Backreaction observed for first time in water tank black hole simulation
2021-02-01
(Press-News.org) Scientists have revealed new insights into the behaviour of black holes with research that demonstrates how a phenomenon called backreaction can be simulated.
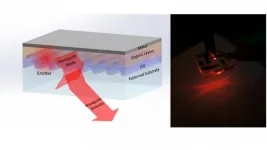
The team from the University of Nottingham have used their simulation of a black hole, involving a specially designed water tank, for this latest research published in Physical Review Letters. This study is the first to demonstrate that the evolution of black holes resulting from the fields surrounding them can be simulated in a laboratory experiment.
The researchers used a water tank simulator consisting of a draining vortex, like the one that forms when you pull the plug in the bath. This mimics a black hole since a wave which comes too close to the drain gets dragged down the plug hole, unable to escape. Systems like these have grown increasingly popular over the past decade as a means to test gravitational phenomena in a controlled laboratory environment. In particular, Hawking radiation has been observed in an analogue black hole experiment involving quantum optics.
Using this technique the researchers showed for the first time that when waves are sent into an analogue black hole, the properties of the black hole itself can change significantly. The mechanism underlying this effect in their particular experiment has a remarkably simple explanation. When waves come close to the drain, they effectively push more water down the plug hole causing the total amount of water contained in the tank to decrease. This results in a change in the water height, which in the simulation corresponds to a change in the properties of the black hole.
Lead author, Post-doctoral researcher Dr Sam Patrick from the University of Nottingham School of Mathematical Sciences explains: "For a long time, it was unclear whether the backreaction would lead to any measurable changes in analogue systems where the fluid flow is driven, for example, using a water pump. We have demonstrated that analogue black holes, like their gravitational counterparts, are intrinsically backreacting systems. We showed that waves moving in a draining bathtub push water down the plug hole, modifying significantly the drain speed and consequently changing the effective gravitational pull of the analogue black hole.
What was really striking for us is that the backreaction is large enough that it causes the water height across the entire system to drop so much that you can see it by eye! This was really unexpected. Our study paves the way to experimentally probing interactions between waves and the spacetimes they move through. For example, this type of interaction will be crucial for investigating black hole evaporation in the laboratory."
Black hole research at the University of Nottingham has recently received a £4.3 million funding boost for a three-year project that aims to provide further insights into the physics of the early universe and black holes.
The research team will use quantum simulators to mimic the extreme conditions of the early universe and black holes. The Nottingham team will be using a new state laboratory to set up a novel hybrid superfluid optomechanical system to mimic quantum black hole processes in the laboratory.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-01
Protein alteration in the family of lamins causes several diseases, known as laminopathies, such as progeria or precocious ageing. A study in which UB researchers have taken part states that alterations in the levels of one of these proteins, lamin B1, contribute to the degeneration of different brain neuronal populations in Huntington's disease. Caused by a mutation in the huntingtin gen, this pathology features involuntary movements, cognitive deficit and psychiatric disorders, and has no cure yet.
According to the study, published in the journal EMBO Molecular Medicine, these results open new therapeutic pathways for the treatment of this disease, since research shows pharmacological normalization of levels of lamin ...
2021-02-01
As COVID-19 spread across the world, so did conspiracy theories and false information about the virus. This proliferation of misinformation--labeled an "infodemic" by the World Health Organization (WHO)--makes it difficult to identify trustworthy sources and can threaten public health by undermining confidence in science, governments, and public health recommendations.
The consequences of misinformation can be tragic: hundreds died and thousands were poisoned in Iran after consuming toxic methanol alcohol, falsely believing it could cure COVID-19.
In a new article in the Journal of Public ...
2021-02-01
The COVID-19 pandemic is straining health systems across the country, especially intensive care units. New research from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine shows that people treated in the ICU for COVID-19 are twice as likely to die when the ICU capacity is strained by the number of COVID-19 patients.
"These results demonstrate that patients with COVID-19 are more likely to die if they are admitted to an ICU during times with peak COVID-19 caseload," said Dawn Bravata, M.D., first author of the study. "We know that strain on hospital ...
2021-02-01
Amsterdam, December 29, 2020 - This new pioneering study by Prof. Ricardo Maccioni and coworkers of the International Center for Biomedicine, "New Frontiers in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer´s disease" was published in the special issue of Latin American investigators of the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease(JAD). This supports a growing body of research on the Alzheimer's prevention value of an integrated approach using daily exercise, nutraceuticals, oriental practices such as QiGong along with meditation, and social life. These elements of a healthy style of life are supplemented with the use of reliable biomarkers for early detection of this disease that allows the detection of Alzheimer up to 20 years before ...
2021-02-01
Chronic stress could be the prevailing condition of our time. In the short term, our jaws or stomachs may clench; in the long term, stress can lead to metabolic disease and speed up diseases of aging, as well as leading to more serious psychological disorders. The physical manifestations of stress originate in the brain, and they move along a so-called "stress axis" that ends in the adrenal glands. These glands then produce the hormone cortisol. When the stress axis is continually activated, changes occur in the cells and organs along the way, and the continual production of cortisol then substantially contribute the symptoms of chronic stress.
The stress response axis starts with the hypothalamus in the brain, ...
2021-02-01
Scientists say stable seafood consumption amongst the world's poorer coastal communities is linked to how local habitat characteristics influence fishing at different times of the year.
In the coastal communities of low-income countries, the seafood people catch themselves is often a main food source. In a new study, scientists focused on an often-overlooked type of fishing called gleaning: collecting molluscs, crabs, octopus and reef fish by hand close to shore.
"We surveyed 131 households in eight coastal communities on a small island off Timor-Leste," said study lead author Ruby Grantham from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies.
Grantham said even though gleaning is important for food security ...
2021-02-01
(Boston)--There have been great advances in treating melanoma over the past five years, however, even with these treatments many patients quickly develop drug resistance and die from their disease. A new study from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) has discovered that a drug (YK-4-279) that was previously created to target one specific type of protein has much broader use against a family of proteins that act to promote melanoma.
"We find that this drug inhibited melanoma from becoming more aggressive in human cells and in experimental models. We also found a specific pathway that this drug acts through to be anti-cancer: inhibiting proteins that drive genes that promote cancer cell growth and metastasis," ...
2021-02-01
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Antarctic ice is melting, contributing massive amounts of water to the world's seas and causing them to rise - but that melt is not as linear and consistent as scientists previously thought, a new analysis of 20 years' worth of satellite data indicates.
The analysis, built on gravitational field data from a NASA satellite system, shows that Antarctica's ice melts at different rates each year, meaning the models scientists use to predict coming sea level rise might also need adjusting.
"The ice sheet is not changing with a constant rate - it's more complicated than a linear change," said Lei Wang, assistant professor ...
2021-02-01
Researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of Texas have developed and demonstrated a new approach for designing photonic devices. The advance allows them to control the direction and polarization of light from thin-film LEDs, paving the way for a new generation of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies.
"This is a fundamentally new device architecture for photonic devices," says Franky So, corresponding author of a paper describing the work. "And we've demonstrated that, using our approach, directional and polarized emissions from an organic LED or a perovskite LED without external optical elements can be realized." So is the ...
2021-02-01
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health and their collaborators found that inhaling unfragmented hyaluronan improves lung function in patients suffering from severe exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Hyaluronan, a sugar secreted by living tissue that acts as a scaffold for cells, is also used in cosmetics as a skin moisturizer and as a nasal spray to moisturize lung airways. Utilized as a treatment, hyaluronan shortened the amount of time COPD patients in intensive care needed breathing support, decreased their number of days in the hospital, and saved money by reducing their hospital stay.
The study, published online in Respiratory Research, is a good example of how examining the impacts of environmental pollution on the lungs can ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Backreaction observed for first time in water tank black hole simulation