NYUAD scientists uncover the genomic differences of marine and freshwater microalgae
2021-01-11
(Press-News.org) Fast facts:
This study describes essential differences between marine and freshwater species and the contributions of viruses to such differences
The results may help guide future bioengineering efforts to develop plant strains adapted to grow in salt-water, which is of local and regional food security interest
Microalgae are fundamental to global ecosystems due to their ability to sustain coral reef species and produce atmospheric oxygen
Before this study, many important algal phyla did not have sequenced representatives
Viruses have contributed to the evolution of algae and their genome makeups
Abu Dhabi, UAE, January 11, 2021: NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) Associate Professor of Biology Kourosh Salehi-Ashtiani and NYUAD Senior Research Scientist David Nelson report in a new study that they have successfully cultured and sequenced 107 microalgae species from 11 different phyla indigenous to varied locations and climates to gain insights on genomic differences in saltwater and freshwater microalgae. The researchers have also discovered that these algae genomes show widespread widespread viral-origin gene content.
In the paper titled Large-scale genome sequencing reveals the driving forces of viruses in microalgal evolution , published in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, the researchers present the whole-genome sequencing of 107 different species of microalgae from a broad range of evolutionary groups. In addition to these newly-sequenced algal genomes, microalgal genomes from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) were included to investigate genomic differences between microalgae from a more extensive variety of habitats, specifically salt-water (marine) and fresh-water. The comparison of genomes led to the conclusion that freshwater and marine species had fundamental differences in their nuclear and cellular membranes. Additionally, marine species contained significantly more viral-origin genes in their genomes.
The paper describes differences in marine and freshwater algae to better understand how organisms deal with salt-water. These results may help guide future bioengineering efforts to develop plant strains adapted to grow in salt-water, which is of local and regional food security interest. The discovery of viral families in marine algae species shows that many genes were shared between viruses and algae in the past, likely due to viral infections, and retained by the algae to help them deal with habitat-specific challenges. These findings provide new perspectives on the positive contributions that viruses can make to the evolution of organisms they infect.
"The discovery that genes containing mainly membrane and viral proteins were shared among marine microalgae from different lineages indicates their importance for the maintenance of membrane integrity in a saline environment," said Salehi-Ashtiani. "This brand-new genomic information can guide the development of bio-saline agriculture in regions where the water has a high salinity."
"Recent studies have shown that viruses frequently acquire host genes. Here, we show that the reverse has occurred repeatedly throughout algal evolution. Viruses appear to be a major driving force in microalgal evolution through widespread gene donation to diverse lineages," said Nelson.
Salehi-Ashtiani and Nelson point out that the discoveries from the genomic sequencing of microalgae species have shown that environmental sources of viruses should be more seriously considered and evaluated to anticipate future potential public health crises.
INFORMATION:
About NYU Abu Dhabi
NYU Abu Dhabi is the first comprehensive liberal arts and science campus in the Middle East to be operated abroad by a major American research university. NYU Abu Dhabi has integrated a highly-selective liberal arts, engineering, and science curriculum with a global advanced research and scholarship center, enabling its students to succeed in an increasingly interdependent world and advance cooperation and progress on humanity's shared challenges. NYU Abu Dhabi's high-achieving students have come from more than 115 nations and speak over 115 languages. Together, NYU's campuses in New York, Abu Dhabi, and Shanghai form the backbone of a unique global university, giving faculty and students opportunities to experience varied learning environments and immersion in other cultures at one or more of the numerous study-abroad sites NYU maintains on six continents.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-11
It is well known that the expansion of the universe is accelerating due to a mysterious dark energy. Within galaxies, stars also experience an acceleration, though this is due to some combination of dark matter and the stellar density. In a new study to be published in Astrophysical Journal Letters researchers have now obtained the first direct measurement of the average acceleration taking place within our home galaxy, the Milky Way. Led by Sukanya Chakrabarti at the Institute for Advanced Study with collaborators from Rochester Institute of Technology, University of Rochester, and ...
2021-01-11
Moms are not more likely than other women to support gun control efforts. In fact, a new study finds that parenthood doesn't have a substantial effect on the gun control views of men or women.
"Everybody 'knows' that moms are more politically liberal on gun control issues," says Steven Greene, corresponding author of the study and a professor of political science at North Carolina State University. "We wanted to know if that's actually true. And, as it turns out, it's not true - which was surprising."
To explore the impact of parenthood on people's gun control views, the researchers drew on data collected by the Pew Center for Research in 2017 as part of Pew's nationally ...
2021-01-11
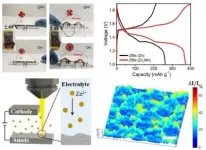
Lithium-ion batteries are critical for modern life, from powering our laptops and cell phones to those new holiday toys. But there is a safety risk - the batteries can catch fire.
Zinc-based aqueous batteries avoid the fire hazard by using a water-based electrolyte instead of the conventional chemical solvent. However, uncontrolled dendrite growth limits their ability to provide the high performance and long life needed for practical applications.
Now researchers have reported in Nature Communications that a new 3D zinc-manganese nano-alloy anode has overcome the limitations, resulting in a stable, high-performance, dendrite-free aqueous battery using seawater ...
2021-01-11
In diseases characterized by bone loss -such as periodontitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoporosis- there is a lot that scientists still don't understand. What is the role of the immune response in the process? What happens to the regulatory mechanisms that protect bone?
In a paper published recently in Scientific Reports, researchers from the Forsyth Institute and the Universidad de Chile describe a mechanism that unlocks a piece of the puzzle. Looking at periodontal disease in a mouse model, scientists found that a specific type of T cell, known as regulatory T cells, start behaving in unexpected ways. These cells lose their ability to regulate bone ...
2021-01-11
WASHINGTON -- As LEDs replace traditional lighting systems, they bring more smart capabilities to everyday lighting. While you might use your smartphone to dim LED lighting at home, researchers have taken this further by tapping into dynamically controlled LEDs to create a simple illumination system for 3D imaging.
"Current video surveillance systems such as the ones used for public transport rely on cameras that provide only 2D information," said Emma Le Francois, a doctoral student in the research group led by Martin Dawson, Johannes Herrnsdorf and Michael Strain at the University of Strathclyde in the ...
2021-01-11
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Scientists have known for years that mutations in the MLL4 gene can cause Kabuki syndrome, a rare developmental disorder.
But a study published on Jan. 11 in Nature Communications illuminates new details regarding how this occurs. (Images are available by contacting Charlotte Hsu in UB Media Relations at chsu22@buffalo.edu.)
The research suggests that MLL4 controls the production of neurons that secrete growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) in a part of the brain called the hypothalamus. Mice without working copies of the MLL4 gene in this area had stunted growth and markedly fewer GHRH neurons. Mice with only one functioning ...
2021-01-11
CLEVELAND - As reported in Nature Communications, researchers from Cleveland Clinic's Lerner Research Institute have developed a novel, patient-derived model of ulcerative colitis, which will help advance studies into new treatments for the chronic inflammatory bowel disease.
The team used the model to identify a promising target that could be inhibited to slow disease progression.
Ulcerative colitis is characterized by abnormal reactions of the immune system that lead to inflammation and ulcers on the inner lining of the large intestines. It is a highly heterogeneous condition, both in terms of patients' symptoms and disease pathology.
Suppressing the overactive immune response with anti-inflammatory drugs is the current ...
2021-01-11
Use of telehealth jumped sharply during the first months of the coronavirus pandemic shutdown, with the approach being used more often for behavioral health services than for medical care, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Between mid-March and early May 2020, telehealth was used by more than 40% of patients with a chronic physical health condition and by more than 50% of those with a behavioral health condition, according to findings published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
Overall, almost half of the people who were undergoing treatment when the pandemic shutdown ...
2021-01-11
In countries with a severe shortage of surgeons it is common for some operations to be carried out by medical staff with lower formal qualifications. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet, Sweden, have led an international study on the safety and efficacy of a common surgical procedure. The study, published in
JAMA Network Open, shows that inguinal hernia operations performed by associate clinicians at a hospital in Sierra Leone were just as safe and effective as those performed by doctors.
Many Sub-Saharan countries have a desperate shortage of surgeons, and to ensure that as many patients as possible can be treated, some operations are carried out by medical professionals who are not specialists in surgery. Such task sharing is supported by several bodies, including the World Health ...
2021-01-11
Would you like to capture a chemical transformation inside a cell live? Or maybe revolutionize microchips' production by printing paths in a layer that has a thickness of just 100 nanometers? These and many other goals can now be achieved with the latest femtosecond laser created by a team of scientists led by Dr. Yuriy Stepanenko.
These days, there is a multitude of laser light sources. They each have their characteristics and different applications, such as observing stars, treating illnesses, and surface micro-machining. "Our goal is to develop new ones," says Yuriy Stepanenko, head of the team of Ultrafast Laser Techniques at the Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences. "We deal with sources that produce ultrashort pulses of light. Really very, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NYUAD scientists uncover the genomic differences of marine and freshwater microalgae