INFORMATION:
Other contributors include LIU Lu and XU Jian, Single-Cell Center, CAS Key Laboratory of Biofuels, Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT); CUI Wenzhi, College of Control Science and Engineering, China University of Petroleum; and ZHANG Yufeng, College of Computer Science and Technology, Qingdao University.
The Natural Science Foundation of China, the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation supported this work.
Meta-Apo supports cheaper, quicker microbiome functional assessment
2021-01-22
(Press-News.org) A new algorithm may reduce the need for expensive, time-consuming whole-genome sequencing computations to understand how a microbiome functions. A team led by JING Gongchao of the Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and SU Xiaoquan of Qingdao University, published their approach, called Meta-Apo, on Jan. 6 in BMC Genomics.
Researchers routinely sequence samples of microbial communities found on human skin, in human guts, and in the environment to understand what genes they contain with the ultimate goal of understanding how they function.
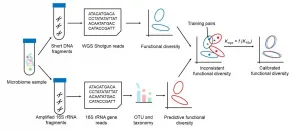
According to JING, the first author of the study, two main approaches exist: shotgun whole-genome sequencing and 16S rRNA gene amplicons. Whole-genome sequencing requires significant sequencing cost as well as computing power to determine all of the genes and their functions in a single sample, while 16S rRNA gene amplicons can quickly tease out a sample's specific gene for taxonomy information and thus predict how they function.
"However, due to the potential biases in how the amplicons are prepared and gene profile variation among genomes, functional profiles predicted from 16S amplicons may deviate from whole-genome sequencing ones, resulting in misleading results," said JING. "Our approach, Meta-Apo, greatly reduces or even eliminates such deviation, deducing more consistent diversity patterns between the two approaches."
Meta-Apo matches pairs of data from whole-genome sequencing and 16S amplicons - each pair is sequenced via both methods - to teach new 16S amplicon samples to better recognize gene function. The results are much more consistent with the whole-genome sequencing results.
"Tests of Meta-Apo on more than 5,000 16S amplicon human microbiome samples from four body sites showed the deviation between the two strategies is significantly reduced by using only 15 training sample pairs," JING added. "Moreover, Meta-Apo enables cross-platform functional comparison between whole-genome sequencing and amplicon samples, greatly improving 16S-based microbiome diagnoses."
To test this experimentally, the researchers were able to improve the accuracy of a gingivitis diagnosis from 65% to 95% percent using the 16S-derived functional profiles, produced by training the whole-genome sequencing pairs.
"With the low cost of 16S-amplicon sequencing, Meta-Apo can produce a reliable, high-resolution view of microbiome function equivalent to that offered by shotgun whole-genome sequencing," SU, senior author of the study, explained.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cargo delivery by polymers
2021-01-22
Degradable, bio-based polymers offer options for chemical recycling, and they can be a tool to store and release useful molecules. Scientists have developed a class of sugar-based polymers that are degradable through acid hydrolysis. The researchers also integrated "cargo" molecules in the polymer, which are designed to split off after polymer degradation. Degradable, cargo-bearing polymers are important for medical and sensor applications, says the study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Most plastics resist natural degradation processes. Consequently, increasing contamination of the environment with plastics has led to a call for degradable plastics. Such materials can be subjected to chemical recycling processes, in which chemical reactions break up polymer bonds. ...
Microbiome Search Engine 2 helps researchers explore microbiome space
2021-01-22
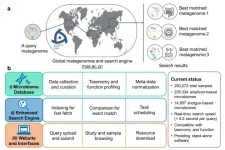
Metagenomics - the study of genetic material from an environmental sample - is growing as species evolve or are discovered across the globe. To correlate the newly developed microbiomes with existing data sets, a team of researchers based in China has developed the Microbiome Search Engine 2 (MSE 2). It was published on Jan. 19 in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Here, we introduce MSE 2, a microbiome database platform for searching query microbiomes in the global metagenome data space based on taxonomic or functional similarity of the whole microbiome," ...
Research shows preference for male children is declining in Bangladesh
2021-01-22
Research from the University of Kent has demonstrated a decline in 'son preference' by women of childbearing age in Bangladesh. However, the study also shows that fertility decisions are still influenced according to son preference.
The paper, 'Is son preference disappearing from Bangladesh?', surveyed a nationally representative sample of Bangladeshi women of childbearing age, born between 1975 and 1994, to assess how son preference is evolving.
The term 'son preference' refers to any situation where parents value sons over daughters and make resulting choices accordingly, which can have a strong economic and demographic impact.
The study finds that among women of childbearing age in ...
CT identifies patients with high-risk nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
2021-01-22
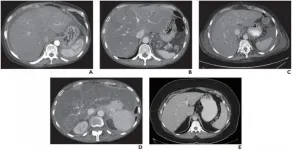
Leesburg, VA, January 22, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) and multiple CT findings can identify patients with high-risk nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)--advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis, that is--though the presence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) remains elusive on CT.
"Subjective assessment of multiple morphologic and separately quantified parameters by trained readers and a simple quantitative three-parameter model combining two CT features, liver surface nodularity (LSN) and liver segmental volume ratio (LSVR), and a clinical score (FIB-4) showed good association with presence of advanced fibrosis," wrote first author Meghan G. Lubner from the department of radiology at the University of Wisconsin School ...
Magnetic waves explain mystery of Sun's outer layer
2021-01-22
The Sun's extremely hot outer layer, the corona, has a very different chemical composition from the cooler inner layers, but the reason for this has puzzled scientists for decades.
One explanation is that, in the middle layer (the chromosphere), magnetic waves exert a force that separates the Sun's plasma into different components, so that only the ion particles are transported into the corona, while leaving neutral particles behind (thus leading to a build-up of elements such as iron, silicon and magnesium in the outer atmosphere).
Now, in a new study published ...
Patients of Asian and black backgrounds more likely to die from COVID, large study reveals
2021-01-22
Patients of Asian and black backgrounds suffered disproportionate rates of premature death from COVID-19, according to a study of 1,737 patients by Queen Mary University of London and Barts Health NHS Trust.
The study, published in BMJ Open, is one of the most comprehensive studies exploring COVID-19 outcomes in black, Asian and minority ethnic populations so far reported, from one of the largest and most diverse UK hospital COVID-19 cohorts, representing a majority ethnically diverse population (only 35.2 per cent of patients identified as White ethnicity).
The work resulted from a new interdisciplinary collaboration between intensive care physicians and HIV physicians. The researchers looked at data from all patients ...
Geoscientists reconstruct 6.5 million years of sea level stands
2021-01-22
TAMPA, Fla. (January 22, 2021)- The pressing concern posed by rising sea levels has created a critical need for scientists to precisely predict how quickly the oceans will rise in coming centuries. To gain insight into future ice sheet stability and sea-level rise, new research from an international team led by University of South Florida geoscientists is drawing on evidence from past interglacial periods when Earth's climate was warmer than today.
Using deposits in the caves of the Mediterranean island of Mallorca, known as phreatic overgrowths ...
Stanford: forecasting coastal water quality
2021-01-22
Less than two days of water quality sampling at local beaches may be all that's needed to reduce illnesses among millions of beachgoers every year due to contaminated water, according to new Stanford research. The study, published in Environmental Science & Technology, presents a modeling framework that dependably predicts water quality at beaches after only a day or two of frequent water sampling. The approach, tested in California, could be used to keep tabs on otherwise unmonitored coastal areas, which is key to protecting the well-being of beachgoers and thriving ocean economies ...
Methods in studying cycad leaf nutrition found to be inconsistent and incomplete
2021-01-22
Collective research to date regarding nutrients found in the leaves of contemporary cycad species has been inconsistent as far as data collection and narrow in scope, according to a University of Guam-led literature review published on Nov. 19 in Horticulturae journal.
Understanding nutrient accumulation within cycads is essential to effective horticultural management, and more importantly, conservation of this plant group, which is highly prized within the horticulture trade and also threatened worldwide.
"Cycads comprise the most threatened group of plants worldwide, ...
PTSD link to pandemic panic
2021-01-22
Even at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic last year, people around the world became more fearful of what could happen to them or their family.
A new Flinders University study of 1040 online participants from five western countries published in PLOS ONE explores people's response to the stresses of the escalating pandemic, finding more than 13% of the sample had post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) related symptoms consistent with levels necessary to qualify for a clinical diagnosis.
With ongoing economic and social fallout, and death toll of more than 2 million, the team of psychology researchers warn more needs to be done to cope with ...