New IU study finds most high-school age youth are willing to wear masks
2021-01-25
(Press-News.org) A new study from Indiana University researchers finds that most high-school age youth are willing to wear masks to help prevent the spread of the COVID-19 virus, but that more education is needed on how to wear masks properly and on the importance of consistent commitment to public health guidelines.
The study, published today in the Journal of Adolescent Health looked at 1,152 youth's mask wearing and social distancing behaviors during five, in-person live-streamed high school graduations from one U.S. public school district in early July 2020. These broadcasts allowed the researchers to systematically document social-distancing behaviors throughout the ceremonies and mask-wearing as students crossed the graduation stage to receive their diplomas and as they posed for photos with the school principal.
Each graduation ceremony, which took place outdoors, included safety protocols approved by the local public health department. The district also provided students with free masks bearing their school's logo and had students seated in socially-distanced chairs.
"The key to preventing the spread of the COVID-19 virus relies on scientifically-backed best practices and buy-in from the public to engage in these safety protocols," said Anna Mueller, the Luther Dana Waterman Associate Professor in sociology at IU Bloomington and co-lead author on the study. "As schools navigate how to keep students safe, young people's participation in these protocols is vital. And the good news is that teens seem willing."
The study had several key findings:
Nearly 70 percent of students wore their masks properly while receiving their diploma
Almost 10 percent wore no mask
Nearly 20 percent struggled with mask fit - the masks kept slipping low on their nose, requiring students to repeatedly pull it back up
Mask wearing varied significantly across schools, with some doing better than others
All schools struggled with social distancing, except when students were seated in socially-distanced chairs
Student graduation speakers at all schools expressed altruistic concern for the safety and well-being of their community during the pandemic
The high rate of student mask wearing is particularly interesting since the school district is in a community with low rates of community mask-wearing and no local or state mask mandate at the time of these graduations. With additional public health interventions - in schools and in the community at large - it is likely that conformity would be even higher.
"We did find evidence that adults can influence youth's mask-wearing behaviors," said Sarah Diefendorf, the other co-lead author. "This was particularly evident during the graduation pictures. When teens approached their principal for their picture, all but one student took off their mask after an adult suggested they could. Most of these students [80 percent] were wearing their mask properly just seconds before."
The study also found that how stringently school staff role modeled or facilitated public health behaviors mattered. Schools with adults who consistently wore their own masks or where adults verbally encouraging students to keep their mask on had greater youth adherence to COVID-19 guidelines.
Visible differences in schools' conformity to COVID-19 guidelines also aligned with differences in how student graduation speakers discussed the pandemic and their senior year. At the three high schools with higher rates of mask-wearing, students talked about COVID-19 alongside broader social justice issues, including the Black Lives Matter protests of 2020. However, across all five schools, students noted the seriousness of the pandemic and expressed concern for their communities.
"Students clearly cared about the health and wellbeing of their peers and their broader community, suggesting that they can be important allies in keeping schools open and as safe as possible given our circumstances," Mueller said. "But youth also learn from adults, in schools and out. So it's crucial that we make sure that parents, teachers, and other community adults get the message that masks and social-distancing are crucial to getting life back to normal and keeping schools open."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-25
Coconut oil has increasingly found its way into German kitchens in recent years, although its alleged health benefits are controversial. Scientists at the University of Bonn have now been able to show how it is metabolized in the liver. Their findings could also have implications for the treatment of certain diarrheal diseases. The results are published in the journal Molecular Metabolism.
Coconut oil differs from rapeseed or olive oil in the fatty acids it contains. Fatty acids consist of carbon atoms bonded together, usually 18 in number. In coconut oil, however, most of these chains are much shorter and contain only ...
2021-01-25
Research from North Carolina State University shows that extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and increased precipitation, affect both the amount and the composition of picophytoplankton in the Neuse River Estuary. The work is a first step in determining how a wetter climate may affect the estuarine ecosystem.
Picophytoplankton are defined as any phytoplankton measuring less than three micrometers in size. Although well studied as part of the oceanic ecosystem and food web, picophytoplankton are understudied in estuarine systems, even though they occur in significant numbers within these environments.
"Picophytoplankton are important primary producers in aquatic ecosystems," says Ryan Paerl, assistant professor of ...
2021-01-25
DALLAS - Jan. 25, 2021 - Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cells are missing a surface protein that triggers an immune response, allowing them to hide from one of the body's key cancer defenses, a new study led by UT Southwestern researchers suggests. The findings, reported online today in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, could lead to new treatments for SCLC, which has no effective therapies.
Despite decades of study, SCLC - a subset of lung cancer that makes up about 13 percent of lung cancer diagnoses - has a very poor prognosis, with only about 6 percent of patients surviving five years after ...
2021-01-25
Massive earthquakes are, fortunately, rare events. But that scarcity of information blinds us in some ways to their risks, especially when it comes to determining the risk for a specific location or structure.
"We haven't observed most of the possible events that could cause large damage," explained Kevin Milner, a computer scientist and seismology researcher at the Southern California Earthquake Center (SCEC) at the University of Southern California. "Using Southern California as an example, we haven't had a truly big earthquake since 1857 -- that was the last time the southern San Andreas broke into a massive magnitude ...
2021-01-25
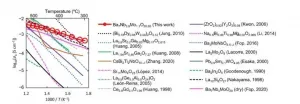
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Imperial and High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) Institute of Materials Structure Science, discover new Ba7Nb4MoO20-based materials with high oxygen-ion (oxide-ion O2-) conductivities--"the hexagonal perovskite-related oxides"--and shed light on the underlying mechanisms responsible for their conductivity. Their findings lead the way to uncovering other similar materials, furthering research on developing low-cost and scalable renewable energy technologies.
Over the past few years, fuel cells have become a focal point of research in eco-friendly technology because of their ...
2021-01-25
Researchers from the Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy (MBI) have developed a new method to modify the spectral width of extreme-ultraviolet (XUV) light. By employing a novel phase-matching scheme in four-wave mixing, they could compress the spectral width of the initial broadband light by more than hundred times. The detailed experimental and theoretical results have been published in Nature Photonics.
Light, as emitted by the sun, consists of many different colors and typically appears as white. Sometimes, however, only certain colors reach our eyes, leading to stunning phenomena like an afterglow. For technical or scientific applications that require a specific color, gratings and prisms can be used to extract this color ...
2021-01-25
What The Study Did: The results of this study suggest that cumulative exposure to cigarette smoke is an independent risk factor for hospital admission and death from COVID-19.
Authors: Katherine E. Lowe, M.Sc., of the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve in Cleveland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.8360)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for ...
2021-01-25
What The Study Did: The association of a shelter-in-place order with lower rates of seasonal respiratory viral activity was examined in this study.
Authors: Elizabeth Partridge, M.D., of the University of California at Davis School of Medicine in Sacramento, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35281)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
2021-01-25
A study designed to study how the immune system impacts gut bacteria - has led to the extraordinary discovery of two molecules that can not only provide profound protection in experimental models of asthma but can also substantially reduce the severity of an attack.
Neither of these molecules, one of which is already commercially available as a dietary supplement, were previously known to have an effect on asthma - and they also appear, from animal studies, to have a role in treating the respiratory illness that is prevalent, and often fatal, in people with serious COVID-19.
The researchers aim to test one of the molecules in a clinical trial in 2021 in asthmatics.
As further evidence that these two molecules ...
2021-01-25
As the planet's burden of rubber and plastic trash rises unabated, scientists increasingly look to the promise of closed-loop recycling to reduce waste. A team of researchers at Princeton's Department of Chemistry announces the discovery of a new polybutadiene molecule - from a material known for over a century and used to make common products like tires and shoes - that could one day advance this goal through depolymerization.
The Chirik lab reports in Nature Chemistry that during polymerization the molecule, named (1,n'-divinyl)oligocyclobutane, enchains in a repeating sequence of squares, a previously ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New IU study finds most high-school age youth are willing to wear masks