 3D-printed parts, such as enhancing part strength or electrical conductivity. The challenge is that these properties are based on the directions or "orientations" of the short fibers, which has been difficult to control during the 3D printing process, until now.
"When 3D printing with the morphing nozzle, the power lies on ...
A survey of approximately 5,000 Americans suggests that 31.1 percent of the U.S. public does not intend to get the COVID-19 vaccine once it becomes available to them - and the likelihood of vaccine refusal is highest among Black Americans, women and conservatives.
Timothy Callaghan, assistant professor at the Texas A&M University School of Public Health, led the study with the aim of better understanding the intentions of the American public regarding vaccines. The results were recently published in Social Science and Medicine.
According to the study, survey respondents answered a series of questions about their behaviors and attitudes about COVID-19, including why or why not they intend to pursue vaccination. Women are 71 percent ...
In a paper published by the journal Matter, engineers from the University of Surrey together with partners from Harvard University, University of Science and Technology of China, UK National Physical Laboratory, George Washington University and Zhejiang University Ningbo Research Institute report on how they have developed a breakthrough sensor system and manufacturing process.
The global team of engineers reveal that the new contact lens sensor system contains a photodetector for receiving optical information, a temperature sensor for diagnosing potential corneal disease and a glucose sensor ...
Musical masterworks as the Queen of the Night's Aria from Mozart's The Magic Flute, are examples of the sounds trained human voices can produce. The precondition for vocal virtuosity as well as for any spoken word is vocal learning, the ability to imitate auditory input. Some songbirds and bats can do this, but humans excel. We can acquire new languages into old age. To shed light on the evolution of vocal learning, a team led by Julia Fischer from the German Primate Center (DPZ) - Leibniz Institute for Primate Research has analyzed the sound structures of Guinea baboons and was ...
CLEVELAND - In a new paper, researchers describe their development of a near-real time spatial assessment of COVID-19 cases to help guide local medical responses to clusters of outbreaks of the virus at the local level.
The paper, entitled "Geographic monitoring for early disease detection (GeoMEDD)," appeared in the Dec. 10 issue of Nature Scientific Reports and comes from researchers at Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) School of Medicine, University Hospitals (UH) Cleveland Medical Center, and Texas A & M University.
While developing a tracking system during the beginning stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, ...
A first-of-its-kind study conducted under the bed of the Dead Sea reveals that a devastating earthquake measuring 6.5 on the Richter scale is expected to hit our region in the coming years. The study showed that an earthquake of this magnitude occurs in the land of Israel on an average cycle of between 130 and 150 years, but there have been cases in history where the lull between one earthquake and another was only a few decades long.
The last earthquake with a magnitude of 6.5 on the Richter scale was felt in the Dead Sea valley in 1927, when hundreds of people were injured in Amman, Jerusalem, Bethlehem and even Jaffa. Now, in the wake of the findings ...
A microbe found in the colon and commonly associated with the development of colitis and colon cancer also may play a role in the development of some breast cancers, according to new research from investigators with the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and its Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy. Breast tissue cells exposed to this toxin retain a long-term memory, increasing the risk for disease.
In a series of laboratory experiments, researchers discovered that when enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis (ETBF) was introduced to the guts or breast ducts of mice, it always induced growth and metastatic progression of tumor cells. A description of the work is published in the January 6 issue of the journal Cancer Discovery.
While microbes are known to be present in ...
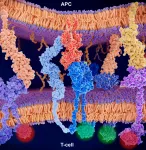
DALLAS - Jan. 6, 2020 - UT Southwestern scientists have developed a new method to study the molecular characteristics of T cells, critical immune cells that recognize and attack invaders in the body such as viruses, bacteria, and cancer.
The approach, described today in the journal Nature Methods, enables researchers to more easily analyze the roles of T cell receptors (TCRs) - the molecules on the surfaces of T cells that are responsible for recognizing pathogens.
"This could lead to a better understanding of how T cells work as well as new ways to harness T cells to fight disease," ...
Philadelphia, January 6, 2021 - A multidisciplinary team of researchers led by Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) has discovered several genetic markers associated with bone mineral accrual, which could ultimately help identify causes of eventual osteoporosis earlier in life through genetic testing. The findings, which were made possible by following a group of children over several years, were published online by the journal Genome Biology.
Osteoporosis is widely considered a disease of old age. However, the accrual of bone density early in life is critical for achieving optimal bone mass in adulthood ...