(Press-News.org) People on a low-fat, plant-based diet ate fewer daily calories but had higher insulin and blood glucose levels, compared to when they ate a low-carbohydrate, animal-based diet, according to a small but highly controlled study at the National Institutes of Health. Led by researchers at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), the study compared the effects of the two diets on calorie intake, hormone levels, body weight, and more. The findings, published in Nature Medicine, broaden understanding of how restricting dietary carbohydrates or fats may impact health.
"High-fat foods have been thought to result in excess calorie intake because they have many calories per bite. Alternatively, high-carb foods can cause large swings in blood glucose and insulin that may increase hunger and lead to overeating," said NIDDK Senior Investigator Kevin Hall, Ph.D., the study's lead author. "Our study was designed to determine whether high-carb or high-fat diets result in greater calorie intake."
The researchers housed 20 adults without diabetes for four continuous weeks in the NIH Clinical Center's Metabolic Clinical Research Unit. The participants, 11 men and nine women, received either a plant-based, low-fat diet or an animal-based, low-carbohydrate diet for two weeks, immediately followed by two weeks on the alternate diet. The low-fat diet was high in carbohydrates. The low-carbohydrate diet was high in fats. Both diets were minimally processed and had equivalent amounts of non-starchy vegetables. The participants were given three meals a day, plus snacks, and could eat as much as desired.
The main results showed that people on the low-fat diet ate 550 to 700 fewer calories per day than when they ate the low-carb diet. Despite the large differences in calorie intake, participants reported no differences in hunger, enjoyment of meals, or fullness between the two diets. Participants lost weight on both diets, but only the low-fat diet led to a significant loss of body fat.
"Despite eating food with an abundance of high glycemic carbohydrates that resulted in pronounced swings in blood glucose and insulin, people eating the plant-based, low-fat diet showed a significant reduction in calorie intake and loss of body fat, which challenges the idea that high-carb diets per se lead people to overeat. On the other hand, the animal-based, low-carb diet did not result in weight gain despite being high in fat," said Hall.
These findings suggest that the factors that result in overeating and weight gain are more complex than the amount of carbs or fat in one's diet. For example, Hall's laboratory showed last year that a diet high in ultra-processed food led to overeating and weight gain in comparison to a minimally processed diet matched for carbs and fat.
The plant-based, low-fat diet contained 10.3% fat and 75.2% carbohydrate, while the animal-based, low-carb diet was 10% carbohydrate and 75.8% fat. Both diets contained about 14% protein and were matched for total calories presented to the subjects, although the low-carb diet had twice as many calories per gram of food than the low-fat diet. On the low-fat menu, dinner might consist of a baked sweet potato, chickpeas, broccoli and oranges, while a low-carb dinner might be beef stir fry with cauliflower rice. Subjects could eat what and however much they chose of the meals they were given.
"Interestingly, our findings suggest benefits to both diets, at least in the short-term. While the low-fat, plant-based diet helps curb appetite, the animal-based, low-carb diet resulted in lower and more steady insulin and glucose levels," Hall said. "We don't yet know if these differences would be sustained over the long term."
The researchers note that the study was not designed to make diet recommendations for weight loss, and results may have been different if participants were actively trying to lose weight. Further, all meals were prepared and provided for participants in an inpatient setting, which may make results difficult to repeat outside the lab, where factors such as food costs, food availability, and meal preparation constraints can make adherence to diets challenging. The tightly controlled clinical environment, however, ensured objective measurement of food intake and accuracy of data.
"To help us achieve good nutrition, rigorous science is critical ? and of particular importance now, in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, as we aim to identify strategies to help us stay healthy," said NIDDK Director Griffin P. Rodgers, M.D. "This study brings us closer to answering long-sought questions about how what we eat affects our health."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the NIDDK Intramural Research Program. Additional NIH
support came from the National Institute of Nursing Research under grant 1Z1ANR000035-01.
About the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): The NIDDK, a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), conducts and supports research on diabetes and other endocrine and metabolic diseases; digestive diseases, nutrition and obesity; and kidney, urologic and hematologic diseases. Spanning the full spectrum of medicine and afflicting people of all ages and ethnic groups, these diseases encompass some of the most common, severe, and disabling conditions affecting Americans. For more information about the NIDDK and its programs, see http://www.niddk.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
Hall KD, et al. Effect of a plant-based, low-fat diet versus an animal-based, ketogenic diet on ad libitum energy intake. Nature Medicine. January 21, 2021.
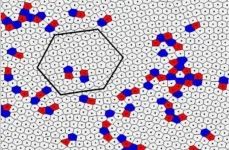
Scientists from the Joint Institute for High Temperatures Russian Academy of Sciences (JIHT RAS) and Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT) have experimentally confirmed the presence of an intermediate phase between the crystalline and liquid states in a monolayer dusty plasma system. The theoretical prediction of the intermediate - hexatic - phase was honoured with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2016: the prize was awarded to Michael Kosterlitz, David Thouless and Duncan Haldane with the formulation "for theoretical discoveries of topological phase transitions and topological phases of matter."
In a scientific article in the journal Scientific Reports, the JIHT RAS scientists published their observations ...
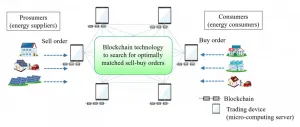
A Tokyo Tech research team led by Specially Appointed Professor Takuya Oda of the Institute of Innovative Research and Professor Keisuke Tanaka of the School of Computing, in collaboration with Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, has developed a new technology an original blockchain[1] technology that can optimize peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading[2]. The technology is expected to contribute to more effective use of surplus electricity from renewable energy by creating trading environments that flexibly respond to shared trading needs, particularly to ...
DANVILLE, Pa. - An analysis of data collected from patients treated for ischemic stroke at Geisinger shows no disparity in outcomes based solely on sex.
Various studies have suggested that women are disproportionately affected by stroke and may have poorer stroke outcomes. Women have a longer life expectancy than men and, therefore, likely have an increased lifetime risk of stroke. Women tend to be older than men at the time of stroke and have a higher pre-stroke degree of disability or dependence in their daily activities, which may contribute to worse outcomes. Rural populations may also have a higher risk of stroke based on a greater incidence of conditions ...
People with anxiety and depression are more likely to report an increase in drinking during the COVID-19 pandemic than those without mental health issues, according to a new study by researchers at NYU School of Global Public Health published in the journal Preventive Medicine. While drinking grew the most among younger people, older adults with anxiety and depression saw a sharper increase in their risk for harmful alcohol use.
"This increase in drinking, particularly among people with anxiety and depression, is consistent with concerns that the pandemic may be triggering an epidemic of problematic ...
Genetic rewiring could have driven an evolutionary explosion in the shapes, sizes and adaptations of cichlid fish, in East Africa's answer to Darwin's Galapagos finches.
Published in BMC Genome Biology, an Earlham Institute (EI) study, with collaborators at the University of East Anglia (UEA) and Wisconsin Institute for Discovery, shows that 'genetic rewiring' at non-coding regions - rather than mutations to protein-coding regions of genes - may play an important role in how cichlid fish are able to rapidly adapt to fill a staggeringly wide range of environmental niches in the East African Rift lakes.
The results ...
ATLANTA - JANUARY 19, 2021 - A new study finds that alcohol consumption accounts for a considerable portion of cancer incidence and mortality in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. The article, which appears in Cancer Epidemiology, states that the proportion of cancer cases attributable to alcohol consumption ranged from a high of 6.7% in Delaware to a low of 2.9% in Utah. Similarly, Delaware had the highest proportion of alcohol-related cancer deaths (4.5%) and Utah had the lowest (1.9%).
This study conducted by Farhad Islami, MD, PhD, and colleagues at the American Cancer Society is the first to estimate contemporary proportions and counts of alcohol-attributable ...
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by erythematous (red) patches and plaques. In some patients, psoriasis may be associated with comorbidities such as arthritis, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, hyperlipidemia, or depression. Psoriasis lesions can occur on the scalp and face, in addition to all other areas of the body, causing considerable physical discomfort and psychosocial trauma from the stigma surrounding appearance defects.
More than 90% of patients with psoriasis have what is called psoriasis vulgaris, which is characterized ...
Researchers in the UK and the United States have succeeded in 'fine tuning' a new thermoplastic biomaterial to enable both the rate at which it degrades in the body and its mechanical properties to be controlled independently.
The material, a type of polyester, has been designed for use in soft tissue repair or flexible bioelectronics by a team at the University of Birmingham in the UK and Duke University in the US.
Materials that successfully replicate the necessary elasticity and strength of biological tissues but which also biodegrade over an appropriate timescale are extremely ...
DANVILLE, Pa. - A team of Geisinger researchers has identified a common genetic variant as a risk factor for stroke, especially in patients older than 65.
Cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) causes about a quarter of ischemic strokes worldwide and is the most common cause of vascular dementia. SVD can manifest as lesions on the brain, which typically appear on brain scan images. SVD is commonly associated with aging and hypertension, but a minority of cases are caused by cysteine altering variants in the NOTCH3 gene. Approximately 1 in 300 people have this type of gene variant. A rare hereditary condition known as cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, or CADASIL, which is caused by this gene variant, has been associated with ...
Fear of losing your job, worrying about you or a loved one getting sick, and online meetups with family and friends you have not seen for months. The COVID-19 lockdown has completely changed everyday life for most people around the world. Physical distancing is the new normal and an extremely important tool in the fight against the pandemic.
However, the effects of the lockdown on mental health are alarming - especially for young people under 30 and people with preexisting mental health issues. This is the conclusion of a new study from the University ...