Methamphetamine overdose deaths rise sharply nationwide
NIH-supported study finds biggest increase among American Indians and Alaska Natives
2021-01-20
(Press-News.org) Methamphetamine overdose deaths surged in an eight-year period in the United States, according to a study published today in JAMA Psychiatry. The analysis revealed rapid rises across all racial and ethnic groups, but American Indians and Alaska Natives had the highest death rates overall. The research was conducted at the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health.
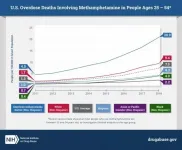
Deaths involving methamphetamines more than quadrupled among non-Hispanic American Indians and Alaska Natives from 2011-2018 (from 4.5 to 20.9 per 100,000 people) overall, with sharp increases for both men (from 5.6 to 26.4 per 100,000 from 2011-2018) and women (from 3.6 to 15.6 per 100,000 from 2012-2018) in that group. The findings highlight the urgent need to develop culturally tailored, gender-specific prevention and treatment strategies for methamphetamine use disorder to meet the unique needs of those who are most vulnerable to the growing overdose crisis. Long-term decreased access to education, high rates of poverty and discrimination in the delivery of health services are among factors thought to contribute to health disparities for American Indians and Alaska Natives.
"While much attention is focused on the opioid crisis, a methamphetamine crisis has been quietly, but actively, gaining steam--particularly among American Indians and Alaska Natives, who are disproportionately affected by a number of health conditions," said Nora D. Volkow, M.D., NIDA director and a senior author of the study. "American Indian and Alaska Native populations experience structural disadvantages but have cultural strengths that can be leveraged to prevent methamphetamine use and improve health outcomes for those living with addiction."
Shared decision-making between patient and health care provider and a holistic approach to wellness are deeply rooted traditions among some American Indian and Alaska Native groups and exist in the Indian health care system. Traditional practices, such as talking circles, in which all members of a group can provide an uninterrupted perspective, and ceremonies, such as smudging, have been integrated into the health practices of many Tribal communities. Leveraging traditions may offer a unique and culturally resonant way to promote resilience to help prevent drug use among young people. Development and implementation of other culturally appropriate and community-based prevention; targeting youth and families with positive early intervention strategies; and provider and community education may also aid prevention efforts among this population.
The study found markedly high death rates among non-Hispanic American Indians and Alaska Natives, as well as a pattern of higher overdose death rates in men compared to women within each racial/ethnic group. However, non-Hispanic American Indian and Alaska Native women had higher rates than non-Hispanic Black, Asian, or Hispanic men during 2012-2018, underscoring the exceptionally high overdose rates in American Indian and Alaska Native populations. The results also revealed that non-Hispanic Blacks had the sharpest increases in overdose death rates during 2011-2018. This represents a worrying trend in a group that had previously experienced very low rates of methamphetamine overdose deaths.
Methamphetamine use is linked to a range of serious health risks, including overdose deaths. Unlike for opioids, there are currently no FDA-approved medications for treating methamphetamine use disorder or reversing overdoses. However, behavioral therapies such as contingency management therapy can be effective in reducing harms associated with use of the drug, and a recent clinical trial reported significant therapeutic benefits with the combination of naltrexone with bupropion in patients with methamphetamine use disorders.
NIDA investigators led by Beth Han, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., obtained data used in the analysis from the 2011-2018 Multiple Cause-of-Death records from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's National Vital Statistics System, the nation's most complete database of births and deaths.
Recent national data show that most people who use methamphetamine are between 25 and 54 years old, so the investigators limited their analysis to this age group. When they examined data from this population as a whole, they found a surge in overdose deaths. Deaths involving methamphetamines rose from 1.8 to 10.1 per 100,000 men, and from 0.8 to 4.5 per 100,000 women. This represents a more than five-fold increase from 2011 to 2018.
"Identifying populations that have a higher rate of methamphetamine overdose is a crucial step toward curbing the underlying methamphetamine crisis," said Dr. Han. "By focusing on the unique needs of individuals and developing culturally tailored interventions, we can begin to move away from one-size-fits-all approaches and toward more effective, tailored interventions."
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by The National Institutes of Health's National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Han B, et al. Methamphetamine overdose deaths in the United States: Sex and racial/ethnic differences [Methamphetamine overdose deaths in the United States: Sex and racial/ethnic differences]. JAMA Psychiatry DOI: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.4321 (2021).
For more information on methamphetamines, go to: NIDA's Methamphetamine Resources.
About the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA): The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) is a component of the National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIDA supports most of the world's research on the health aspects of drug use and addiction. The Institute carries out a large variety of programs to inform policy, improve practice, and advance addiction science. Fact sheets on the health effects of drugs and information on NIDA research and other activities can be found at http://www.drugabuse.gov, which is compatible with your smartphone, iPad or tablet. To order publications in English or Spanish, call NIDA's DrugPubs research dissemination center at 1-877-NIDA-NIH or 240-645-0228 (TDD) or email requests to drugpubs@nida.nih.gov. Online ordering is available at drugpubs.drugabuse.gov. NIDA's media guide can be found at http://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/media-guide/dear-journalist, and its easy-to-read website can be found at http://www.easyread.drugabuse.gov. You can follow NIDA on Twitter and Facebook.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-20
BOSTON -- While deaths related to heart disease have declined among older people, studies suggest that death rates among younger patients have remained stagnant or increased slightly. To understand what factors put younger individuals at higher risk of premature coronary heart disease (CHD), researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital and the Mayo Clinic analyzed more than 50 risk factors in 28,024 women who participated in the decades-long Women's Health Study. Notably, women under 55 with type-2 diabetes had a tenfold greater risk of having CHD over the next two decades, with lipoprotein insulin resistance ...
2021-01-20
Over the past 20 years, scientists have been developing metamaterials, or materials that don't occur naturally and whose mechanical properties result from their designed structure rather than their chemical composition. They allow researchers to create materials with specific properties and shapes. Metamaterials are still not widely used in everyday objects, but that could soon change. Tian Chen, a post-doc at two EPFL labs - the Flexible Structures Laboratory, headed by Pedro Reis, and the Geometric Computing Laboratory, headed by Mark Pauly - has taken metamaterials one step further, ...
2021-01-20
What The Study Did: This observational study examined how COVID-19-related government-mandated closures and restrictions were associated with changes in mobility and the spread of COVID-19 in Nigeria.
Author: Daniel O. Erim, M.D., Ph.D., M.Sc., of Parexel International in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.32101)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# ...
2021-01-20
Suppose Smokey the Bear were to go on a tear and start setting forest fires instead of putting them out. That roughly describes the behavior of certain cells of our immune system that become increasingly irascible as we grow older. Instead of stamping out embers, they stoke the flames of chronic inflammation.
Biologists have long theorized that reducing this inflammation could slow the aging process and delay the onset of age-associated conditions, such as heart disease, Alzheimer's disease, cancer and frailty, and perhaps even forestall the gradual loss of mental acuity that happens to nearly everyone.
Yet the question of ...
2021-01-20
What The Study Did: Researchers examined individuals' motivation to self-test and to distribute self-test kits given the urgent need to increase COVID-19 testing coverage and contact tracing.
Author: Cedric Bien-Gund, M.D., of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.34001)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # ...
2021-01-20
What The Study Did: This investigation analyzed U.S. county-level associations of income inequality, racial/ethnic composition and political attributes with COVID-19 cases and mortality.
Author: Tim F. Liao, Ph.D., of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.34578)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: ...
2021-01-20
Many patients with multiple myeloma, a type of blood cancer, eventually develop resistance to one treatment after another. That's in part because cancer stem cells drive the disease -- cells that continually self-renew. If a therapy can't completely destroy these malignant stem cells, the cancer is likely to keep coming back.
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Ionis Pharmaceuticals are taking a new, targeted approach to myeloma treatment -- silencing IRF4, a gene that allows myeloma stem cells and tumor cells to proliferate and survive. Past studies have shown that high IRF4 levels are associated with lower overall survival rates for patients with the disease.
In a study published ...
2021-01-20
Attine ants are farmers, and they grow fungus as food. Pseudonocardia and Streptomyces bacteria are their farmhands, producing metabolites that protect the crop from pathogens. Surprisingly, these metabolites lack common structural features across bacteria from different geographic locations, even though the ants share a common ancestor. Now, researchers report in ACS Central Science they have identified the first shared antifungal compound among many of these bacteria across Brazil. The compound could someday have medical applications.
Attine ants originated as one species at a single location in the Amazon 50 million years ago. They have evolved to 200 species that have spread their farming practices ...
2021-01-20
Renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, could help decrease the world's reliance on fossil fuels. But first, power companies need a safe, cost-effective way to store the energy for later use. Massive lithium-ion batteries can do the job, but they suffer from safety issues and limited lithium availability. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Nano Letters have made a prototype of an anode-free, zinc-based battery that uses low-cost, naturally abundant materials.
Aqueous zinc-based batteries have been previously explored for grid-scale energy storage ...
2021-01-20
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Approximately 1.5 million heart attacks and strokes occur every year in men and women in the U.S. Sex and age play a large part in who experiences a heart attack, the methods used to treat these heart attacks, and the eventual post hospital outcomes of the people who experience heart attacks. Mayo Clinic researchers discuss these sex and age differences in study findings published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
In this study, Mayo Clinic researchers wanted to see if age was a key factor in sex-related differences in patients with a heart attack. Using public all-payer hospitalization data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, the team of researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Methamphetamine overdose deaths rise sharply nationwide
NIH-supported study finds biggest increase among American Indians and Alaska Natives
