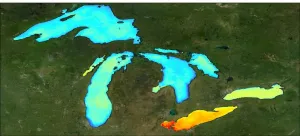
(Press-News.org) NASA-funded research on the 11 largest freshwater lakes in the world coupled field and satellite observations to provide a new understanding of how large bodies of water fix carbon, as well as how a changing climate and lakes interact.
Scientists at the Michigan Tech Research Institute (MTRI) studied the five Laurentian Great Lakes bordering the U.S. and Canada; the three African Great Lakes, Tanganyika, Victoria and Malawi; Lake Baikal in Russia; and Great Bear and Great Slave lakes in Canada.
These 11 lakes hold more than 50% of the surface freshwater that millions of people and countless other creatures rely on, underscoring the importance of understanding how they are being altered by climate change and other factors.
The two Canadian lakes and Lake Tanganyika saw the greatest changes in primary productivity -- the growth of algae in a water body. Productivity fluctuations point to big changes in lake ecosystems.
"The base of the food chain in these lakes is algal productivity. These lakes are oceanic in size, and are teaming with phytoplankton -- small algae," said co-author Gary Fahnenstiel, a fellow at MTRI and recently retired senior research scientist for NOAA's Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory. "We measured the carbon fixation rate, which is the rate at which the algae photosynthesize in these lakes. As that rate changes, whether increasing or decreasing, it means the whole lake is changing, which has ramifications all the way up the food chain, from the zooplankton to the fish."
Many factors affect these lakes. Climate change, increasing nutrients (eutrophication) and invasive species all combine to wreak systemwide change -- making it difficult to pinpoint specific causes, particularly from the ground with limited on-site observations.
Counting Phytoplankton with Color
But satellite imagery has made sorting through the noise easier and provides insights over time and space. Michael Sayers, MTRI research scientist and study lead author, uses ocean color remote sensing -- making inferences about type and quantity of phytoplankton based on the color of the water -- to track freshwater phytoplankton dynamics.
"We've relied on NASA assets -- the MODIS satellite, which has been flying since 2002, to which we apply the algorithm and model we've been developing at MTRI for a decade," Sayers said. "When we start to tally the numbers of pixels as observations globally for 11 lakes for 16 years, it is really quite remarkable." The pixels observed per lake number "in the millions," he added.
One of the most remarkable aspects of the results is just how fast changes in these freshwater lakes have occurred -- a noticeable amount in fewer than 20 years. The research contributes to NASA's Carbon Monitoring System's goal of determining how much freshwater lakes contribute to the global carbon cycle.
"Three of the largest lakes in the world are showing major changes related to climate change, with a 20-25% change in overall biological productivity in just the past 16 years," Fahnenstiel said.
More Than Algae
In the 16 years of data, Great Bear and Great Slave lakes in northern Canada saw the greatest increases in productivity, while Lake Tanganyika in southeastern Africa has seen decreases. The trends are linked to increases in water temperatures, as well as solar radiation and a reduction in wind speed.
Sayers said looking at productivity, algal abundance, water clarity, water temperature, solar radiation and wind speeds at freshwater lakes provides a richer picture of the overall ecosystem.
"Temperature and solar radiation are factors of climate change," Sayers said. "Chlorophyll and water transparency changes are not necessarily caused by climate change, but could be caused by eutrophication or invasive species, like quagga mussels."
The researchers used lake measurements performed by the Great Lakes Research Center research vessel fleet to ground truth the satellite observations and to provide input for model estimates.
The article "Carbon Fixation Trends in Eleven of the World's Largest Lakes: 2003-2018" is published in the journal Water. The researchers plan to continue their research, applying what they've learned so far to the role harmful algal blooms have on carbon flux to the atmosphere.
As the saying goes, water is life. Gaining a better understanding of how lake productivity changes affect the bodies of water so many people rely on is important to the communities who live on the lakeshores. It's also significant to the global community as we delve deeper into the role freshwater lakes play in the global carbon cycle and climate change.
Sidebar: How Do Lakes Fix Carbon?
Phytoplankton are microscopic algae that photosynthesize, or make energy from sunlight. Carbon fixation is a part of photosynthesis -- inorganic carbon (particularly carbon dioxide) is converted into an organic compound by an organism. All living things on Earth contain organic carbon. The amount of phytoplankton and the rate at which they photosynthesize equal the carbon fixation rate in a lake.
INFORMATION:
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- In the dark waters of Lake Superior, a fish species adapted to regain a genetic trait that may have helped its ancient ancestors see in the ocean, a study finds.
The research focuses on kiyis, which inhabit Lake Superior at depths of about 80 to over 200 meters deep. These fish, known to scientists as "Coregonus kiyi," belong to a group of closely related salmonids known as ciscoes.
In contrast to three other Lake Superior ciscoes that dwell and feed in shallower regions of water, the kiyis are far more likely to carry a version of the rhodopsin gene that probably improves vision in dim "blue-shifted" waters, ...
Curtin University researchers have uncovered a method of making silicon, found commonly in electronics such as phones, cameras and computers, at room temperature.
The new technique works by replacing extreme heat with electrical currents to produce the same chemical reaction that turns silica into silicon at a reduced economic and environmental cost.
Lead researcher, PhD candidate Song Zhang from Curtin's School of Molecular and Life Sciences said that while the team's discovery was made at the nanoscale, it defines a way of replacing thermochemical processes with electrochemical processes, which ...
With the recent explosive demand for data storage, ranging from data centers to various smart and connected devices, the need for higher-capacity and more compact memory devices is constantly increasing. As a result, semiconductor devices are now moving from 2D to 3D. The 3D-NAND flash memory is the most commercially successful 3D semiconductor device today, and its demand for supporting our data-driven world is now growing exponentially.
The scaling law for 3D devices is achieved by stacking more and more semiconductor layers, well above 100 layers, in a more reliable way. As each layer thickness corresponds to the effective channel length, accurate characterization and control of layer-by-layer thickness is critical. To date, ...
Giant ambush-predator worms, possible ancestors of the 'bobbit worm', may have colonized the seafloor of the Eurasian continent around 20 million years ago. The findings, based on the reconstruction of large, L-shaped burrows from layers of seafloor dating back to the Miocene (23 million to 5.3 million years ago) of northeast Taiwan, are reported in Scientific Reports this week.
Ludvig Löwemark and colleagues reconstructed a new trace fossil, which they name Pennichnus formosae, using 319 specimens preserved within layers of seafloor formed during the Miocene era across northeast Taiwan. Trace fossils are geological features such as burrows, track marks and plant root cavities preserved ...
BOSTON - Four years after patients with melanoma were treated with a personalized cancer vaccine, the immune response kindled by the vaccine remains robust and effective in keeping cancer cells under control, researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Brigham and Women's Hospital, and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard report in a new study.
The findings, published online today by the journal Nature Medicine, demonstrate the staying power of the immune response generated by the vaccine, known as NeoVax, which works by targeting specific proteins on each patient's tumor cells. The researchers found that, nearly four ...
While it has been reported that opioid overdose deaths have increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, a new study looking at data in Philadelphia showed that this hardship has been overwhelmingly suffered by Black individuals. Researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania analyzed the period of time after the city's stay-at-home order was announced in 2020 and showed that, compared to the year before, the number of fatal overdoses suffered by Black individuals spiked by more than 50 percent. At the same time, the rate for white individuals actually fell by 31 percent over the same period. This research ...
PORTLAND, OR - A first-of-its-kind randomized clinical trial found that patients with pancreatic cancer didn't live any longer than expected after receiving pre-operative chemotherapy from either of the two standard regimens, according to trial results published in JAMA Oncology.
While the trial findings did not show a direct patient benefit, they do show that it's possible to safely administer chemotherapy prior to pancreatic cancer surgery. They also pave the way for better treatment testing for this notorious killer. With no symptoms in the early stages, and few effective therapies, pancreatic cancer is the fourth-most deadly cancer type in the United ...
What The Study Did: This study monitored suicide-related internet search rates during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States and researchers report searches for suicide decreased during that time. Although this study cannot independently confirm that changes in search rates were caused by changes in population-level suicide rates, it showed that COVID-19 may have been inversely associated with population suicide trends between March and July 2020.
Authors: John W. Ayers, Ph.D., M.A., of theUniversity of California San Diego, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.34261)
Editor's ...
What The Study Did: Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in human corneas was examined in this study.
Authors: Maria Casagrande, M.D., of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Hamburg, Germany, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2020.6339)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full article is linked to this news release.
Embed ...
What The Study Did: Researchers assembled suicide death data for people 10 and older from January 2015 through May 2020 in this observational study and they report stable rates of suicide deaths during the COVID-19 stay-at-home advisory in Massachusetts, a finding that paralleles others following ecological disasters.
Authors: Jeremy Samuel Faust, M.D., M.S., of Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.34273)
Editor's ...