Helium nuclei at the surface of heavy nuclei discovered
Research team confirms a new nuclear property predicted by theory
2021-01-15
(Press-News.org) The experiment was performed at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) in Osaka. The research team, lead by scientists from TU Darmstadt and the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy-Ion Research, and from the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science, discuss the new findings in a contribution to the latest issue of the journal "Science".
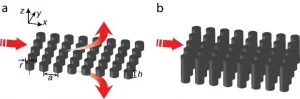
The strong interaction binds neutrons and protons together to atomic nuclei. The knowledge of properties of nuclei and their theoretical description is basis for our understanding of nuclear matter and the development of the universe. Laboratory-based studies of reactions between atomic nuclei provide means to explore nuclear properties. These experiments allow to test and verify theories that describe properties of extended nuclear matter at different conditions, as present, for instance, in neutron stars in the universe. Several theories predict the formation of nuclear clusters like helium nuclei in dilute nuclear matter. This effect is expected to occur at densities significantly lower than saturation density of nuclear matter, as present in the inner part of heavy nuclei. A theory developed in Darmstadt by Dr. Stefan Typel predicts that such a condensation of helium nuclei should also occur at the surface of heavy nuclei. Goal of the experiment, which is presented in the latest issue of "Science", was the verification of this prediction.
The present experiment bombarded tin isotopes with high-energy protons and detected and identified the scattered protons as well as knocked-out helium nuclei. Dr. Junki Tanaka and Dr. Yang Zaihong could demonstrate that the reaction occurs as a direct "quasi-elastic" scattering of the protons off preformed helium nuclei in the surface of tin nuclei. The extracted cross sections for different tin isotopes reveal a decrease of the formation probability with the neutron excess of the nuclei, which impressively confirms the theoretical prediction. This new finding, which has far-reaching consequences for our understanding of nuclei and nuclear matter, will now be studied in more detail in experimental programs planned at RCNP, and in inverse kinematics at RIKEN and the new FAIR facility at GSI, where also unstable heavy neutron-rich nuclei are accessible.
INFORMATION:
The publication:
„Formation of α clusters in dilute neutron-rich matter",
https://science.sciencemag.org/content/371/6526/260
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Thomas Aumann
Institut für Kernphysik der TU Darmstadt
Tel.: 06151/16-23530
E-Mail: taumann@ikp.tu-darmstadt.de
About TU Darmstadt
The Technical University (TU) of Darmstadt is one of Germany's leading technical universities. TU Darmstadt incorporates diverse science cultures to create its characteristic profile. The focus is set on engineering and natural sciences, which cooperate closely with outstanding humanities and social sciences. Three research fields shape the profile of TU Darmstadt: I+I (Information and Intelligence), E+E (Energy and Environment) sowie M+M (Matter and Materials). We dynamically develop our portfolio of research and teaching, innovation and transfer, in order to continue opening up important opportunities for the future of society. Our 312 professors, about 4,500 scientific and administrative employees and about 25,400 students devote their talents and best efforts to this goal. In the UNITE! network, which unites universities from seven European countries, the TU Darmstadt is promoting the idea of the European university. Together with Goethe University Frankfurt and Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, TU Darmstadt has formed the strategic Rhine-Main Universities alliance.
http://www.tu-darmstadt.de
MI-Nr. 03e/2021, Aumann/Typel/sip
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-15
Diabetes is characterized by elevated levels of sugar or glucose (hyperglycemia) in the blood. This occurs due to the lack of the hormone insulin in type 1 diabetes, and to reduced insulin levels in combination with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. A recent review of data supports stricter control of hemoglobin A1C levels (HbA1C) among pediatric patients with T1D. This review was led by Dr. Maria J. Redondo, pediatric endocrinologist at Texas Children's Hospital and professor at Baylor College of Medicine, in collaboration with Dr. Sarah Lyons, pediatric endocrinologist at Texas Children's and assistant professor at Baylor College of Medicine, ...
2021-01-15
A refractive index of zero induces a wave vector with zero amplitude and undefined direction. Therefore, light propagating inside a zero-index medium does not accumulate any spatial phase advance, resulting in perfect spatial coherence. Such coherence brings several potential applications, including arbitrarily shaped waveguides, phase-mismatch-free nonlinear propagation, large-area single-mode lasers, and extended super radiance. A promising platform to achieve these applications is an integrated Dirac-cone material that features an impedance-matched zero index. However, although this platform eliminates ohmic losses via its purely dielectric structure, it still entails out-of-plane radiation loss (about 1 dB/μm), restricting the applications to a small scale.
In ...
2021-01-15
The development of ultrafast all-optical switches has long been a popular topic in photonics, while the speed of magnetization reversal triggered by means other than magnetic fields has recently attracted intense interest in spintronics. The discovery of all-optical helicity-dependent switching in metallic GdFeCo has promised a merger of the fields of photonics and spintronics, paving the way for faster and more energy-efficient information processing technologies. However, the real potential of all-optical switching is still poorly understood because it is still unclear whether magnetic switching by light can keep up with the GHz frequencies required by photonics technologies. ...
2021-01-15
"The lotus roots may break, but the fiber remains joined" is an old Chinese saying that reflects the unique structure and mechanical properties of the lotus fiber. The outstanding mechanical properties of lotus fibers can be attributed to their unique spiral structure, which provides an attractive model for biomimetic design of artificial fibers.
In a new study published in Nano Letters, a team led by Prof. YU Shuhong from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported a bio-inspired lotus-fiber-mimetic spiral structure bacterial cellulose (BC) hydrogel fiber with high strength, ...
2021-01-15
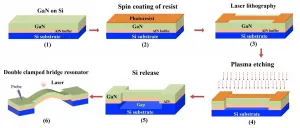
Liwen Sang, independent scientist at International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics, National Institute for Materials Science (also JST PRESTO researcher) developed a MEMS resonator that stably operates even under high temperatures by regulating the strain caused by the heat from gallium nitride (GaN).
High-precision synchronization is required for the fifth generation mobile communication system (5G) with a high speed and large capacity. To that end, a high-performance frequency reference oscillator which can balance the temporal stability and temporal resolution is necessary as a timing device to generate signals ...
2021-01-15
PULLMAN, Wash. - Scientists have identified the presence of a non-tobacco plant in ancient Maya drug containers for the first time.
The Washington State University researchers detected Mexican marigold (Tagetes lucida) in residues taken from 14 miniature Maya ceramic vessels.
Originally buried more than 1,000 years ago on Mexico's Yucatán peninsula, the vessels also contain chemical traces present in two types of dried and cured tobacco, Nicotiana tabacum and N. rustica. The research team, led by anthropology postdoc Mario Zimmermann, thinks the Mexican marigold was mixed with the tobacco to make smoking more enjoyable.
The discovery of the vessels' contents paints a clearer picture of ancient Maya drug use practices. The research, which was published ...
2021-01-15
Partially protected areas - marine reserves that allow some forms of fishing - are no more effective socially or ecologically than open marine areas in Australia's Great Southern Reef, a new UNSW study has concluded.
The research, published in Conservation Biology today, comes at a time when the High Ambition Coalition of 50 countries of the world (which does not include Australia) have pledged to protect more than 30 per cent of the planet's lands and seas by the end of this decade. But not all protected areas are created equal.
The UNSW study discovered partially protected areas in southern Australia had no more fish, invertebrates or algae and no difference in ...
2021-01-15
Researchers from Kumamoto University (Japan) have found an Edo period document that clearly indicates the Hosokawa clan, rulers of the Kokura Domain (modern-day Fukuoka Prefecture), completely stopped producing wine in 1632, the year before the shogunate ordered them to move to the Higo Domain (now Kumamoto Prefecture). The researchers believe that the discontinuation of wine production was directly related to this move and because it was considered to be a drink of a religion that was harshly suppressed in Japan at that time, Christianity.
Previous analysis of historical documents revealed that the lord of the Hosokawa clan, Tadatoshi Hosokawa, ordered wine production from 1627 to 1630 for medicinal use. His ...
2021-01-15
Divergences between scientific and Indigenous and Local Knowledge can provide a better understanding of why local pastoralists may be willing, or not, to participate in conservation initiatives for carnivores, a study from University of Helsinki suggests.
Carnivore conservation has historically been based primarily on scientific knowledge using a wide range of sampling methods, such as camera trapping and track surveys. However, the estimates of these common ecological sampling methods can be quite uncertain and can depend on accessibility and geology, which is the case of many remote areas, such as Sibiloi National Park in Northern Kenya. For this reason, the inclusion of local communities that share ...
2021-01-15
A research team led by scientists at the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science (RNC) has successfully created larger-than-usual strains of zooplankton -- which are used in fish nurseries -- by creating mutations with a heavy ion beam. The new strains of zooplankton could contribute to improving the survival rate and optimizing the growth of juvenile fish in aquaculture.
Economically important fish species, such as bluefin tuna, yellowtail, flatfish and groupers, are fed live bait until they are large enough to be fed with artificial foods. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Helium nuclei at the surface of heavy nuclei discovered
Research team confirms a new nuclear property predicted by theory