Using VR training to boost our sense of agency and improve motor control
2021-01-21
(Press-News.org) With Japan's society rapidly aging, there has been a sharp increase in patients who experience motor dysfunctions. Rehabilitation is key to overcoming such ailments.
A researcher from Tohoku University has developed a new virtual reality (VR) based method that can benefit rehabilitation and sports training by increasing bodily awareness and?improving motor control.
His research was published in the Journal Scientific Report.
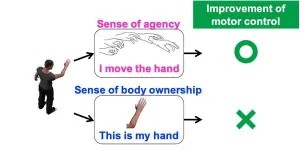
Not only can we see and touch our body, but we can sense it too. Our body is constantly firing off information to our brains that tell us where our limbs are in real-time. This process makes us aware of our body and gives us ownership over it. Meanwhile, our ability to control the movement and actions of our body parts voluntarily affords us agency over our body.
Ownership and agency are highly integrated and are related to our motor control. However, separating our sense of body ownership from our sense of agency has long evaded researchers, making it difficult to ascertain whether both ownership and agency truly affect motor control.
Professor Kazumichi Matsumiya from the Graduate School of Information Sciences at Tohoku University could isolate these two senses by using VR. Participants viewed a computer-generated hand, and Matsumiya independently measured their sense of ownership and agency over the hand.
"I found that motor control is improved when participants experienced a sense of agency over the artificial body, regardless of their sense of body ownership," said Matsumiya. "Our findings suggest that artificial manipulation of agency will enhance the effectiveness of rehabilitation and aid sports training techniques to improve overall motor control."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-21
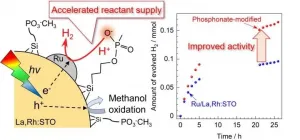
Water splitting research for solar hydrogen production has focused on physical processes inside the semiconductor, such as light absorption, charge separation, and chemical processes on the surface that are highly complex and rely on the development of new materials. However, processes inside the solution had yet to be thoroughly explored.
One recent approach to improve photocatalytic hydrogen production was proposed by loading phosphonate groups on the surface of the visible-light-responsive photocatalyst lanthanum and rhodium-doped strontium titanate (La,Rh:STO) with a silane coupling agent. The phosphonate functional group functions as a mediator of proton supply (i.e., promotes the supply of reactants) and improves hydrogen production activity.
There have been ...
2021-01-21
Just a few millimetres thick, articular cartilage plays a crucial role in our musculoskeletal system, since it is responsible for smooth (in the truest sense of the word) movement. However, the downside of its particular structure is that even minor injuries do not regenerate. Timely treatment of cartilage damage is therefore essential. Biomaterials are often used to support the cells, their distribution and protection. In most cases, this treatment significantly improves the patient's clinical symptoms but fails to fully restore the cartilage to its original state. The working group led by Sylvia Nürnberger (MedUni Vienna's Department of Orthopedics and Trauma Surgery) ...
2021-01-21
One of Brazil's worst environmental disasters - a dam collapse that also killed more than 200 people - could have been foreseen with the right monitoring technology, according to a new study by the University of Nottingham and Durham University.
The high-profile catastrophe took place on 25 January 2019 at a tailings dam near the Córrego do Feijão iron ore mine, close to the town of Brumadinho, in Minas Gerais state, south-east Brazil.
When the dam collapsed, it caused a torrent of sludge to cover surrounding land; taking lives, destroying homes and livelihoods and polluting rivers with toxic material.
Owned by Vale, Brazil's largest mining company, the tailings dam was ...
2021-01-21
A protein found commonly in human blood might help with the detection of hard-to-diagnose pancreatic tumours. Researchers at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), the Alfried Krupp Hospital in Essen and the University of Witten/Herdecke have developed approach using the protein's structure and its function as a proxy for this. In a first study in ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science, the team shows how its method can also be used to differentiate between benign and malignant tumours.
Pancreatic cancer is particularly insidious: "It remains asymptomatic for a long time, which leads to very late diagnoses and therefore a low chance of treating it successfully," says Dr Marcos Gelos from the Alfried Krupp Hospital and Witten/Herdecke University who ...
2021-01-21
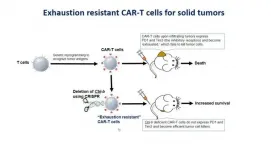
DALLAS - Jan. 19, 2021 - Eliminating a single gene can turn exhausted cancer-fighting immune cells known as CD8+ T cells back into refreshed soldiers that can continue to battle malignant tumors, a new study led by UT Southwestern researchers suggests. The findings, published online this week in the Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer, could offer a new way to harness the body's immune system to attack cancers.
In 2017, the Food and Drug Administration approved treatments involving chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells, which consist of immune cells known as T cells that ...
2021-01-21
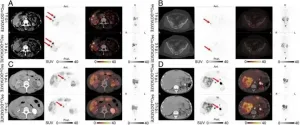
Reston, Virginia--The imaging time window of 64Cu-DOTATATE positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) for patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms can be expanded from one hour to three hours post-injection, according to new research published in the January issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine. In a head-to-head comparison of scans performed at the two time intervals, there were no significant differences in the number of lesions detected, and tumor-to-normal tissue ratios remained high in all key organs.
Previous research has demonstrated that 64Cu-DOTATATE PET imaging at one hour post-injection provides excellent lesion detection in patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms. "Given the long half-life and excellent image resolution of 64Cu-DOTATATE, ...
2021-01-21
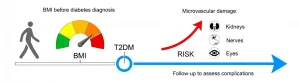
Successful weight loss is considered to be an integral part of the therapy for type 2 diabetes. Nevertheless, studies keep appearing that question the importance of losing weight. However, new data from a large-scale observational study carried out at DIfE in cooperation with the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) support the current recommendations of physicians. The findings, published in the journal Diabetologia, suggest that obesity and weight gain can lead to vascular disorders, the leading cause of disease and death for people with type 2 diabetes.
A close look at vascular disorders
Weight plays a crucial role in the development of type 2 diabetes. However, ...
2021-01-21
Chemical engineers at UNSW Sydney have found a way to make 'green' ammonia from air, water and renewable electricity that does not require the high temperatures, high pressure and huge infrastructure currently needed to produce this essential compound.
And the new production method - demonstrated in a laboratory-based proof of concept - also has the potential to play a role in the global transition towards a hydrogen economy, where ammonia is increasingly seen as a solution to the problem of storing and transporting hydrogen energy.
In a paper published today in Energy and Environmental Science, the authors from UNSW and University of Sydney say that ammonia synthesis was one of the critical achievements of the 20th century. When used in fertilisers ...
2021-01-21
It takes a lot to make a wooden table. Grow a tree, cut it down, transport it, mill it ... you get the point. It's a decades-long process. Luis Fernando Velásquez-García suggests a simpler solution: "If you want a table, then you should just grow a table."
Researchers in Velásquez-García's group have proposed a way to grow certain plant tissues, such as wood and fiber, in a lab. Still in its early stages, the idea is akin in some ways to cultured meat -- an opportunity to streamline the production of biomaterials. The team demonstrated the concept by growing structures made of wood-like cells from an initial sample of cells extracted from zinnia leaves.
While that's still ...
2021-01-21
Hokkaido University scientists have found a way to prevent gold nanoparticles from clumping, which could help towards their use as an anti-cancer therapy.
Attaching ring-shaped synthetic compounds to gold nanoparticles helps them retain their essential light-absorbing properties, Hokkaido University researchers report in the journal Nature Communications.
Metal nanoparticles have unique light-absorbing properties, making them interesting for a wide range of optical, electronic and biomedical applications. For example, if delivered to a tumour, they could react with applied light to kill cancerous tissue. A problem with this approach, though, is that they easily clump together in solution, losing their ability to absorb light. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Using VR training to boost our sense of agency and improve motor control