New method heals skeletal injuries with synthetic bone
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) Researchers at Lund University in Sweden, in collaboration with colleagues in Dresden, Germany, have developed a way of combining a bone substitute and drugs to regenerate bone and heal severe fractures in the thigh or shin bone. The study, published in the research journal Science Advances, was conducted on rats, but the researchers think that the method in various combinations will soon be commonplace in clinical settings.
"The drugs and materials we used in the study for the regeneration of bone are already approved. We simply packaged them in a new combination. Therefore, there are no real obstacles to already using the method in clinical studies for certain major bone defects that are difficult to resolve in patients. But we want to introduce the technique in a controlled form via clinical studies and have recently been granted ethical approval", says Deepak Raina, orthopaedics researcher and the lead author of the study.
Bones in the human body have a fantastic ability to repair injury, but some defects are so large or complicated that the healing process is delayed or absent. This may be due to the bone having been subjected to a major trauma in connection with a traffic accident for example, or a tumour or infection causing a major bone defect. These cases are currently treated through bone transplantation, usually with bone taken from the patient's own pelvis.
"In cases involving severe open fractures in the lower leg, over 5 per cent of all fractures fail to heal. With our method, we will be able to avoid taking bone from the pelvis, which is a major gain for the patient."
There is a need for new solutions and several research teams, both in Europe and in the USA, are working on improving the bone healing process. So far, the injectable cocktail successfully mixed by the Swedish and German researchers consists of three different components: an artificial ceramic material developed in Lund, a bioactive bone protein (rhBMP-2) and a drug, bisphosphonate, that combats bone resorption.
"The bone protein we use has had negative effects in previous studies due to a secondary premature bone resorption, among other things. We have successfully mitigated this effect with the bisphosphonate and, by packaging the drug in a slowly resorbing bone substitute, we can control the speed of release. In the current study with the combination, we achieved a six-fold reduction in the amount of protein compared to previous efforts, while still inducing bone formation. The result was that even fractures with an extensive bone defect could heal without complications. We believe this finding will be of great clinical use in the future", says Deepak Raina.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-19
The Messina Strait, a submarine bridge separating the island of Sicily from the Italian Peninsula, is the area with the largest marine litter density worldwide -more than a million objects per square kilometre in some parts-, as reported in a new review paper published in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
Also, over the next thirty years, the volume of rubbish in the sea could surpass three billion metric tons (Mt), as cited in the study, whose corresponding authors are the experts Miquel Canals, from the Faculty of Earth Sciences of the University of Barcelona, and Georg Hanke from the European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC), where ...
2021-01-19
A new study in Frontiers in Psychiatry has for the first time, demonstrated differences in the prevalence of post-traumatic stress symptoms (PTSS) in different groups of rescue workers and emergency personnel, including firefighters, police officers and psychiatric nurses. The researchers showed that the varying experiences and circumstances these workers encounter, such as handling aggressive people, working with families or dealing with deaths and suicide, are tied to varying levels of PTSS and suicidal thoughts, with emergency department staff and psychiatric nurses showing the highest levels of PTSS and suicidal thoughts out of the emergency professions studied. The findings highlight the urgent need for bespoke training and counselling services ...
2021-01-19
INSECTS The spirea aphid, Aphis spiraecola, an invasive pest, has been discovered for the first time in Denmark by University of Copenhagen researchers. The extent of its current distribution remains unknown, but in time, it could prove to be a troublesome pest for Danish apple growers.
Aphis
Whether the discovery of this aphid in Denmark is an isolated incident, or if the species has made itself at home due to a milder climate, remains unknown to the researchers. Closer investigation is needed. Photo: UCPH/Uni.Budapest
In a collaboration with colleagues at the University of Budapest, University of Copenhagen researchers have analysed and compared a number of samples of green aphids from apples around ...
2021-01-19
The psychological well-being of both men and women declined when Denmark closed down during the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic in the spring of 2020 - with women being hit the hardest. But during the second wave, it is the other way round in terms of gender: The psychological well-being of men and women is generally low, but it has fallen most in men.
This is shown in a survey conducted by Søren Dinesen Østergaard, among others. He is professor at the Department of Clinical Medicine and affiliated with the Department of Affective Disorders at Aarhus University Hospital - Psychiatry in Denmark.
The survey is the latest of three assessments of Danes' psychological well-being ...
2021-01-19
Climate researchers have found a simple but efficient way to improve estimations of ultimate global warming from complex climate models. The finding is relevant for the evaluation and comparison of climate models and thus for accurate projections of future climate change - especially beyond the year 2100. The study is published in Geophysical Research Letters by Dr. Robbin Bastiaansen and colleagues at the Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Research Utrecht, Utrecht University, The Netherlands. The work is part of the European TiPES project coordinated by the University of Copenhagen, Denmark.
Complex climate models are rarely used to simulate the effect of global warming for a given amount of CO2 beyond a couple of centuries into the future. ...
2021-01-19
A system that uses flexible, breathable magnetic skin allows people with severe quadriplegia to move around and choose their surroundings. Developed by KAUST researchers, the high-tech system relies on the user's facial expressions to accomplish a wide variety of tasks, from moving down the street to using an elevator.
There are a wide variety of assistive technologies for people with quadriplegia, but most systems are not suitable for patients with severe quadriplegia as they often rely on head or neck movements to work. For these patients, the options are limited to camera, tongue control, voice-assistant and neural detector systems. But these either offer a limited range of gestures or are not compatible with outdoor applications. Some also require invasive attachments or ...
2021-01-19
Naltrexone, used either alone or together with disulfiram or acamprosate, is associated with a decreased risk of hospitalization due to alcohol use disorder (AUD) when compared with non-use of AUD drugs, a new register-based study shows. The same associations were noticed for hospitalization due to any cause. Disulfiram use and polytherapy with two or more drugs indicated for AUD was associated with a decreased risk of hospitalization due to alcohol-related somatic causes. None of the studied medications were associated with mortality or work disability (sickness absence or disability pension). The study was published in Addiction.
Benzodiazepine use linked to harmful effects
As benzodiazepine use is common among persons with AUD, the ...
2021-01-19
Various glass materials have been essential to the development of modern civilization due to their advantageous properties. Specifically, glasses have a liquid-like disordered structure but solid-like mechanical properties. This leads to one of the central mysteries of glasses: "Why don't glasses flow like liquids?" This question is so important that it was selected by the journal Science in 2005 as one of 125 key, unanswered scientific questions, and one of 11 unsolved important physical issues.
We can hardly observe the movements of atoms at a ~0.1 nanometer length scale and a ~1 ...
2021-01-19
Overview:
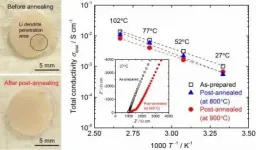
A research team in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology and the Department of Chemistry at University of Calgary has investigated the effect of post-annealing for healing Li garnet solid electrolyte degraded by the growth of Li dendrites. The ionic conductivity of the annealed solid electrolyte was slightly lower than that of the electrolyte before annealing but was retained above 10?4 S cm?1 at room temperature. The electrochemical results obtained indicate the possibility of reusing the solid electrolyte degraded by the growth of Li dendrites in another all-solid-state Li battery.
Details:
A ...
2021-01-19
Overview:
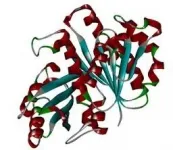
The research team of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at the Toyohashi University of Technology and the Institute of Food Biotechnology and Genomics at the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine have proposed a new drug to treat tuberculosis (TB), utilizing the state-of-the-art molecular simulations. This drug may inhibit the cell division of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) and suppress its growth. In addition, because this drug acts on the enzymes secreted by M. tuberculosis instead of acting on M. tuberculosis itself, M. tuberculosis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New method heals skeletal injuries with synthetic bone