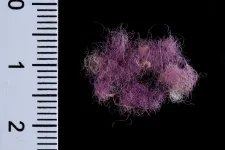
For the first time, rare evidence has been found of fabric dyed with royal purple dating from the time of King David and King Solomon. While examining the colored textiles from Timna Valley - an ancient copper production district in southern Israel - in a study that has lasted several years, the researchers were surprised to find remnants of woven fabric, a tassel and fibers of wool dyed with royal purple. Direct radiocarbon dating confirms that the finds date from approximately 1000 BCE, corresponding to the biblical monarchies of David and Solomon in Jerusalem. The dye, which is produced from species of mollusk found in the Mediterranean, over 300 km from Timna, is often mentioned in the Bible and appears in various Jewish and Christian contexts. This is the first time that purple-dyed Iron Age textiles have been found in Israel, or indeed throughout the Southern Levant. The research was carried out by Dr. Naama Sukenik from the Israel Antiquities Authority and Prof. Erez Ben-Yosef, from the Jacob M. Alkow Department of Archaeology and Ancient Near Eastern Cultures at Tel Aviv University, in collaboration with Prof. Zohar Amar, Dr. David Iluz and Dr. Alexander Varvak from Bar-Ilan University and Dr. Orit Shamir from the Israel Antiquities Authority. The unexpected finds are being published today in the prestigious PLOS ONE journal.
"This is a very exciting and important discovery," explains Dr. Naama Sukenik, curator of organic finds at the Israel Antiquities Authority. "This is the first piece of textile ever found from the time of David and Solomon that is dyed with the prestigious purple dye. In antiquity, purple attire was associated with the nobility, with priests, and of course with royalty. The gorgeous shade of the purple, the fact that it does not fade, and the difficulty in producing the dye, which is found in minute quantities in the body of mollusks, all made it the most highly valued of the dyes, which often cost more than gold. Until the current discovery, we had only encountered mollusk-shell waste and potsherds with patches of dye, which provided evidence of the purple industry in the Iron Age. Now, for the first time, we have direct evidence of the dyed fabrics themselves, preserved for some 3000 years".
Prof. Erez Ben-Yosef from Tel Aviv University's Archaeology Department says, "Our archaeological expedition has been excavating continuously at Timna since 2013. As a result of the region's extremely dry climate, we are also able to recover organic materials such as textile, cords and leather from the Iron Age, from the time of David and Solomon, providing us with a unique glimpse into life in biblical times. If we excavated for another hundred years in Jerusalem, we would not discover textiles from 3000 years ago. The state of preservation at Timna is exceptional and it is paralleled only by that at much later sites such as Masada and the Judean Desert Caves. In recent years, we have been excavating a new site inside Timna known as 'Slaves' Hill'. The name may be misleading, since far from being slaves, the laborers were highly skilled metalworkers. Timna was a production center for copper, the Iron Age equivalent of modern-day oil. Copper smelting required advanced metallurgical understanding that was a guarded secret, and those who held this knowledge were the 'Hi-Tech' experts of the time. Slaves' Hill is the largest copper-smelting site in the valley and it is filled with piles of industrial waste such as slag from the smelting furnaces. One of these heaps yielded three scraps of colored cloth. The color immediately attracted our attention, but we found it hard to believe that we had found true purple from such an ancient period".
According to the researchers, true purple [argaman] was produced from three species of mollusk indigenous to the Mediterranean Sea: The Banded Dye-Murex (Hexaplex trunculus), the Spiny Dye-Murex (Bolinus brandaris) and the Red-Mouthed Rock-Shell (Stramonita haemastoma). The dye was produced from a gland located within the body of the mollusk by means of a complex chemical process that lasted several days. Today, most scholars agree that the two precious dyes, purple [argaman] and light blue, or azure [tekhelet] were produced from the purple dye mollusk under different conditions of exposure to light. When exposed to light, azure is obtained whereas without light exposure, a purple hue is obtained. These colors are often mentioned together in the ancient sources, and both have symbolic and religious significance to this day. The Temple priests, David and Solomon, and Jesus of Nazareth are all described as having worn clothing colored with purple.
The analytical tests conducted at Bar Ilan University's laboratories, together with dyes that were reconstructed by Prof. Zohar Amar and Dr. Naama Sukenik, can identify the species used to dye the Timna textiles and the desired hues. In order to reconstruct the mollusk dyeing process, Prof. Amar traveled to Italy where he cracked thousands of mollusks (which the Italians eat) and produced raw material from their dye glands that was used in hundreds of attempts to reconstruct ancient dyeing. "The practical work took us back thousands of years," says Prof. Amar, "and it has allowed us to better understand obscure historical sources associated with the precious colors of azure and purple."
The dye was identified with an advanced analytical instrument (HPLC) that indicated the presence of unique dye molecules, originating only in certain species of mollusk. According to Dr. Naama Sukenik, "Most of the colored textiles found at Timna, and in archaeological research in general, were dyed using various plant-based dyes that were readily available and easier to dye with. The use of animal-based dyes is regarded as much more prestigious, and served as an important indicator for the wearer's high economic and social status. The remnants of the purple-dyed cloth that we found are not only the most ancient in Israel, but in the Southern Levant in general. We also believe that we have succeeded in identifying the double-dyeing method in one of the fragments, in which two species of mollusk were used in a sophisticated way, to enrich the dye. This technology is described by the Roman historian Pliny the Elder, from the first century CE, and the dye it produced was considered the most prestigious."
Prof. Ben-Yosef identifies the copper-production center at Timna as part of the biblical Kingdom of Edom, which bordered the kingdom of Israel to the south. According to him, the dramatic finds should revolutionize our concepts of nomadic societies in the Iron Age. "The new finds reinforce our assumption that there was an elite at Timna, attesting to a stratified society. In addition, since the mollusks are indigenous to the Mediterranean, this society obviously maintained trade relations with other peoples who lived on the coastal plain. However, we do not have evidence of any permanent settlements in the Edomite territory. The Edomite Kingdom was a kingdom of nomads in the early Iron Age. When we think of nomads, it is difficult for us to free ourselves from comparisons with contemporary Bedouins, and we therefore find it hard to imagine kings without magnificent stone palaces and walled cities. Yet in certain circumstances, nomads can also create a complex socio-political structure, one that the biblical writers could identify as a kingdom. Of course, this whole debate has repercussions for our understanding of Jerusalem in the same period. We know that the Tribes of Israel were originally nomadic and that the process of settlement was gradual and prolonged. Archaeologists are looking for King David's palace. However, David may not have expressed his wealth in splendid buildings, but with objects more suited to a nomadic heritage such as textiles and artifacts." According to Ben-Yosef, "It is wrong to assume that if no grand buildings and fortresses have been found, then biblical descriptions of the United Monarchy in Jerusalem must be literary fiction. Our new research at Timna has showed us that even without such buildings, there were kings in our region who ruled over complex societies, formed alliances and trade relations, and waged war on each other. The wealth of a nomadic society was not measured in palaces and monuments made of stone, but in things that were no less valued in the ancient world - such as the copper produced at Timna and the purple dye that was traded with its copper smelters."
INFORMATION: