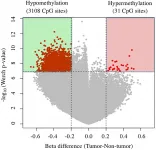
(Press-News.org) The cover for issue 52 of Oncotarget features Figure 1, "Volcano plots of DNA methylation in tumor tissues compared with nontumor tissue," published in "Reduction of T-Box 15 gene expression in tumor tissue is a prognostic biomarker for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma" by Morine, et al. which reported that the authors conducted a genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation of the tumor and non-tumor tissue of 15 patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and revealed TBX15 was the most hypermethylated gene of the tumor.
Another validation set, which comprised 58 HCC with radical resection, was analyzed to investigate the relationships between tumor phenotype and TBX15 mRNA expression.
TBX15 mRNA levels in tumor tissues were significantly lower compared with those of nontumor tissues.
Multivariate analysis identified low TBX15 expression as an independent prognostic factor for overall and disease-free survival.
Therefore, genome-wide DNA methylation profiling indicates that hypermethylation and reduced expression of TBX15 in tumor tissue represents a potential biomarker for predicting poor survival of patients with HCC.
Reduced expression of TBX15 in tumor tissue represents a potential biomarker for predicting poor survival of patients with HCC
Dr. Yuji Morine from the Tokushima University Graduate School said, "Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most prevalent human cancer and third-highest cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, and its incidence is significantly increasing."
Several genome-wide studies of the molecular alterations in tumor and non-tumor liver tissues addressed DNA, mRNA, and microRNA expression as well as epigenetic alterations to predict recurrence and hepatocarcinogenesis after treating patients with curative intent according to distinct gene expression or alteration patterns.
Here the Oncotarget authors focused on the epigenetic alterations of the genomes of the tumor and non-tumor cells of patients with HCC to identify the mechanisms of tumor progression and hepatocarcinogenesis because of global DNA hypomethylation or cancer specific DNA hypermethylation occurs in certain carcinomas.
They firstly chose long interspersed nuclear element-1 sequences that provided a surrogate marker of global DNA methylation levels and detected hypomethylation of LINE-1 in HCC tissues, which was significantly associated with poor prognosis of patients with HCC through the activation of MET.
Further, they investigated epigenetic characteristics with array-based analysis of DNA methylation using the Illumina Human Methylation 450 BeadChip and identified specific DNA methylation profiling in nontumor liver tissue of patients without HCV and HBV detectable infection, which possibly contributed to the development of HCC.
In this study, they analyzed DNA methylation profiles in tumor tissue of HCC using those case series of their recent study, and found the most hypermethylated gene in tumor compared with nontumor tissues, encodes T-box 15, implicating TBX15 as a candidate regulator of tumor progression.
The Morine Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Paper that together, the present and previous findings support the importance of conducting further investigations to determine the role of TBX15 in cancer, particularly in tumor progression.
Second, selection bias was possible, because of the retrospective one.
Third, the authors did not determine the actual mechanism of TBX15 for tumor malignancy in a basic experiment.
Those issues should be solved in several cancers, to clarify the true function of TBX15 for tumor malignancy in each cancer.
In conclusion, reduced expression of TBX15 may serve as a potential biomarker for predicting tumor progression and poor survival as well as a target for antitumor therapy in HCC.
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27852
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/27852/text/
Correspondence to - Yuji Morine - ymorine@tokushima-u.ac.jp
Keywords -
genome-wide analysis,
methylation,
tumor suppressor gene,
prognostic biomarker,
hepatocellular carcinoma
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a biweekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit http://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
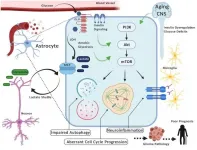
Aging-US Issue 1 Volume 13 features "PAM (PIK3/AKT/mTOR) signaling in glia: potential contributions to brain tumors in aging" which reported that despite a growing proportion of aged individuals at risk for developing cancer in the brain, the prognosis for these conditions remains abnormally poor due to limited knowledge of underlying mechanisms and minimal treatment options.
While cancer metabolism in other organs is commonly associated with upregulated glycolysis and hyperactivation of PIK3/AKT/mTOR pathways, the unique bioenergetic demands of the central nervous system ...
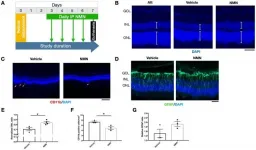
Aging-US published "Neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of action of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) in a photoreceptor degenerative model of retinal detachment" which reported that here, the authors investigated nicotinamide mononucleotide, a precursor of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, in a retinal detachment induced photoreceptor degeneration.
NMN administration after RD resulted in a significant reduction of TUNEL photoreceptors, CD11b macrophages, and GFAP labeled glial activation; a normalization of protein carbonyl content, and a preservation of the outer nuclear layer thickness.
NMN administration significantly increased NAD levels, SIRT1 protein expression, and heme oxygenase-1 expression.
Delayed NMN administration still exerted protective effects after RD.
This ...
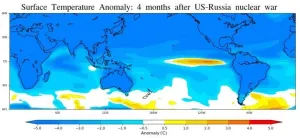
A nuclear war could trigger an unprecedented El Niño-like warming episode in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, slashing algal populations by 40 percent and likely lowering the fish catch, according to a Rutgers-led study.
The research, published in the journal END ...
DALLAS, Jan. 25, 2021 -- Psychological health can positively or negatively impact a person's health and risk factors for heart disease and stroke, according to "Psychological Health, Well-Being, and the Mind-Heart-Body Connection," a new American Heart Association Scientific Statement, published today in the Association's flagship journal Circulation. The statement evaluates the relationship between psychological health and heart health, summarizing ways to help improve psychological health for people with and at risk for heart disease.
"A person's mind, heart and body are all interconnected and interdependent in what can be termed 'the mind-heart-body-connection,'" said Glenn N. Levine, M.D., FAHA, master clinician and professor of medicine at ...
DALLAS, Jan. 25, 2021 -- The continued global burden of stroke and how it disproportionately affects women are highlighted in new science published online today in the February issue of Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association. Stroke editors selected nine manuscripts focused on stroke disparities in women in this collaboration with Go Red for Women®, the Association's global movement to end heart disease and stroke in women.
"Stroke continues to be a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, with women being more adversely affected by the global burden of stroke," said Stroke Editor-In-Chief Ralph L. Sacco, M.D., M.S., FAHA, ...
Scientists have identified a key nutrient source used by algae living on melting ice surfaces linked to rising sea levels.
The Greenland ice sheet - the second largest ice body in the world after the Antarctic ice sheet - covers almost 80% of the surface of Greenland. Over the last 25 years, surface melting and water runoff from the ice sheet has increased by about 40%.
The international research team, led by the University of Leeds, analysed samples from the southwestern margin on Greenland's 1.7 million km² ice sheet over two years.
They discovered that phosphorus containing minerals may be driving ever-larger algal blooms on the Greenland Ice Sheet. As the algal blooms grow they darken the ice surface, decreasing albedo - ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. - An international team of researchers led by Michigan State University's Morteza Mahmoudi has developed a new method to better understand how nanomedicines -- emerging diagnostics and therapies that are very small yet very intricate -- interact with patients' biomolecules.
Medicines based on nanoscopic particles have the promise to be more effective than current therapies while reducing side effects. But subtle complexities have confined most of these particles to research labs and out of clinical use, said Mahmoudi, an assistant professor in the Department of Radiology and the Precision Health Program.
"There's been a considerable investment of taxpayer money in cancer nanomedicine research, but that research hasn't successfully translated ...
Even before public announcements of the first cases of COVID-19 in Europe were made, at the end of January 2020, signals that something strange was happening were already circulating on social media. A new study of researchers at IMT School for Advanced Studies Lucca, published in END ...
The rate at which ice is disappearing across the planet is speeding up, according to new research.
And the findings also reveal that the Earth lost 28 trillion tonnes of ice between 1994 and 2017 - equivalent to a sheet of ice 100 metres thick covering the whole of the UK.
The figures have been published today (Monday, 25 January) by a research team which is the first to carry out a survey of global ice loss using satellite data.
The team, led by the University of Leeds, found that the rate of ice loss from the Earth has increased markedly within the past three decades, from 0.8 trillion tons per year in the 1990s to 1.3 trillion tons per year by 2017.
Ice melt across the globe ...
Female childhood cancer survivors face a lower likelihood of becoming pregnant than women in the general population, but once pregnant, they are not more likely to undergo an abortion. The findings come from a new study published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Cancer survivors might be reluctant to start a family due to concerns for their children's health as well as the potential recurrence of their own cancer. This could lead to a greater likelihood of induced abortions in female survivors who become pregnant.
To examine whether pregnancies of childhood cancer survivors are more likely to end with ...