Machine-learning models of matter beyond interatomic potentials
2021-01-07
(Press-News.org) Combining electronic structure calculations and machine learning (ML) techniques has become a common approach in the atomistic modelling of matter. Using the two techniques together has allowed researchers, for instance, to create models that use atomic coordinates as the only inputs to inexpensively predict any property that can be computed by the first-principles calculations that had been used to train them.
While the earliest and by now most advanced efforts have focused on using predictions of total energies and atomic forces to construct interatomic potentials, more recent efforts have targeted additional properties of crystals and molecules such as ionization energies, NMR chemical shieldings, dielectric response properties and charge density. In the paper "Learning the electronic density of states in condensed matter," Ceriotti and colleagues focus on the electronic density of states (DOS), another quantity that underlies many useful materials properties, some of which can be observed experimentally.
The DOS is essentially the number of different states that electrons can occupy at a particular energy level and can be used, for instance, to calculate the electronic contribution to heat capacity in metals and the density of free charge carriers in semiconductors. It is an indirect proxy for properties such as the energy band gap, the band energy and the optical absorption spectrum.
"Predicting the DOS is an interesting exercise in itself because it is essentially the simplest possible description of the electronic structure beyond the ground state picture," Ceriotti said. "It's also useful because there are many properties that you can compute starting from the DOS, making it a great example of how the next generation of ML models can be used in a similar way as electronic structure calculations, using them in an indirect way to compute intermediate quantities that can then be easily processed to evaluate properties that are harder to learn directly."
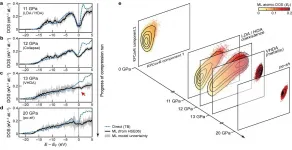
In developing the model, the group looked to assure transferability across different phases as well as scalability to large system sizes. Their ultimate approach, which looks at how different atomic configurations affect the distribution of energy levels, meets these goals--it was able to learn and predict DFT-computed DOS for a diverse data set of silicon structures, covering a broad range of thermodynamic conditions and different phases. It also scales linearly, rather than with the cube of the number of atoms as with electronic structure calculations, making it applicable to large structures. Finally, the model allowed for an analysis of the local DOS, giving researchers the chance to examine the interplay between structural motifs and electronic structure.
The combination of transferability, and scalability of predictions to large system sizes, make the model applicable to address long-standing open questions in materials science. The new framework has already been used to elucidate the electronic properties of a 100'000-atoms simulation of amorphous silicon, undergoing a series of phase transitions when compressed to 20 Gpa, in a paper published in Nature today in collaboration with a team comprising researchers from Oxford, Cambridge, the US Naval Research Laboratory and Ohio University. The predicted DOS is also used to explain how the pressure-induced structural transformations couple to the electronic structure of the material.
Combining the new model with one of the well-established potential energy models also makes it possible to compute the electronic contributions to macroscopic properties such as the heat capacity of metals and to perform simulations that take into account finite-electronic-temperature effects - as demonstrated in another soon-to-be published article discussing the high-temperature properties of nickel. Indeed, the new model is a critical step towards MARVEL's goal of developing integrated machine learning models that augment - and perhaps eventually replace - costly electronic structure calculations.
"There are other properties aside from the electron density of states, such as optical excitations, and NMR response, which we have been able to accurately predict with machine learning." Ceriotti said. "If we can use them all in combination with cheap and accurate interatomic potentials it will allow us to describe all of the properties of materials with the same accuracy achieved with electronic structure calculation, but at a tiny fraction of the cost."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-07
It is during rare merging events that galaxies undergo dramatic changes in their appearance and in their stellar content. These systems are excellent laboratories to trace the formation of star clusters under extreme physical conditions.
The Milky Way typically forms star clusters with masses that are 10 thousand times the mass of our Sun. This doesn't compare to the masses of the star clusters forming in colliding galaxies, which can reach millions of times the mass of our Sun.
These dense stellar systems are also very luminous. Even after the collision, when the resulting galactic system begins to fade into a more quiescent phase, these very massive star clusters will shine throughout their host galaxy, as long-lasting witnesses of past merging events.
By studying the six galaxy ...
2021-01-07
Autoimmune diseases are diseases of "mistaken identity", where the immune system - which is supposed to protect us against infectious diseases and neoplasias - mistakenly attacks and destroys components of our own body. The incidence of autoimmune diseases is increasing on a worldwide basis, and these diseases - including type 1 diabetes (T1D), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis (MS) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) - now affect up to 5% of the population in different regions. There is no cure for autoimmune diseases, and while the immune target of T1D, SLE, MS, and RA are distinct, they share several similar elements, including up to 50% common genetic risk, chronic local inflammation and mechanisms ...
2021-01-07
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg now suggest a possible cure for children with hard-to-treat forms of neuroblastoma using a new combination of drugs. In a new study in the journal Cancer Research, they describe how a two small molecule-based drug combination likely inhibit the tumor's growth.
Neuroblastoma is the most common form of childhood cancer, derived from the peripheral nervous system, i.e., the part of the nervous system that is not the brain or spinal cord. The disease can occur in the chest, neck, abdomen and adrenal glands and can also spread to the spine. Symptoms include general aches, anemia and skeletal pain.
The ...
2021-01-07
Stomach cancer, or gastric cancer, is a common gastrointestinal malignancy. Peritoneal metastasis occurs in a majority of patients with advanced stomach cancer and is considered as an aggressive disease with poor outcomes.
Patients with peritoneal metastasis are typically not eligible for curative surgery. Therefore, preoperative detection and diagnosis of peritoneal metastasis are critical to inform treatment decision-making and avoid unnecessary surgery.
A new study published in the JAMA Network Open on Jan. 5 shows that deep learning can help predicting the occult peritoneal metastasis in stomach cancer. It provides a novel and noninvasive approach for ...
2021-01-07
Olduvai (now Oldupai) Gorge, known as the Cradle of Humankind, is a UNESCO World Heritage site in Tanzania, made famous by Louis and Mary Leakey. New interdisciplinary field work has led to the discovery of the oldest archaeological site in Oldupai Gorge as reported in Nature Communications, which shows that early human used a wide diversity of habitats amidst environmental changes across a 200,000 year-long period.
Located in the heart of eastern Africa, the Rift System is a prime region for human origins research, boasting extraordinary records of extinct human species and environmental records spanning several million years. For more than a century, archaeologists and human palaeontologists have been exploring the East African Rift outcrops and unearthing hominin fossils in surveys ...
2021-01-07
New research by scientists at the University of Bristol explains how a 'stop-start' pattern of evolution, governed by environmental change, could explain why crocodiles have changed so little since the age of the dinosaurs.
Crocodiles today look very similar to ones from the Jurassic period some 200 million years ago. There are also very few species alive today - just 25. Other animals such as lizards and birds have achieved a diversity of many thousands of species in the same amount of time or less.
Prehistory also saw types of crocodile we don't see today, including giants as big as dinosaurs, plant-eaters, fast ...
2021-01-07
Scientists at the University of Birmingham, UK, have shown that a novel low molecular weight dextran-sulphate, ILB® could play a key role in treating open angle glaucoma (OAG), a neurodegenerative disease that affects over 70 million people worldwide and causes irreversible blindness.
OAG develops slowly over many years. Excessive matrix deposition (fibrosis) within the eye's main fluid drainage site can lead to increased intraocular pressure (IOP), resulting in damage to the optic nerve.1
The research, reported in npj Regenerative Medicine, has ...
2021-01-07
The North Sea is a heavily trafficked area, with major shipping routes crossing its waters, and fisheries, offshore oil rigs, and wind farms populating its waves. All this activity inevitably has an effect on marine wildlife, and scientists are particularly interested in how the harbor porpoise population has fared in the face of such disturbances.
The harbor porpoise is known as a "sentinel species" - animals which indicate the health of an ecosystem and point to potential risks (think of the canary in the coal mine). According to a recent study published in Frontiers ...
2021-01-07
A new study in the Oxford Economic Papers finds that migration flows the last 500 years from high sunlight regions to low sunlight regions influence contemporary health outcomes in destination countries.
The researchers here noted that people's ability to synthesize vitamin D from sunlight declines with skin pigmentation, and that vitamin D deficiency is directly associated with higher risk of mortality, from illnesses including cardiovascular disease, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers. Recent research even .finds that vitamin D affects the severity of COVID-19.
Researchers here focused on ...
2021-01-07
Sophia Antipolis, 7 January 2021: Patients with acute heart failure nearly double their risk of dying if they get COVID-19, according to research published today in ESC Heart Failure, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 The small, single centre study highlights the need for patients with heart failure to take extra precautions to avoid catching COVID-19.
"Our results support prioritising heart failure patients for COVID-19 vaccination once it is available," said study lead investigator Dr. Amardeep Dastidar, a consultant interventional cardiologist at North Bristol NHS Trust and Bristol Heart Institute, UK. "In the meantime, heart failure patients of all ages should ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Machine-learning models of matter beyond interatomic potentials