Algorithm for algal rhythms
2021-02-01
(Press-News.org) An atlas of harmful algal blooms across the Red Sea reveals their link with industrial aquaculture and how these blooms have changed in recent decades.
Warming oceans and anthropogenic pollution have led to more frequent and extensive harmful algal blooms (HABs) worldwide. These rapid surges in productivity occur when algae suddenly experience advantageous conditions, usually an influx of nutrients, and take over their environment, suffocating other marine life and spreading toxins through the food chain. These blooms harm wild and farmed fish and reduce marine biodiversity.
"HABs are a global problem," says Elamurugu Alias Gokul, a Ph.D. student at KAUST, "and are often associated with socio-economic and environmental issues that affect public health, fisheries and aquaculture."
The Red Sea supports the countries situated along its shores through its thriving coral reefs, excellent biodiversity and growing aquaculture industry. "Aquaculture is essential for the economic prosperity of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia," says Gokul, "but it is also a major source of marine pollution." Despite growing concerns that HABs are exacerbated by climate change and aquaculture, there is a lack of studies dedicated to understanding their seasonal and interannual variability across the region.
Gokul and his colleagues analyzed high-resolution satellite data to map HABs across the Red Sea between 2003 and 2017. They studied changes in ocean color to determine the presence or absence of HABs and used remotely sensed concentrations of chlorophyll-a -- a photosynthetic pigment in aquatic algae -- as a proxy for phytoplankton abundance. As the researchers expected, most events occurred during warm summer months in the southern Red Sea, where they were also longer lasting (up to 32 days) and more widespread (up to 5000 square kilometers), possibly due to the monsoon winds that drive nutrient-rich waters from the Indian Ocean.
The researchers then focused on the area around NAQUA, the largest fish farm in the Red Sea, and compared variations in HABs with aquaculture production. Between 2002 and 2010, annual aquaculture output increased from around 4000 tonnes to 22,370 tonnes, and the average size of HABs near the site grew from 65 square kilometers to 392 square kilometers. "The high chlorophyll concentrations in the vicinity of the facility's discharge point suggest that elevated nutrients from aquaculture waste have contributed to the spread of HABs," says Gokul.
The team is already developing an algorithm that can distinguish between individual phytoplankton species. "This information is vital for understanding which species were responsible for past HAB outbreaks across the Red Sea," adds Ibrahim Hoteit, who oversaw the research. "But we also intend to develop an automated remote-sensing system that can detect and report HABs in real time."
These remote-sensing tools could help identify and monitor areas at higher risk from harmful algal blooms, particularly around aquaculture facilities, helping the development of a sustainable waste management plan that protects the marine environment and the future of fisheries in the Red Sea.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-01
Per capita income, population volume and density, the structure of cities, transport infrastructure or whether districts have their own schools are all factors that can affect the spread of COVID-19. This has been confirmed by a study carried out in 73 districts in Barcelona by researchers from the departments of Geography and Economics of the Universitat Rovira i Virgili, the results of which have been published in the Journal of Public Health. The research reveals that the analysis of the characteristics of every district can facilitate decisions on the specific measures to be applied to individual districts ...
2021-02-01
Flinders University researchers have discovered a new anti-inflammatory role for well-known blood clot protein fibrinogen, which could support targeted new treatments for kidney, heart and other common diseases.
The study in Redox Biology describes how fibrinogen can be protective against hypochlorite - a chemical generated by the body during inflammation - and so act as a kind of antioxidant in blood plasma.
"Our team found that fibrinogen, which forms extraordinarily large assemblies when it reacts with hypochlorite, doesn't harm cells in the same way as hypochlorite-modified albumin which exacerbates kidney and heart disease, ...
2021-02-01
Researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research have discovered that three patients with a severe genetic immunodeficiency spontaneously repaired the harmful variants in their DNA and restored normal immune function over time.
As cells grow and divide to produce new cells, DNA is copied from the parent cell to provide instructions for the new daughter cells. Random changes that occur as the DNA is copied are usually harmless but in some cases are associated with the development of diseases like cancer.
However, the Garvan-led Clinical Immunogenomics Research Consortium Australasia (CIRCA) found three patients with DOCK8 deficiency had repaired the faulty genes through a ...
2021-02-01
New research from the Prevention Research Center of the Pacific Institute for Research and Evaluation examines whether recreational marijuana legalization in Oregon and marijuana and alcohol retail outlet density levels are associated with co-use and beliefs supportive of use of each among teens.
Using data from 11th graders who participated in the Student Wellness Survey from 2010-2018, researchers assessed past-30-day co-use changes in counties with low, medium, and high densities of licensed marijuana and alcohol outlets.
Findings include:
A significant post-legalization increase ...
2021-02-01
Australians love their beaches, and now a new study also confirms the broad appeal of other coastal assets such as tidal wetlands, nature trails and protected areas including bird and dolphin sanctuaries.
In one of the first studies of its kind in Australia, ahead of World Wetlands Day (2 February), Flinders University environment and marine ecology experts have conducted an Adelaide-based survey of how residents connect with and rate the attributes of Adelaide's northern metropolitan coastal wetlands.
The findings, just published in the journal Environmental Science and Policy, report strong appreciation of the natural features of these coastal places, with study participants ...
2021-02-01
Soil temperature has a significant impact on land-atmosphere interaction within the Earth system, affecting surrounding ecology, agriculture, and much more. This influence is a primary component of what is called a "thermal regime" of land, or a regular pattern of temperature change within the soil. Climatologists are intrigued by fluctuating soil temperatures, especially during the first decade of the 21st century where global surface warming has slowed down. The thermal regime, according to scientists, is greatly influential on climate, particularly seasonal climate prediction. Now, ...
2021-02-01
Humoral and cellular adaptive immunity are two immune mechanisms that act against pathogens. Humoral immunity is mediated by antibodies, while cellular immunity does not involve antibodies and is, instead, facilitated by T cells. Studying how these immune mechanisms mediate SARS-CoV-2 infections could be beneficial in controlling the progression of the disease. However, their roles in viral control or disease pathogenesis is not fully understood and only a few studies have thoroughly monitored COVID-19 patients longitudinally, especially during the acute phase of infection.
To fill this knowledge gap, the team of ...
2021-02-01
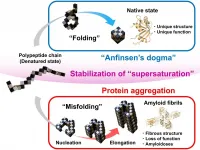
Correct, or native, protein folding is essential for correct protein function. Protein misfolding can lead to the formation of amyloid fibrils, and amyloidosis, which is implicated in various human neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and Huntington's diseases. In this study Yuji Goto and colleagues describe, for the first time, a dynamic link between protein folding and misfolding, and the threshold that must be overcome for the formation of amyloid fibrils.
Technological advances are at the forefront of many scientific discoveries. The atomic structures of some amyloid fibrils were recently revealed as a result of advances in solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance and cryogenic electron microscopy. While an important step forward for the ...
2021-02-01
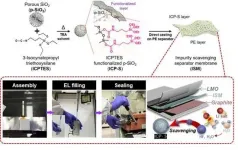
The honor of the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry went to those who developed lithium-ion rechargeable batteries. These batteries have become an essential energy source for electronic devices ranging from small IT devices to electric vehicles. Tesla, a leading U.S. automaker, recently emphasized the need to establish an innovative production system and reduce battery cost. The price of batteries accounts for a large portion of electric vehicles and cost reduction is vital to popularizing them.
A joint research team, led by Professor Soojin Park and Ph.D. candidate Hye Bin Son ...
2021-02-01
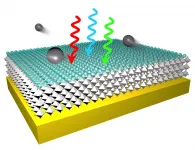
HOUSTON - (Feb. 1, 2021) - Rice University engineers have discovered technology that could slash the cost of semiconductor electron sources, key components in devices ranging from night-vision goggles and low-light cameras to electron microscopes and particle accelerators.
In an open-access Nature Communications paper, Rice researchers and collaborators at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) describe the first process for making electron sources from halide perovskite thin films that efficiently convert light into free electrons.
Manufacturers spend billions of dollars each year on photocathode electron sources ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Algorithm for algal rhythms