NIH scientists study salmonella swimming behavior as clues to infection
2021-01-13
(Press-News.org) WHAT:
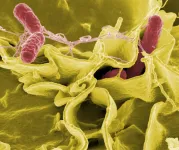
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium bacteria (S. Typhimurium) commonly cause human gastroenteritis, inflammation of the lining of the intestines. The bacteria live inside the gut and can infect the epithelial cells that line its surface. Many studies have shown that Salmonella use a "run-and-tumble" method of short swimming periods (runs) punctuated by tumbles when they randomly change direction, but how they move within the gut is not well understood.
National Institutes of Health scientists and their colleagues believe they have identified a S. Typhimurium protein, McpC (Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein C), that allows the bacteria to swim straight when they are ready to infect cells. This new study, published in Nature Communications, describes S. Typhimurium movement and shows that McpC is required for the bacteria to invade surface epithelial cells in the gut.
The study authors suggest that McpC is a potential target for developing new antibacterial treatments to hinder the ability of S. Typhimurium to infect intestinal epithelial cells and colonize the gut. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases scientists at Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, led the study. Collaborators included groups from the University of Texas A&M campuses in College Station and Kingsville.
S. Typhimurium use flagella--long whip-like projections--to move through fluids. When the flagella rotate counterclockwise, they form a rotating bundle behind the bacteria and propel them forward. However, the flagella frequently switch rotation from counterclockwise to clockwise, disrupting the bundle and causing the bacteria to tumble and change direction. Using special microscopes and cameras to observe live S. Typhimurium, the scientists found that bacteria grown under conditions that activate their invasive behavior swam in longer straight runs because the flagella did not switch rotation from counterclockwise to clockwise. Bacteria lacking McpC still demonstrated the "run-and-tumble" method of swimming under these conditions and had an invasion defect in a calf intestine model, indicating that straight swimming is important for efficient invasion of intestinal epithelial cells.
The researchers hypothesize that controlled smooth swimming could be a widespread bacterial infection strategy. Similar smooth swimming behavior can be seen in unrelated enteric bacteria, such as Vibrio, which can cause infection when undercooked seafood is eaten. These findings may inform the development of novel antibiotics.
INFORMATION:
ARTICLE:
K Cooper et al. Regulatory protein HilD stimulates Salmonella Typhimurium invasiveness by promoting smooth swimming via the methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein McpC. Nature Communications DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20558-6 (2021).
WHO:
Olivia Steele-Mortimer, Ph.D., chief of NIAID's Salmonella-Host Cell Interactions Section, and Kendal G. Cooper, Ph.D., in the Salmonella-Host Cell Interactions Section, are available to comment.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact Ken Pekoc,
(301) 402-1663,
kpekoc@niaid.nih.gov.
NIAID conducts and supports research--at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide--to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov/.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-13
Research into the neuronal basis of emotion processing has so far mostly taken place in the laboratory, i.e. in unrealistic conditions. Bochum-based biopsychologists have now studied couples in more natural conditions. Using electroencephalography (EEG), they recorded the brain activity of romantic couples at home while they cuddled, kissed or talked about happy memories together. The results confirmed the theory that positive emotions are mainly processed in the left half of the brain.
A group led by Dr. Julian Packheiser, Gesa Berretz, Celine Bahr, Lynn Schockenhoff and Professor Sebastian Ocklenburg from the Department of Biopsychology at Ruhr-Universität Bochum ...
2021-01-13
(Boston)--Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) provide a new genomics resource that details the small RNA transcriptomes (gene expression) of four bio-medically important mosquito species.
This is the first study to provide a platform for biologists to compare the characteristics of these small RNAs between these four mosquitoes as well as the most widely used insects for genetic experiments, the fruit fly, Drosophila. Although previous studies looked at each of the individual mosquito species separately, this study is the first to allow comparisons between all four species.
"Although ...
2021-01-13
As anxious passengers are often reassured, commercial aircrafts can easily continue to fly even if one of the engines stops working. But for drones with four propellers - also known as quadcopters - the failure of one motor is a bigger problem. With only three rotors working, the drone loses stability and inevitably crashes unless an emergency control strategy sets in.
Researchers at the University of Zurich and the Delft University of Technology have now found a solution to this problem: They show that information from onboard cameras can be used to stabilize the drone and keep it flying autonomously after one rotor suddenly gives out.
Spinning like a ballerina
"When one rotor fails, the drone begins to spin ...
2021-01-13
A recent Point of Reference article, "The meat of the matter: Environmental dissemination of beef cattle agrochemicals," published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, points at synthetic chemical cocktails being emitted from cattle feed yards into the environment and how they can impact our ecosystem and our health.
Industrial meat production facilities have a bad reputation for their impact on the environment. Concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs) are known to release greenhouse gases related to global warming and for discharge of manure to watersheds, which affects water quality. A less publicized impact of modern beef production is the excessive use of ...
2021-01-13
Our immune system is never idle. Their task is to detect and eliminate invasive pathogens, and they have no time to lose. The adaptive immune system identifies infectious organisms by recognizing foreign proteins on the surfaces of bacteria, viruses and unicellular protozoans. The interaction of these antigens with immune cells triggers a series of downstream events, which in most cases leads to the elimination of the pathogen.
But pathogenic organisms have developed strategies that enable them to escape detection by the immune system, and the strategies employed by remotely related organisms are often remarkably similar to each other. One way of confusing the immune system is to increase the structural heterogeneity of the antigens it encounters. ...
2021-01-13
(Philadelphia, PA) - Like a failing fuel pump that causes a loss of engine power in a car, a diseased heart can take a serious toll on the body's performance. For some patients, tasks like walking up a flight of stairs or walking across a room eventually turn into exhausting endeavors. This is because, over time, regardless of the underlying cause, heart damage typically progresses, owing to a constant barrage of oxidative stress and toxic lipids that alter heart cell energetics and, ultimately, the ability of the heart to function normally.
Oxidative stress occurs when harmful oxygen-containing molecules outnumber helpful antioxidants, leading to damaging reactions with proteins, DNA, and other cell components. ...
2021-01-13
New data released this week by Australian researchers reveals the impact of the COVID-19 lockdown period on aeromedical retrievals in rural and remote regions.
Researchers say while the social isolation measures led to a reduction in overall aeromedical activity during the lockdown in 2020, once the restrictions were lifted, evacuations increased significantly.
These findings are published in the Internal Medicine Journal, comparing aeromedical evacuation trends in Australia during the pre-restriction, lockdown and post-restriction periods last ...
2021-01-13
A Simon Fraser University study on public perceptions of police officers wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) during the current pandemic finds that most PPE renders positive perceptions of police, while some equipment, including full-face respirator masks, may be viewed more negatively. The research was published January 9 in the Journal of Experimental Criminology.
Led by SFU criminology assistant professor Rylan Simpson and MA student Ryan Sandrin, the online experimental study drew on a sample of 117 participants residing in North America. The participants were randomly assigned to read one of three fictitious news articles that were either pro-PPE (highlighting health benefits), neutral or anti-PPE (lacking health benefits). Participants were then asked to rate 12 ...
2021-01-13
The Granzyme B (GzmB) enzyme, which accumulates in certain tissues as we age, has been identified as a driver of itchy and sometimes life-threatening autoimmune conditions known as pemphigoid diseases (PDs), which cause blistering and skin erosion below the skin's surface.
New research led by University of British Columbia (UBC) and Vancouver Coastal Health Research Institute (VCHRI) scientists has found that a gel containing a specific and potent inhibitor of GzmB activity, VTI-1002, resulted in significant improvements on skin affected by PDs.
"Blisters caused by these conditions can be extremely discomforting, unsightly and ...
2021-01-13
A proton exchange membrane fuel cell is a chemical cell that converts energy released when a substance reacts into electrical energy with zero emission. It is an excellent substitute for fossil fuel.
However, low activity and stability of the Pt-based catalysts in the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) of the battery cathode restricted the output power and the number of charge and discharge cycles, thus increasing the cost of the whole fuel cells. The preparation of cathode catalysts with high activity and stability is a difficult problem.
In a study ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NIH scientists study salmonella swimming behavior as clues to infection


