Street trees close to the home may reduce the risk of depression
Researchers show positive effect of urban nature on mental health
2021-01-25
(Press-News.org) Depression, especially in urban areas, is on the rise, now more than ever. Mental health outcomes are influenced by, among other things, the type of environment where one lives. Former studies show that urban greenspace has a positive benefit on people experiencing mental ill health, but most of these studies used self-reported measures, which makes it difficult to compare the results and generalise conclusions on the effects of urban greenspace on mental health.
An interdisciplinary research team of UFZ, iDiv and Leipzig University tried to improve this issue by involving an objective indicator: prescriptions of antidepressants. To find out whether a specific type of 'everyday' green space - street trees dotting the neighbourhood sidewalks - could positively influence mental health, they focused on the questions, how the number and type of street trees and their proximity close to home correlated to the number of antidepressants prescribed.
The researchers analysed data from almost 10,000 Leipzig inhabitants, a mid-size city in Germany, who took part in the LIFE-Adult health study running at the University of Leipzig Medical Faculty. Combining that with data on the number and species type of street trees throughout the city of Leipzig, the researchers were able to identify the association between antidepressants prescriptions and the number of street trees at different distances from people's homes. Results were controlled for other factors known to be associated with depression, such as employment, gender, age, and body weight.
More trees immediately around the home (less than 100 meters) was associated with a reduced risk of being prescribed antidepressant medication. This association was especially strong for deprived groups. As these social groups are at the greatest risk for being prescribed antidepressants in Germany, street trees in cities can thereby serve as a nature-based solution for good mental health, the researchers write. At the same time, street trees may also help reduce the 'gap' in health inequality between economically different social groups. No association of tree types, however, and depression could be shown in this study.
"Our finding suggests that street trees - a small scale, publicly accessible form of urban greenspace - can help close the gap in health inequalities between economically different social groups," says lead author of the study Dr Melissa Marselle. "This is good news because street trees are relatively easy to achieve and their number can be increased without much planning effort." As an environmental psychologist, she conducted the research at UFZ and iDiv and is now based at the De Montford University of Leicester, UK. Marselle hopes that the research "should prompt local councils to plant street trees to urban areas as a way to improve mental health and reduce social inequalities. Street trees should be planted equally in residential areas to ensure those who are socially disadvantaged have equal access to receive its health benefits."
"Importantly, most planning guidance for urban greenspace is often based on purposeful visits for recreation", adds Dr Diana Bowler (iDiv, FSU, UFZ), data analyst in the team. "Our study shows that everyday nature close to home - the biodiversity you see out of the window or when walking or driving to work, school or shopping - is important for mental health." This finding is especially now in times of the COVID-19 lock-downs, Bowler adds.
And it's not only human health which could benefit. "We propose that adding street trees in residential urban areas is a nature-based solution that may not only promote mental health, but can also contribute to climate change mitigation and biodiversity conservation," says senior author Prof Aletta Bonn, who leads the department of ecosystem services at UFZ, iDiv and Friedrich-Schiller-University Jena. "To create these synergy effects, you don't even need large-scale expensive parks: more trees along the streets will do the trick. And that's a relatively inexpensive measure."
"This scientific contribution can be a foundation for city planners to save and, possibly, improve the life quality for inhabitants, in particular, in densely populated areas and in central city areas," adds Prof Toralf Kirsten from Leipzig University. "Therefore, this aspect should be taken into account when city areas are recreated and planned, despite high and increasing land cover costs. A healthy life of all living being is unaffordable."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-25
A lot is known about galaxies. We know, for instance, that the stars within them are shaped from a blend of old star dust and molecules suspended in gas. What remains a mystery, however, is the process that leads to these simple elements being pulled together to form a new star.
But now an international team of scientists, including astrophysicists from the University of Bath in the UK and the National Astronomical Observatory (OAN) in Madrid, Spain have taken a significant step towards understanding how a galaxy's gaseous content becomes organised into a new generation of stars.
Their findings have important implications for our understanding of how stars formed during the early days of the universe, when galaxy collisions were frequent and dramatic, and star and galaxy formation ...
2021-01-25
Children of mothers experiencing depressive symptoms are more at risk, as adolescents, of experiencing suicidal thoughts and attempting suicide.
New research suggests that this link may be explained by loneliness, potentially opening new ways for youth suicide prevention.
The study - by the universities of Exeter, Montréal, Laval and McGill - used data from more than 1,600 families from the Québec Longitudinal Study of Child Development, a representative sample of new-borns in Quebec followed from birth to 20 years of age.
Mothers were asked about depressive symptoms (such as sadness and losing interest ...
2021-01-25
As the world becomes aware of the imminent environmental crisis, scientists have begun a search for sustainable energy sources. Rechargeable batteries like lithium-ion batteries are seeing a popularity surge, concurrent with production of "greener" technologies such as electric propulsion ships (which are being developed to meet the environmental regulations by the International Maritime Organization) and other electric vehicles. But, lithium is rare and difficult to distribute, putting its sustainability in doubt while also risking sharp increases in cost. Researchers have thus turned ...
2021-01-25
To predict when earthquakes are likely to occur, seismologists often use statistics to monitor how clusters of seismic activity evolve over time. However, this approach often fails to anticipate the time and magnitude of large-scale earthquakes, leading to dangerous oversights in current early-warning systems. For decades, studies outside the seismology field have proposed that these major, potentially devastating seismic events are connected to a range of non-seismic phenomena - which can be observed days or even weeks before these large earthquakes occur. So far, however, this idea hasn't caught on in the wider scientific community. In this special issue, EPJ Special Topics proposes the Global Earthquake Forecasting System (GEFS): the first collaborative initiative ...
2021-01-25
Scientists have shown where bird species would exist in the absence of human activity under research that could provide a new approach to setting conservation priorities.
A study by Durham University, UK, in collaboration with the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB), investigated how human activities such as agriculture, deforestation, and the drainage of wetlands have shaped where bird species are found in Great Britain today.
Researchers used data on the geographical distributions of bird species alongside simulation models to predict where bird species would exist today if the effects of human activities on the landscape were removed.
In this scenario there were winners ...
2021-01-25
Public health researchers, led by UNSW Sydney, have estimated the number of cancer cases requiring surgery globally each year, predicting the number will rise from 9.1 million to 13.8 million from 2018 to 2040 - an increase of 52 per cent or 4.7 million cases.
Their research shows the greatest relative increase will occur in 34 low-income countries, where the number of cases requiring surgery is expected to more than double by 2040 (314,355 cases to 650,164, or 107 per cent).
The modelling study, published in The Lancet Oncology on Friday, analysed global demand for cancer surgery and estimated surgical and anaesthesia ...
2021-01-25
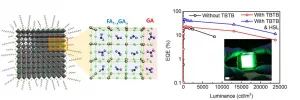
Research team at Seoul National University (Prof. Tae-Woo Lee) and University of Pennsylvania (Prof. Andrew M. Rappe) developed perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs) with an external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 23.4%. The research results were published in Nature Photonics, which is the world-renowned international academic journal, on January 4th (Title: Comprehensive defect suppression in perovskite nanocrystals for high-efficiency light-emitting diodes).
Metal halide perovskites have very narrow spectral emission, excellent color purity, low material cost, and wide and easy color-tunability. ...
2021-01-25
The Nagoya University Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM) research team of Designated Associate Professor Tsuyoshi Hirota, Postdoctoral Fellow Simon Miller, Professor Kenichiro Itami and graduate student Tsuyoshi Oshima (Research Fellowship for Young Scientists, JSPS), in collaboration with the group of Professor Ben Feringa and Postdoctoral Fellow Dušan Kolarski of Groningen University in the Netherlands, have achieved a world first: fully reversible manipulation of the period of the circadian clock using light, by exchanging part of a compound with a light-activated switch.
Waking in the ...
2021-01-25
Greater sports participation among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children is linked with better academic performance, according to new research from the University of South Australia.
Conducted in partnership with the University of Sydney and the University of Technology Sydney, the world-first study found that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children who played organised sports every year over four years, had numeracy skills which were advanced by seven months, compared to children who did less sport.
The study used data from four successive waves of Australia's Longitudinal Study of Indigenous Children, following 303 students (with a baseline age of five to six years old) to assess cumulative sports participation against ...
2021-01-25
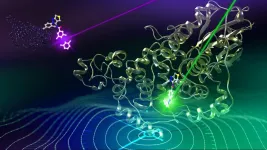
A world-first discovery by researchers at Monash University and The University of Queensland could lead to faster and more effective treatments for chronic health complications, such as cardiovascular disease and cancer, with 'fluorescent' in vivo biosensors.
The research team, led by Dr Simon Corrie from Monash University's Department of Chemical Engineering and the ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology, took an antibody that binds EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) proteins and engineered it to monitor the concentration of EGFR proteins in serum solutions over time.
Co-authors of the paper, published in ACS Sensors, are Dr Christian Fercher, Dr Martina ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Street trees close to the home may reduce the risk of depression
Researchers show positive effect of urban nature on mental health