BIO Integration journal, Volume 1, Issue number 4, publishes
2021-01-15
(Press-News.org) Guangzhou, January 15, 2021: New journal BIO Integration (BIOI) publishes its fourth issue, volume 1, issue 4. BIOI is a peer-reviewed, open access, international journal, which is dedicated to spreading multidisciplinary views driving the advancement of modern medicine. Aimed at bridging the gap between the laboratory, clinic, and biotechnology industries, it will offer a cross-disciplinary platform devoted to communicating advances in the biomedical research field and offering insights into different areas of life science, in order to encourage cooperation and exchange among scientists, clinical researchers, and health care providers.
The issue contains an original article, three review articles, a mini review article and a commentary:
"Experimental Study on the Viscoelastic Flow Mixing in Microfluidics" by authors Meng Zhang, Wu Zhang, Zihuang Wang and Weiqian Chen. This original article discusses how the integration of microfluidic technology with blood flow research could provide a new approach to understanding related disease mechanisms and analysis of drug mixing and delivery in blood flow.
"A Review for Antimicrobial Peptides with Anticancer Properties: Re-purposing of Potential Anticancer Agents" by Cuiyu Zhong, Lei Zhang, Lin Yu, Jiandong Huang, Songyin Huang and Yandan Yao. This review article assesses several examples of antimicrobial peptides (ACPs) used in tumor therapy for their ability in penetrating or lysing tumor cell membrane, and discusses recent advances and challenges in the application of ACPs.
"Metabolic Syndrome "Interacts" With COVID-19" by Zeling Guo, Shanping Jiang, Zilun Li and Sifan Chen. In this review article, the authors focus on the close interaction between COVID-19 and metabolic syndrome, as well as the potential of repurposing metabolic-related drugs and the importance of treating metabolic diseases in COVID-19 patients.
"Coronavirus Pneumonia and Pulmonary Thromboembolism" by Mingkang Yao, Phei Er Saw and Shanping Jiang. In this review article, the authors summarize the harm that coronavirus pneumonia wreaks and highlight the clinical relationship between PTE and coronavirus infection. The potential mechanism and the prophylaxis and therapeutic measures are also discussed to call for more effort and research to investigate the strategies for PTE in COVID-19.
"Microbes in Oncology: Controllable Strategies for Bacteria Therapy" by Meng Du, Jinsui Yu, Yaozhang Yang, Fei Yan and Zhiyi Chen. In this mini review article, the authors introduce the unique advantages of bacteria in cancer treatment and highlight the issues associated with the application of bacterial therapy, focusing on the incorporation of various methodologies in the advancement of some controllable strategies in bacterial therapy.
"Understanding of the Entry Mechanism of Nanoparticles into Tumors Determines the Future Direction of Nanomedicine Development" by Phei Er Saw and Sangyong Jon. In this commentary, the authors discuss insights on the entry mechanism of nanoparticles into tumors.
INFORMATION:
BIO Integration is a fully open access journal which will allow for the rapid dissemination of multidisciplinary views driving the progress of modern medicine.
As part of its mandate to help bring interesting work and knowledge from around the world to a wider audience, BIOI will actively support authors through open access publishing and through waiving author fees in its first years. Also, publication support for authors whose first language is not English will be offered in areas such as manuscript development, English language editing and artwork assistance.
BIOI is now open for submissions; articles can be submitted online at https://mc04.manuscriptcentral.com/bioi
Please visit http://www.bio-integration.org to learn more about the journal.
Editorial Board: https://bio-integration.org/editorial-board/
BIOI is available on the IngentaConnect platform and at the BIO Integration website.
Submissions may be made using Scholar One.
There are no author submission or article processing fees.
Follow BIOI on Twitter @JournalBio; Facebook and LinkedIn.
ISSN 2712-0074
eISSN 2712-0082
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-15
A clinical trial involving COVID-19 patients hospitalized at UT Health San Antonio and University Health, among roughly 100 sites globally, found that a combination of the drugs baricitinib and remdesivir reduced time to recovery, according to results published Dec. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine. Six researchers from UT Health San Antonio and University Health are coauthors of the publication because of the San Antonio site's sizable patient enrollment in the trial.
The Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial 2 (ACTT-2), which compared the combination therapy versus remdesivir paired with an inactive placebo in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), ...
2021-01-15
Certain snakes have evolved a unique genetic trick to avoid being eaten by venomous snakes, according to University of Queensland research.
Associate Professor Bryan Fry from UQ's Toxin Evolution Lab said the technique worked in a manner similar to the way two sides of a magnet repel each other.
"The target of snake venom neurotoxins is a strongly negatively charged nerve receptor," Dr Fry said.
"This has caused neurotoxins to evolve with positively charged surfaces, thereby guiding them to the neurological target to produce paralysis.
"But some snakes have evolved to replace a negatively charged amino acid on their receptor with a positively charged one, meaning the neurotoxin is repelled.
"It's an inventive genetic mutation and it's been completely missed until now.
"We've ...
2021-01-15
PHILADELPHIA - Our biological or circadian clock synchronizes all our bodily processes to the natural rhythms of light and dark. It's no wonder then that disrupting the clock can wreak havoc on our body. In fact, studies have shown that when circadian rhythms are disturbed through sleep deprivation, jet lag, or shift work, there is an increased incidence of some cancers including prostate cancer, which is the second leading cause of cancer death for men in the U.S. With an urgent need to develop novel therapeutic targets for prostate cancer, researchers at the Sidney Kimmel Cancer - ...
2021-01-15
Oxygen levels in the ancient oceans were surprisingly resilient to climate change, new research suggests.
Scientists used geological samples to estimate ocean oxygen during a period of global warming 56 million years ago - and found "limited expansion" of seafloor anoxia (absence of oxygen).
Global warming - both past and present - depletes ocean oxygen, but the new study suggests warming of 5°C in the Paleocene Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) led to anoxia covering no more than 2% of the global seafloor.
However, conditions are different today to the PETM - today's rate of carbon emissions is much faster, and we are adding nutrient pollution to the oceans - both of which could drive more rapid and expansive oxygen loss.
The study was carried out by an international ...
2021-01-15
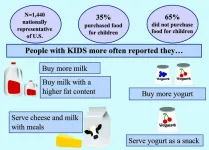
Champaign, IL, January 15, 2021 - American dairy consumers are often influenced by a variety of factors that can affect their buying habits. These factors include taste, preference, government information, cultural background, social media, and the news. In an article appearing in JDS Communications, researchers found that households that frequently bought food for children are interested in dairy as part of their diet and purchased larger quantities of fluid milk and more fluid milk with a higher fat content.
To assess the purchasing habits of households that purchase food for children versus those ...
2021-01-15
Families are complicated. For members of the Alligatoridae family, which includes living caimans and alligators - this is especially true. They are closely related, but because of their similarity, their identification can even stump paleontologists.
But after the recent discovery of a partial skull, the caimans of years past may provide some clarity into the complex, and incomplete, history of its relatives and their movements across time and space.
Michelle Stocker, an assistant professor of vertebrate paleontology in Virginia Tech's Department of Geosciences in the College of Science; Chris Kirk, of the University of Texas at Austin; and Christopher Brochu, of the University of Iowa, have ...
2021-01-15
Researchers from University of Stavanger, University of Melbourne, and University of Wisconsin-Madison published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how major projects undertaken by temporary organizations can be better managed so that cost overruns are minimized.
The study forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing is titled "Mobilizing the Temporary Organization: The Governance Roles of Selection and Pricing" and is authored by Elham Ghazimatin, Erik Mooi, and Jan Heide.
When consumers return to the skies again, they may do so in Boeing's 787 Dreamliner. But the project, or "temporary organization," created to make this plane ...
2021-01-15
Just like humans trying to stick to New Year's resolutions, guppies have varying levels of self-control, a new study shows.
Researchers from the University of Exeter and Ghent University studying the behaviours of Trinidadian guppies tested "inhibitory control" (suppressing unhelpful impulses or urges).
The tiny fish first learned how to swim into a cylinder to get food - then a cover was removed to make the cylinder transparent.
Inhibitory control was measured by whether a guppy resisted the urge to swim directly towards the food - bumping into the cylinder - or still swam around, ...
2021-01-15
Researchers have developed a DNA test to quickly identify secondary infections in COVID-19 patients, who have double the risk of developing pneumonia while on ventilation than non-COVID-19 patients.
For patients with the most severe forms of COVID-19, mechanical ventilation is often the only way to keep them alive, as doctors use anti-inflammatory therapies to treat their inflamed lungs. However, these patients are susceptible to further infections from bacteria and fungi that they may acquire while in hospital - so called 'ventilator-associated pneumonia'.
Now, a team of scientists ...
2021-01-15
Former director of public health Professor John Ashton has said that scientific scepticism may be reinforced by the UK's rush to approve COVID vaccines for public use and the apparent political desire to be the first out of the blocks in contrast to our European neighbours.
Writing in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, Prof Ashton says that to risk the trust of the public for the sake of a couple of weeks propaganda advantage could prove to be unforgivable should vaccine uptake fall below that required for the ubiquitous 'herd immunity' as a result of giving oxygen to the sceptics.
"In this age of scientific rationality, superstition and anti-science still run deep," he writes. "When an overwhelming majority of the public welcomes the arrival of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] BIO Integration journal, Volume 1, Issue number 4, publishes