600-year-old marine sponge holds centuries-old climate records
Temperature records show past volcanic activity, current climate warming trends
2021-01-14
(Press-News.org) MIAMI--Scientists used a 600-year-old marine sponge to reconstruct a record of ocean temperature in the North Atlantic revealing past volcanic activity as well as the current global warming trend from the release of carbon dioxide and other heat trapping gasses into Earth's atmosphere and absorbed by the oceans.
The University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science-led research team used geochemical proxies to reconstruct a 600 year-long record of Atlantic Ocean temperatures from the skeleton of a sclerosponge (Ceratoporella nicholsoni).
The basketball-sized sclerosponge was collected via submersible more than 430 feet (133 meters) below the surface in Exuma Sound, The Bahamas by the study's senior author Peter Swart, a professor of marine geosciences at the UM Rosenstiel School. Sclerosponges are slow growing marine organisms with a soft outer body and hard limestone skeleton that record upper ocean temperature and climate conditions. Although individuals could be as old as 1000-2000 years their distribution is poorly documented because of the difficulty and expense of collection.
"Atlantic Ocean temperatures fluctuate on various timescales, including multi-decadal, and this influences the weather and climate in North America, Europe, and Africa," said Swart. "This 600-year-long temperature reconstruction can help us understand how the climate has changed in the past so that scientists can better project how conditions may change in the future. "
To understand environmental changes beyond what modern instruments can provide, scientists turn to long-lived marine organisms like Sclerosponges that record ambient environmental conditions in their skeletons.
"Predicting and projecting future temperatures in the Atlantic can help us better prepare for hurricanes, as well as fluctuations in summertime precipitation rates in Florida," said the study's lead author Amanda J. Waite, a UM Rosenstiel School alumna.
"This record highlights both the important role volcanic eruptions had on North Atlantic temperature both before and after industrialization and the increasing contribution of manmade factors, such as greenhouse gases and air pollution, to the temperature record over the twentieth century," said Lisa Murphy, a co-author of the study and a lecturer at the Rosenstiel School's department of atmospheric sciences.
The samples were dated using uranium-thorium by scientists at GEOMAR Helmholtz?Zentrum für Ozeanforschung Kiel in Germany.
INFORMATION:
The study, titled "Observational and model evidence for an important role for volcanic forcing driving Atlantic Multidecadal Variability over the last 600 years," was published in the American Geophysical Union's journal Geophysical Research Letters. The study's authors include: Peter K. Swart, Amanda J. Waite, Jeremy M. Klavans, Amy C. Clement and Lisa N. Murphy from the UM Rosenstiel School and Volker Liebetrau, and Anton Eisenhauer from GEOMAR Helmholtz?Zentrum für Ozeanforschung Kiel in Germany.
Funding for the research is a follows: The sclerosponge was collected under NOAA/NURP award 95?340044 to D. McNeill, M. Grammer, and P. K. Swart.
This work was supported by the NSF (OCE 9819147 and OCE 0823636) awards to P. K. Swart.
A. Clement, J. Klavans, and L. Murphy were supported by grants from the NSF Climate and Large Scale Dynamics and Paleo Perspectives on Climate Change programs (AGS 1703076 and AGS 1735245).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-14
These findings validate the significance of the previously described first threshold - the point when the damage to the acinar cells of the pancreas is sufficient to trigger the infamous inflammatory cascade (Barreto and Saccone, 2010) - while highlighting the importance of a second threshold, namely the point when a person develops clinical symptoms of the disease sufficient to warrant going to hospital.
"This transcontinental collaboration of pancreatologists drew on their vast clinical and research experience spanning decades investigating the pathophysiology and treatments ...
2021-01-14
Deep in the Brazilian Amazon River basin, scientists led by the Smithsonian's National Museum of Natural History fish research associate C. David de Santana discovered a small, river-fed lake filled with more than 100 adult electric eels, many of which were upwards of 4 feet long. On its own, this was an intriguing discovery, electric eels--a type of knifefish rather than true eels--were thought to be solitary creatures.
But in this lake along the banks of the Iriri River in Brazil's state of Pará, the researchers witnessed the eels working together to herd small fish called tetras into tightly packed balls. Then groups of up to ...
2021-01-14
Underwater seagrass meadows may trap, extract and carry marine plastic debris to shore, thereby helping to remove plastic litter from the sea, according to a study published in Scientific Reports.
Previous research suggested that most plastics end up in the seafloor and that some are washed back to shore; however, how this occurs was unclear.
Seagrass meadows are widespread in shallow coastal waters and are involved in trapping and binding sediment particles that form the seabed. To assess the role that seagrass may have in trapping and removing marine plastic, Anna Sanchez-Vidal and colleagues measured the amount of plastic debris collected from seagrass litter ...
2021-01-14
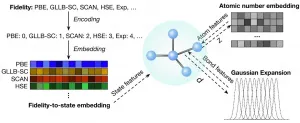
Advancements in energy technologies, healthcare, semiconductors and food production all have one thing in common: they rely on developing new materials--new combinations of atoms--that have specific properties enabling them to perform a needed function. In the not-too-distant past, the only way to know what properties a material had was by performing experimental measurements or using very expensive computations.
More recently, scientists have been using machine learning algorithms to rapidly predict the properties that certain arrangements of atoms would have. The challenge with this approach is it requires a lot of highly accurate data to train the model, which often does not exist.
By combining large ...
2021-01-14
Retinal cells derived from adult human eye stem cells survived when transplanted into the eyes of monkeys, an important early step in the validation of this approach for treating blindness, according to a study by Liu, et al recently published in Stem Cell Reports. The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), a layer of pigmented cells in the retina, is essential for sustaining normal vision. Blindness due to RPE dysfunction, such as macular degeneration, affects about 200 million people worldwide.
To restore this population of cells, researchers extracted retinal stem cells from donated cadaver adult eyes, grew them into RPE cells and transplanted them into the eyes of monkeys. ...
2021-01-14
Retinal cells derived from a cadaver human eye survived when transplanted into the eyes of primate models, an important advance in the development of cell therapy to treat blindness, according to a study published on January 14 in Stem Cell Reports.
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), a layer of pigmented cells in the retina, functions as a barrier and regulator in the eye to maintain normal vision. RPE dysfunction can lead to eye disorders including macular degeneration and can cause blindness, which affects about 200 million people worldwide.
To restore this population of cells, ...
2021-01-14
A major roadblock to computational design of high-entropy alloys has been removed, according to scientists at Iowa State University and Lehigh University. Engineers from the Ames Lab and Lehigh University's Department of Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics have developed a process that reduces search time used for predictive design 13,000-fold.
According to Ganesh Balasubramanian, an associate professor at Lehigh, the goal of the team's research was to accelerate the computational modeling of complex alloys. The tools available for creating random distribution of atoms in materials simulation models, he says, have been used for many, many years now and are limited in ...
2021-01-14
What The Study Did: The number of patients undergoing cancer screening tests and of subsequent cancer diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic in the largest health care system in the northeastern United States was assessed in this study.
Authors: Toni K. Choueiri, M.D., of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Quoc-Dien Trinh, M.D., of Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.7600)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict ...
2021-01-14
What The Study Did: Which demographic and socioeconomic factors were associated with patient participation in telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic surge was examined in this observational study.
Authors: Ilaaf Darrat, M.D., M.B.A., of the Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5161)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
2021-01-14
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated the association of home confinement during the COVID-19 outbreak with myopia (nearsightedness) development in school-age children in China.
Authors: Xuehan Qian, M.D., Ph.D., of Tianjin Medical University Eye Hospital in Tianjin, China, is the corresponding author. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the CC-BY License. © 2021 Wang J et al. JAMA Ophthalmology.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2020.6239)
Editor's Note: The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 600-year-old marine sponge holds centuries-old climate records
Temperature records show past volcanic activity, current climate warming trends